Fumagillin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
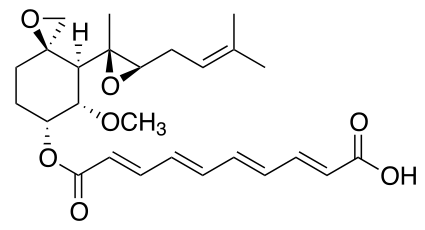
| Formula | C26H34O7 |
| Molar mass | 458.54 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Fumagillin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Fumagillin |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Fumagillin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Fumagillin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Fumagillin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Fumagillin Discussion groups on Fumagillin Patient Handouts on Fumagillin Directions to Hospitals Treating Fumagillin Risk calculators and risk factors for Fumagillin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Fumagillin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Fumagillin is a complex biomolecule and used as an antimicrobial agent. It was isolated in 1949 from the microbial organism Aspergillus fumigatus.[1]
Uses
In animals
It was originally used against microsporidial parasites Nosema apis infections in honey bees.
Some studies found it to be effective against some myxozoan parasites, including Myxobolus cerebralis, an important parasite of fish; however, in the more rigorous tests required for U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval, it was ineffective.
There are reports that fumagillin controls Nosema ceranae,[2] which has recently been hypothesized as a possible cause of colony collapse disorder.[3][4] The latest report, however, has shown it to be ineffective against N. ceranae.[5] Fumagillin is also investigated as an inhibitor of malaria parasite growth.[6][7]
In humans
Fumagillin has been used in the treatment of microsporidiosis.[8][9] It is also an amebicide.[10]
Fumagillin can block blood vessel formation by binding to an enzyme methionine aminopeptidase 2[11] and for this reason, the compound, together with semisynthetic derivatives, are investigated as an angiogenesis inhibitor [12] in the treatment of cancer.
Preliminary clinical trials are being conducted by Zafgen into using the fumagillin analog beloranib for weight loss.[13]
According to Zbidah and coworkers from Germany fumagillin is toxic to erythrocytes in vitro.[14]
Total synthesis
Fumagillin and the related fumagillol (the hydrolysis product) have been a target in total synthesis, with several reported successful strategies, racemic, asymmetric and formal.[15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23]
References
- ↑ F. R. Hanson, T. E. Elbe, J. Bacteriol. 1949, 58, 527
- ↑ Williams, G.R., Sampson, M.A., Shutler, D., Rogers, R.E.L. (2008). "Does fumagillin control the recently detected invasive parasite Nosema ceranae in western honey bees (Apis mellifera)?". Journal of Invertebrate Pathology. 99 (3): 342–344. doi:10.1016/j.jip.2008.04.005. PMID 18550078.
- ↑ Sabin Russell (2007-04-26). "UCSF scientist tracks down suspect in honeybee deaths". San Francisco Chronicle.
- ↑ "Scientists Identify Pathogens That May Be Causing Global Honeybee Deaths" (Portable Document Format). Edgewood Chemical Biological Center. 2007-04-25.Template:Check
- ↑ Huang, Wei-Fone; Leellen Solter; Peter Yau; Brian Imai (7 March 2013). Schneider, David S, ed. "Nosema ceranae Escapes Fumagillin Control in Honey Bees". PLoS Pathogens. 9 (3): e1003185. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003185.
- ↑ Xiaochun Chen et al. "Fumagillin and Fumarranol Interact with P. falciparum Methionine Aminopeptidase 2 and Inhibit Malaria Parasite Growth In Vitro and In Vivo". Chemistry & Biology, Vol. 16 Nr. 2 (2009) blz. 193-202. Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Christopher Arico-Muendel et al. "Antiparasitic activities of novel, orally available fumagillin analogs". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters Vol. 19 Nr. 17 (2009), blz. 5128-5131 Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Lanternier F, Boutboul D, Menotti J; et al. (February 2009). "Microsporidiosis in solid organ transplant recipients: two Enterocytozoon bieneusi cases and review". Transpl Infect Dis. 11 (1): 83–8. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00347.x. PMID 18803616.
- ↑ Molina JM, Tourneur M, Sarfati C; et al. (June 2002). "Fumagillin treatment of intestinal microsporidiosis". N. Engl. J. Med. 346 (25): 1963–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012924. PMID 12075057.
- ↑ Lefkove B, Govindarajan B, Arbiser JL (August 2007). "Fumagillin: an anti-infective as a parent molecule for novel angiogenesis inhibitors". Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 5 (4): 573–9. doi:10.1586/14787210.5.4.573. PMID 17678422.
- ↑ Gilbert, M. A. & Granath, W.O. Jr. (2003). "Whirling disease and salmonid fish: life cycle, biology, and disease". Journal of Parasitology. 89 (4): pp. 658–667. doi:10.1645/GE-82R. PMID 14533670.
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ "Zafgen Announces Positive Topline Phase 1b Data for ZGN-433 in Obesity". MedNews. Drugs.com. 5 January 2011.
- ↑ Zbidah, M; Lupescu, A; Jilani, K; Lang, F (2013). "Stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by fumagillin". Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology. 112 (5): 346–51. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12033. PMID 23121865.
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ A Concise Synthesis of Fumagillol David A. Vosburg, Sven Weiler, Erik J. Sorensen Angewandte Chemie International Edition Volume 38, Issue 7, Date: April 1, 1999, Pages: 971-974 DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- ↑ Template:Cite DOI
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- CS1 maint: Extra text
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Articles with changed DrugBank identifier
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without KEGG source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Epoxides
- Antiprotozoal agents
- Total synthesis
- Drug