|
|
| Line 18: |
Line 18: |
| {{SK}} Congenital aganglionic megacolon | | {{SK}} Congenital aganglionic megacolon |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease overview|Overview]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Hirschsprung's disease''', or '''[[congenital aganglionic megacolon]]''', involves an enlargement of the [[colon (anatomy)|colon]], caused by [[bowel obstruction]] resulting from an [[ganglion|aganglionic]] section of [[bowel]] (the normal [[Enteric nervous system|enteric nerves]] are absent) that starts at the anus and progresses upwards. The length of bowel that is affected varies but seldom stretches for more than a foot or so.
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==History and Description== | | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease classification|Classification]]== |
|
| |
|
| This disease is named for [[Harald Hirschsprung]], the Danish [[physician]] who first described the disease in 1886, describing two infants who had died with swollen bellies. "The autopsies showed identical pictures with a pronounced dilatation and hypertrophy of the colon as the dominant features" (Madsen 17:2).
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
|
| |
|
| Hirschsprung’s disease is a [[congenital]] disorder of the colon in which certain nerve cells, known as ganglion cells, are absent, causing chronic constipation <ref>Worman and Ganiats 1995, Am Fam Physician 51, 487-494 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7840044]</ref>. A [[barium enema]] is the mainstay of diagnosis of Hirschsprung’s, though a rectal [[biopsy]] showing the lack of ganglion cells is the only certain method of diagnosis.
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease causes|Causes]]== |
|
| |
|
| The usual treatment is "pull-through" surgery where the portion of the colon that does have nerve cells is pulled through and sewn over the part that lacks nerve cells (National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse). For a long time, Hirschsprung’s was considered a multi-factorial disorder, where a combination of nature and nurture were considered to be the cause (Madsen 19). However, in August of 1993, two articles by independent groups in ''Nature Genetics'' said that Hirschsprung’s disease could be mapped to a stretch of [[chromosome 10 (human)|chromosome 10]] <ref>{{Cite journal
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease differential diagnosis|Differentiating Hirschsprung's disease from other Diseases]]== |
| | author = [[M. Angrist]], [[E. Kauffman]], [[S. A. Slaugenhaupt]], [[T. C. Matise]], [[E. G. Puffenberger]], [[S. S. Washington]], [[A. Lipson]], [[D. T. Cass]], [[T. Reyna]] & [[D. E. Weeks]]
| |
| | title = A gene for Hirschsprung disease (megacolon) in the pericentromeric region of human chromosome 10
| |
| | journal = [[Nature genetics]]
| |
| | volume = 4
| |
| | issue = 4
| |
| | pages = 351–356
| |
| | year = 1993
| |
| | month = August
| |
| | doi = 10.1038/ng0893-351
| |
| | pmid = 8401581
| |
| | url = http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v4/n4/abs/ng0893-351.html
| |
| }}</ref><ref>Lyonnet et al. 1993, Nature Genetics 4, 346-350 [http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v4/n4/abs/ng0893-346.html]</ref>. This research also suggested that a single gene was responsible for the disorder. However, the researchers were unable to isolate the single gene that they thought caused Hirschsprung’s.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Genetic basis== | | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
| In 2002, scientists thought they found the solution. According to this new research, the interaction between two proteins [[genetic code|encoded]] by two variant genes caused Hirschsprung’s. The [[RET proto-oncogene]] on [[chromosome 10]] was identified one of the [[gene]]s involved, and it was determined that [[mutation|dominant mutation]]s may occur within this [[gene]] leading to a loss of function for the protein it [[genetic code|encoded]] (Passarge 11). The protein with which RET has to interact in order for Hirschsprung’s disease to develop is termed EDNRB, and is encoded by the [[gene]] ''EDNRB'' located on [[chromosome 13 (human)|chromosome 13]]. Six other genes were discovered to be associated with Hirschsprung’s. According to the study, these genes are GDNF on [[chromosome 5 (human)|chromosome 5]], EDN3 on [[chromosome 20 (human)|chromosome 20]], SOX10 on [[chromosome 22 (human)|chromosome 22]], ECE1 on [[chromosome 1 (human)|chromosome 1]], NTN on [[chromosome 19 (human)|chromosome 19]], and SIP1 on [[chromosome 2 (human)|chromosome 2]]. These scientists concluded that the mode of inheritance for Hirschsprung’s is oligogenic inheritance (Passarge 11). This means that two mutated genes interact to cause a disorder. Variations in RET and EDNRB have to coexist in order for a child to get Hirschsprung’s. However, although six other genes were shown to have an effect on Hirschsprung’s, the researchers were unable to determine how they interacted with RET and EDNRB. Thus, the specifics of the origins of the disease are still not completely known. More recently, syndromic cases of Hischprung's disease (that is, associated with other defects of the [[autonomic nervous system]]) were shown to be caused by mutations in the homeobox gene [[PHOX2B]].
