GGA2
| Golgi associated, gamma adaptin ear containing, ARF binding protein 2 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1mhq. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | GGA2 ; FLJ20966; KIAA1080; VEAR | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 22860 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
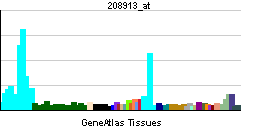
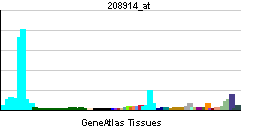
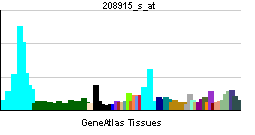
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Golgi associated, gamma adaptin ear containing, ARF binding protein 2, also known as GGA2, is a human gene.[1]
This gene encodes a member of the Golgi-localized, gamma adaptin ear-containing, ARF-binding (GGA) family. This family includes ubiquitous coat proteins that regulate the trafficking of proteins between the trans-Golgi network and the lysosome. These proteins share an amino-terminal VHS domain which mediates sorting of the mannose 6-phosphate receptors at the trans-Golgi network. They also contain a carboxy-terminal region with homology to the ear domain of gamma-adaptins. This family member may play a significant role in cargo molecules regulation and clathrin-coated vesicle assembly.[1]
References
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. PMID 8889548.
- Kikuno R, Nagase T, Ishikawa K; et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XIV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 6 (3): 197–205. PMID 10470851.
- Loftus BJ, Kim UJ, Sneddon VP; et al. (1999). "Genome duplications and other features in 12 Mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q". Genomics. 60 (3): 295–308. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5927. PMID 10493829.
- Poussu A, Lohi O, Lehto VP (2000). "Vear, a novel Golgi-associated protein with VHS and gamma-adaptin "ear" domains". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (10): 7176–83. PMID 10702286.
- Hirst J, Lui WW, Bright NA; et al. (2000). "A family of proteins with gamma-adaptin and VHS domains that facilitate trafficking between the trans-Golgi network and the vacuole/lysosome". J. Cell Biol. 149 (1): 67–80. PMID 10747088.
- Dell'Angelica EC, Puertollano R, Mullins C; et al. (2000). "GGAs: a family of ADP ribosylation factor-binding proteins related to adaptors and associated with the Golgi complex". J. Cell Biol. 149 (1): 81–94. PMID 10747089.
- Boman AL, Zhang C, Zhu X, Kahn RA (2000). "A family of ADP-ribosylation factor effectors that can alter membrane transport through the trans-Golgi". Mol. Biol. Cell. 11 (4): 1241–55. PMID 10749927.
- Takatsu H, Yoshino K, Nakayama K (2000). "Adaptor gamma ear homology domain conserved in gamma-adaptin and GGA proteins that interact with gamma-synergin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 271 (3): 719–25. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2700. PMID 10814529.
- Puertollano R, Randazzo PA, Presley JF; et al. (2001). "The GGAs promote ARF-dependent recruitment of clathrin to the TGN". Cell. 105 (1): 93–102. PMID 11301005.
- Nielsen MS, Madsen P, Christensen EI; et al. (2001). "The sortilin cytoplasmic tail conveys Golgi-endosome transport and binds the VHS domain of the GGA2 sorting protein". EMBO J. 20 (9): 2180–90. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.9.2180. PMID 11331584.
- Puertollano R, Aguilar RC, Gorshkova I; et al. (2001). "Sorting of mannose 6-phosphate receptors mediated by the GGAs". Science. 292 (5522): 1712–6. doi:10.1126/science.1060750. PMID 11387475.
- Zhu Y, Doray B, Poussu A; et al. (2001). "Binding of GGA2 to the lysosomal enzyme sorting motif of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor". Science. 292 (5522): 1716–8. doi:10.1126/science.1060896. PMID 11387476.
- Takatsu H, Katoh Y, Shiba Y, Nakayama K (2001). "Golgi-localizing, gamma-adaptin ear homology domain, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding (GGA) proteins interact with acidic dileucine sequences within the cytoplasmic domains of sorting receptors through their Vps27p/Hrs/STAM (VHS) domains". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (30): 28541–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100218200. PMID 11390366.
- Jacobsen L, Madsen P, Nielsen MS; et al. (2002). "The sorLA cytoplasmic domain interacts with GGA1 and -2 and defines minimum requirements for GGA binding". FEBS Lett. 511 (1–3): 155–8. PMID 11821067.
- Doray B, Bruns K, Ghosh P, Kornfeld S (2002). "Interaction of the cation-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor with GGA proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (21): 18477–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201879200. PMID 11886874.
- Takatsu H, Yoshino K, Toda K, Nakayama K (2002). "GGA proteins associate with Golgi membranes through interaction between their GGAH domains and ADP-ribosylation factors". Biochem. J. 365 (Pt 2): 369–78. doi:10.1042/BJ20020428. PMID 11950392.
- He X, Chang WP, Koelsch G, Tang J (2002). "Memapsin 2 (beta-secretase) cytosolic domain binds to the VHS domains of GGA1 and GGA2: implications on the endocytosis mechanism of memapsin 2". FEBS Lett. 524 (1–3): 183–7. PMID 12135764.
- Wasiak S, Legendre-Guillemin V, Puertollano R; et al. (2002). "Enthoprotin: a novel clathrin-associated protein identified through subcellular proteomics". J. Cell Biol. 158 (5): 855–62. doi:10.1083/jcb.200205078. PMID 12213833.
- Kalthoff C, Groos S, Kohl R; et al. (2003). "Clint: a novel clathrin-binding ENTH-domain protein at the Golgi". Mol. Biol. Cell. 13 (11): 4060–73. doi:10.1091/mbc.E02-03-0171. PMID 12429846.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |