Gallbladder cancer CT: Difference between revisions
(→CT) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*Peritoneal carcinomatosis | *Peritoneal carcinomatosis | ||
*Hepatic and distant metastases<ref>http://radiopaedia.org/articles/gallbladder-adenocarcinoma</ref> | *Hepatic and distant metastases<ref>http://radiopaedia.org/articles/gallbladder-adenocarcinoma</ref> | ||
*CT scans are often used to diagnose gallbladder cancer. It can confirm the location of the cancer and show the organs near the gallbladder, as well as lymph nodes and distant organs where the cancer might have spread. These are helpful in staging the cancer and in determining whether surgery is a good treatment option. CT scans can also be used to guide a biopsy procedure and a biopsy sample is then removed and looked at under a microscope. | |||
====CT Imaging==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Gallbladder-adenocarcinoma-001.jpg|CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma | |||
Image:Gallbladder-adenocarcinoma-002.jpg|CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma | |||
Image:Gallbladder-adenocarcinoma-003.jpg|CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma | |||
Image:Gallbladder-adenocarcinoma-004.jpg|CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma | |||
Image:Gallbladder-adenocarcinoma-005.jpg|CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Case Example=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Gallbladder adenocarcinoma 001.jpg|69 year old women with two month history of right upper quadrant pain . Large heterogenous, hypovascular liver mass which abuts an abnormal - appearing gallbladder | |||
Image:Gallbladder adenocarcinoma 002.jpg|Diagnostic considerations here would include, first, a locally invasive gallbladder adenocarcinoma and second, an occult colon carcinoma. | |||
Image:Gallbladder adenocarcinoma 003.jpg|Cholangiocarcinoma is considered less likely due to the lack of biliary obstruction. | |||
Image:Gallbladder adenocarcinoma 004.jpg|Adenopathies | |||
Image:Gallbladder adenocarcinoma 005.jpg|3.5 cm simple cyst associated with the upper pole of the right kidney. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 19:34, 12 April 2016
|
