Gatifloxacin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{EH}} | {{EH}} | ||
'''Gatifloxacin''' is an [[antibiotic]] of the fourth-generation [[fluoroquinolone]] family, that like other members of that family, inhibits the [[bacteria]]l [[enzyme]]s [[DNA gyrase]] and [[topoisomerase IV]]. [[Bristol-Myers Squibb]] introduced Gatifloxacin in 1999 under the | '''Gatifloxacin''' is an [[antibiotic]] of the fourth-generation [[fluoroquinolone]] family, that like other members of that family, inhibits the [[bacteria]]l [[enzyme]]s [[DNA gyrase]] and [[topoisomerase IV]]. [[Bristol-Myers Squibb]] introduced Gatifloxacin in 1999 under the proprietary name '''Tequin'''® for the treatment of respiratory tract infections, having licensed the medication from Kyorin Pharmaceutical Company of Japan. Allergan produces an eye-drop formulation called '''Zymar'''®. Gatifloxacin is available as [[tablet]]s and in various [[aqueous solution]]s for [[intravenous therapy]]. | ||
==Side-effects and removal from the market== | ==Side-effects and removal from the market== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| url = http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/abstract/354/13/1352 | | url = http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/abstract/354/13/1352 | ||
| accessdate = 2006-05-01 | | accessdate = 2006-05-01 | ||
}} ''Note: publication date 30 March; available on-line 1 March''</ref> An | }} ''Note: publication date 30 March; available on-line 1 March''</ref> An editorial by | ||
Dr. Jerry Gurwitz in the same issue called for the [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) to consider giving Tequin® a black box warning.<ref>{{cite journal | Dr. Jerry Gurwitz in the same issue called for the [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) to consider giving Tequin® a black box warning.<ref>{{cite journal | ||
| last = Gurwitz | | last = Gurwitz | ||
Revision as of 14:58, 19 June 2009
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 20% |
| Elimination half-life | 7 to 14 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
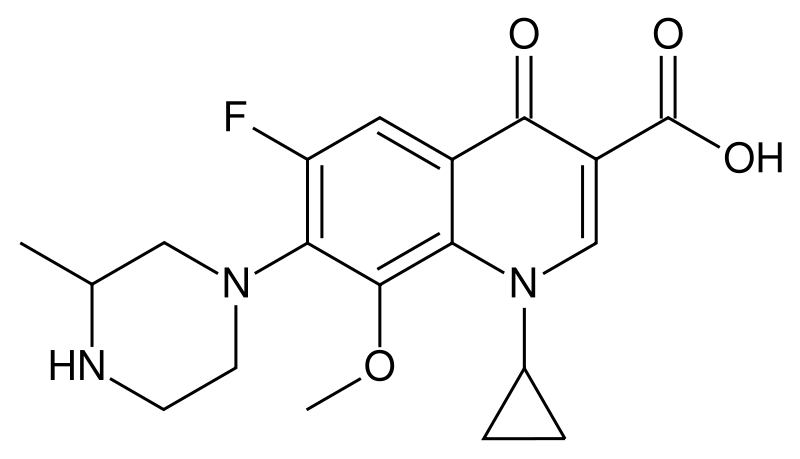
| Formula | C19H22FN3O4 |
| Molar mass | 375.394 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Gatifloxacin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Gatifloxacin Most cited articles on Gatifloxacin |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Gatifloxacin |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Gatifloxacin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Gatifloxacin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Gatifloxacin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Gatifloxacin Discussion groups on Gatifloxacin Patient Handouts on Gatifloxacin Directions to Hospitals Treating Gatifloxacin Risk calculators and risk factors for Gatifloxacin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Gatifloxacin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [2] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Gatifloxacin is an antibiotic of the fourth-generation fluoroquinolone family, that like other members of that family, inhibits the bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Bristol-Myers Squibb introduced Gatifloxacin in 1999 under the proprietary name Tequin® for the treatment of respiratory tract infections, having licensed the medication from Kyorin Pharmaceutical Company of Japan. Allergan produces an eye-drop formulation called Zymar®. Gatifloxacin is available as tablets and in various aqueous solutions for intravenous therapy.
Side-effects and removal from the market
A Canadian study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in March 2006 claims Tequin® can have "life threatening" side effects including serious diabetes.[1] An editorial by Dr. Jerry Gurwitz in the same issue called for the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider giving Tequin® a black box warning.[2] This editorial followed distribution of a letter dated February 15 by Bristol-Myers Squibb to health care providers indicating action taken with the FDA to strengthen warnings for the medication.[3] Subsequently it was reported on May 1, 2006 that Bristol-Myers Squibb would stop manufacture of Tequin, end sales of the drug after existing stockpiles were exhausted, and return all rights to Kyorin.[4]
Gatifloxacin is now only available in the US as an opthalmic solution.
Notes
- ↑ Park-Wyllie, Laura Y. (2006). "Outpatient Gatifloxacin Therapy and Dysglycemia in Older Adults". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (13): 1352&ndash, 1361. PMID 16510739. Retrieved 2006-05-01. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (help) Note: publication date 30 March; available on-line 1 March - ↑ Gurwitz, Jerry H. (2006). "Serious Adverse Drug Effects — Seeing the Trees through the Forest". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (13): 1413&ndash, 1415. PMID 16510740. Retrieved 2006-05-01. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Lewis-Hall, Freda (February 15, 2006). "Dear Healthcare Provider:" (PDF). Bristol-Myers Squibb. Retrieved May 1. Unknown parameter
|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ↑ Schmid, Randolph E. (May 1, 2006). "Drug Company Taking Tequin Off Market". Associated Press. Retrieved May 1, 2006.
- Pages with script errors
- Pages with citations using unsupported parameters
- CS1 errors: dates
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics
- Withdrawn drugs