| |
|
| |
|
| RET codes for proteins that help the neural crest cells (which become ganglion cells) move through the digestive tract during the development of the embryo (Sawin). EDNRB codes for proteins to actually connect these nerve cells to the digestive tract. This means that the absence of certain nerve fibers in the colon could be directly related to these two genes mutating so the wrong proteins are produced. Research published in June of 2004 suggests that there are actually ten genes associated with Hirschsprung’s disease (Puri and Shinkai). Also, new research suggests that mutations in genomic sequences involved in regulating EDNRB have a bigger impact on Hirschsprung’s disease than previously thought.
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease risk factors|Risk Factors]]== |
|
| |
|
| Dr. Bob Sawin of Seattle’s Children's Hospital notes that it is generally accepted in the scientific community that the gene RET is the most important gene when looking for the genetic cause of Hirschsprung’s disease. RET can mutate in many ways, and is associated with Down syndrome. Since [[Down Syndrome]] is comorbid in two percent of Hirschsprung’s cases, there is a likelihood that RET is involved heavily in both Hirschprung's disease and Down Syndrome. RET is also associated with [[thyroid cancer]] and [[neuroblastoma]] (Sawin). Both of these disorders have also been observed in Hirschsprung’s patients with greater frequency than in the general population. One function that RET controls is the travel of the [[neural crest cell]]s through the [[intestine]]s in the developing [[fetus]]. When RET mutations cause Hirschsprung’s disease, “the cells start traveling through the colon, only to be stopped once the mutation occurs” (Sawin). The earlier the mutation of RET occurs in Hirschsprung’s disease, the more severe the disorder becomes (Sawin).
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease screening|Screening]]== |
|
| |
|
| While researchers remain uncertain of the exact genetic cause of Hirschsprung’s disease, Dr. Sawin notes that in familial cases, (in which families have multiple affected patients) Hirschsprung’s disease exhibits autosomal dominant transmission, with the gene RET being dominant. However, in sporadic cases, Sawin notes that there has been no inheritance pattern identified.
| | ==[[Hirschsprung's disease natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
| | |
| Treating Hirschsprung’s is much easier than determining the genetic causes of this disorder. The only way to treat Hirschsprung’s disease is through surgery (National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse). If Hirschsprung’s goes untreated, the patient can develop [[enterocolitis]], the inflammation of the small intestine and the colon (Sawin). This was the cause of death of the two boys that Harald Hirschsprung observed. Surgery is now used to remove the non-functioning portion of the bowel in order to restore bowel function (Sawin).
| |
| | |
| Hirschsprung's disease, hypoganglionosis, gut dysmotility, gut transit disorders and intussusception have been recorded with the dominantly inherited neurovisceral porphyrias (acute intermittent porphyria, hereditary coproporphyria, variegate porphyria). Children may require enzyme or DNA testing for these disorders as they may not produce or excrete porphyrins prepuberty. | |
|
| |
|
| ==Diagnosis== | | ==Diagnosis== |
|
| |
|
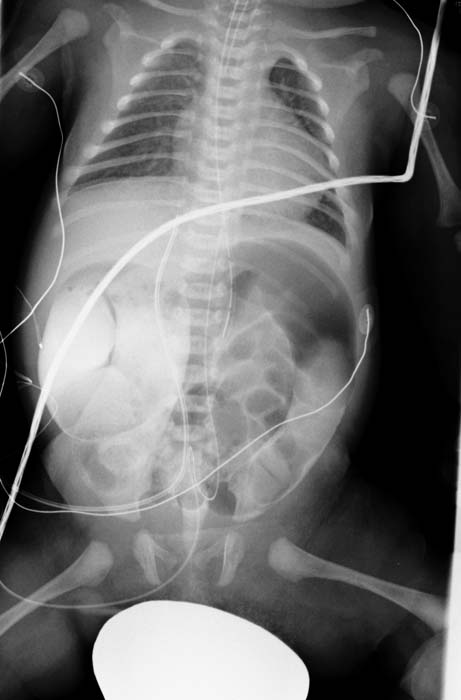
| Imaging findings are
| | [[Hirschsprung's disease diagnostic criteria|Diagnostic Criteria]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease electrocardiogram|EKG]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease CT|CT]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease MRI|MRI]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease echocardiography or ultrasound|Echocardiography or Ultrasound]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease other imaging findings|Other Imaging Findings]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
| * Radiography performed in children with Hirschsprung disease yields findings similar to those in other forms of low small bowel obstruction: variable gaseous distention of the colon and small bowel, often with air-fluid levels.
