Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings
|
Hirschsprung's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] ; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aditya Ganti M.B.B.S. [2]
Overview
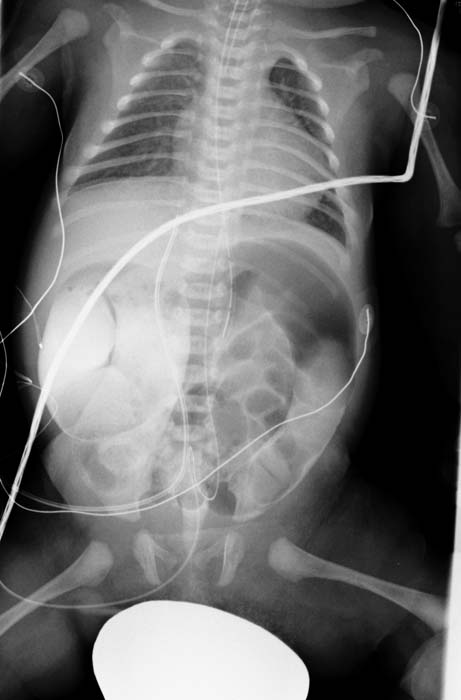
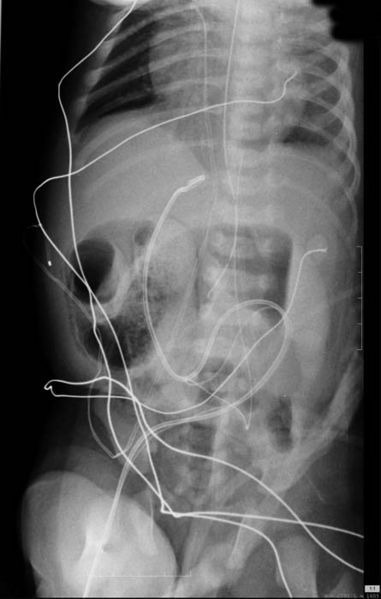
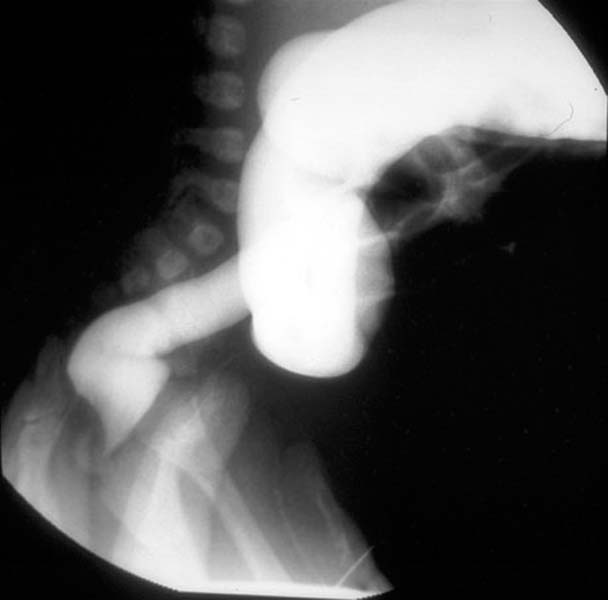
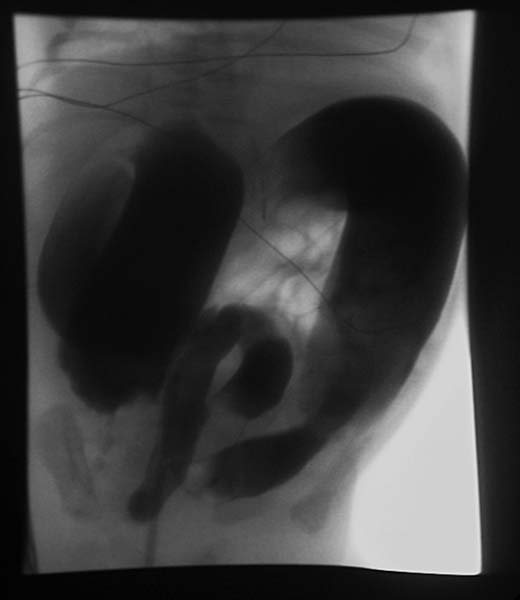
Barium enema is the mainstay of Hirschsprung’s disease diagnosis. Barium enema findings suggestive of Hirschsprung's disease include a transition zone between the narrow and dilated portions of the colon in the shape of an inverted cone, which is the most characteristic radiologic finding.
Other Imaging Findings
Barium Enema
- Barium enema studies demonstrate patency of the colon, which is short but usually normal in caliber.
- A transition zone between the narrow and dilated portions of the colon in the shape of an inverted cone is the most characteristic radiologic finding.
- When this transition zone is observed, the examination should be discontinued because filling of proximal dilated bowel beyond the transition zone may lead to impaction.
- Radiologic diagnosis of total colonic aganglionosis is difficult. Findings from barium enema examination may be normal or may show a short colon of normal caliber, microcolon, or a transition zone in the ileum.[1]
-
Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11495
-
Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11495
-
Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11495
-
Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11495
References
- ↑ Burkardt DD, Graham JM, Short SS, Frykman PK (2014). "Advances in Hirschsprung disease genetics and treatment strategies: an update for the primary care pediatrician". Clin Pediatr (Phila). 53 (1): 71–81. doi:10.1177/0009922813500846. PMID 24002048.