Gallbladder cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Gallbladder cancer CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Gallbladder cancer CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Parminder Dhingra, M.D. [2]
Overview
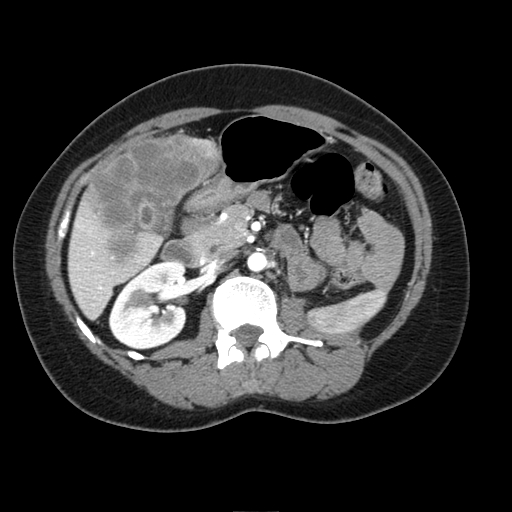
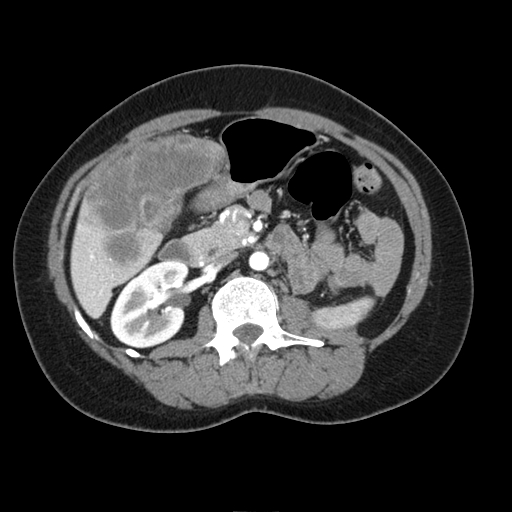
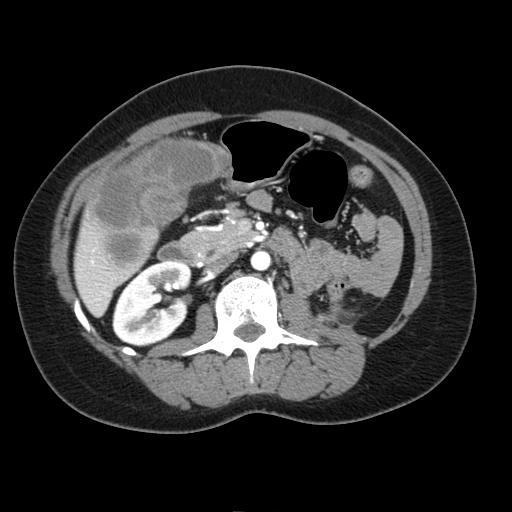
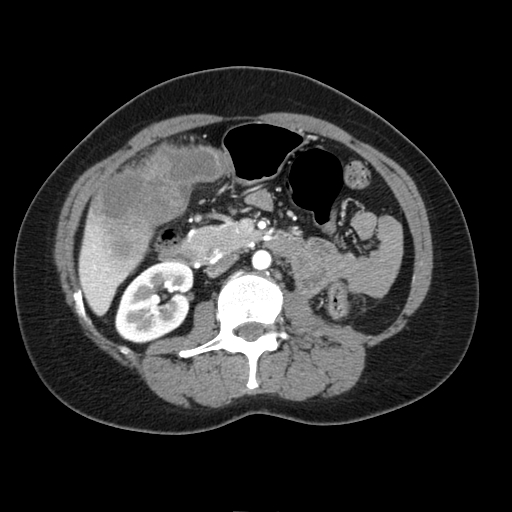
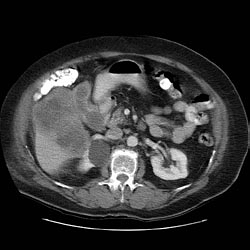
On abdominal CT scan, gallbladder cancer appears as large heterogeneous mass with areas of necrosis.
CT
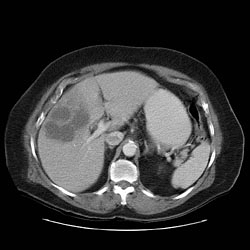
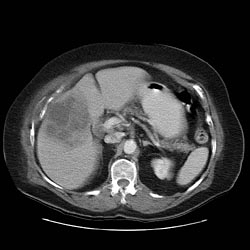
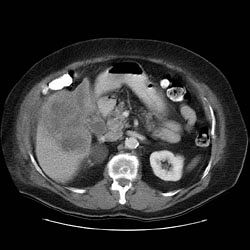
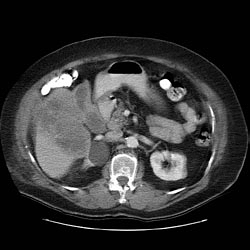
Typically gallbladder adenocarcinomas appear as large heterogeneous masses, which may have engulfed gallstones or areas of necrosis. Patchy moderate contrast enhancement is usually seen.
Features of advanced disease include:
- Intrahepatic biliary dilatation
- Invasion into adjacent structures
- Lymphadenopathy
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis
- Hepatic and distant metastases[1]
- CT scans are often used to diagnose gallbladder cancer. It can confirm the location of the cancer and show the organs near the gallbladder, as well as lymph nodes and distant organs where the cancer might have spread. These are helpful in staging the cancer and in determining whether surgery is a good treatment option. CT scans can also be used to guide a biopsy procedure and a biopsy sample is then removed and looked at under a microscope.
CT Imaging
-
CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
-
CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
-
CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
-
CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
-
CT: Gallbladder adenocarcinoma
Case Example
-
69 year old women with two month history of right upper quadrant pain . Large heterogenous, hypovascular liver mass which abuts an abnormal - appearing gallbladder
-
Diagnostic considerations here would include, first, a locally invasive gallbladder adenocarcinoma and second, an occult colon carcinoma.
-
Cholangiocarcinoma is considered less likely due to the lack of biliary obstruction.
-
Adenopathies
-
3.5 cm simple cyst associated with the upper pole of the right kidney.