| |
| * The colon is usually difficult to identify accurately, and gas is usually absent in the rectum.
| |
| * Barium enema studies demonstrate patency of the colon, which is short but usually normal in caliber.
| |
| * A transition zone between the narrow and dilated portions of the colon in the shape of an '''inverted cone''' is the most characteristic radiologic finding.
| |
| * When this transition zone is observed, the examination should be discontinued because filling of the more proximal dilated bowel beyond the transition zone may lead to impaction.
| |
| *The radiologic diagnosis of total colonic aganglionosis is difficult. Findings at barium enema examination may be normal or may include a short colon of normal caliber, microcolon, or a transition zone in the ileum.
| |
| <gallery>
| |
| Image:
| |
| | |
| Hirschsprung's disease001.jpg | |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| | |
| Hirschsprung's disease004.jpg | |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| | |
| Hirschsprung's disease002.jpg | |
| | |
| Image:
| |
| | |
| Hirschsprung's disease003.jpg | |
| | |
| </gallery>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Treatment== | | ==Treatment== |
|
| |
|
| Treatment of Hirschsprung's disease consists of surgical removal of the abnormal section of the colon. There used to be two steps typically used to achieve this goal.
| | [[Hirschsprung's disease medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease surgery|Surgery]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Hirschsprung's disease future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
| * The first stage used to be a [[colostomy]]. When a colostomy is performed, the large intestine is cut and an opening is made through the abdomen. This allows bowel contents to be discharged into a bag.
| |
| * Later, when the child’s weight, age, and condition is right, a pull-through procedure is performed.
| |
| | |
| Orvar Swenson, the same man who discovered the cause of Hirschsprung’s, first performed it in 1948 (Swenson 839). The pull-through procedure repairs the colon by connecting the functioning portion of the bowel to the anus. The pull through procedure is the typical method for treating Hirschsprung’s in younger patients. Swenson devised the original procedure, but the pull-through surgery has been modified many times. Sawin, an expert in pull-through surgery, notes that, "Although there are about five different pull-through procedures, they are all more or less equally effective in treating the disorder."
| |
| | |
| The Swenson, Soave, Duhamel, and Boley procedures all vary slightly from each other with equivalent results (Sawin).
| |
| * The Swenson procedure leaves a small portion of the diseased bowel.
| |
| * The Soave procedure leaves the outer wall of the colon unaltered.
| |
| * The Boley procedure is just a small modification of the Soave procedure.
| |
| * The Duhamel procedure uses a surgical stapler to connect the good and bad bowel. The front of the bowel will end up with no cells, but the back will be healthy (Sawin).
| |
| | |
| Sawin notes that “Pull-through procedures used to require a colostomy, but with increased awareness among doctors and parents about the symptoms of Hirschsprung’s and with early diagnosis, doctors can keep the colon clean and perform the pull-through procedure without a colostomy”. In general, “85 percent of patients that have the pull-through surgery live normal lives afterwards. The other 15 percent have to take a laxative for the rest of their lives”.
| |
| | |
| In rare cases, if the mother has Hirschsprung’s and passes it on to her child, the child is said to have “total Hirschsprung’s”, where there are no ganglion cells at all in the colon (Sawin). In this case, the Martin pull-through operation is conducted. The Martin operation is the most invasive of the operations, for it requires a colostomy no matter how early you diagnose total Hirschsprung’s.
| |
| | |
| Even rarer, notes Dr. Sawin, "there are times where the disease begins in the small intestine, making treatment even harder". When a child has total Hirschsprung's or small intestine Hirschsprung's, an [[ileostomy]] or jejunostomy is conducted along with the Martin operation, and the child is then treated for [[short bowel syndrome]]. On very rare occasions, pull-through surgery is not the preferred method when it comes to treating Hirschsprung’s disease.
| |
| | |
| If the affected portion of the lower intestine is restricted to the lower portion of the rectum, other surgical procedures, such as the posterior rectal myectomy, can be performed.
| |
| | |
| == Histopathological Findings ==
| |
|
| |
|
| ===Colon: Hirschsprung disease === | | ==Case Studies== |
| {{#ev:youtube|v3mfl0l6Tdo}}
| | [[Hirschsprung's disease case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| ==See also== | | ==Related Chapters== |
| *[[Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia]] | | *[[Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia]] |
|
| |
|