Floxuridine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Floxuridine is an antineoplastic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of palliative management of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma metastatic to the liver. Common adverse reactions include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, enteritis, stomatitis and localized erythema. The more common laboratory abnormalities are anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and elevations of alkaline phosphatase, serum transaminase, serum bilirubin and lactic dehydrogenase..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Metastasis to the liver
- Floxuridine for Injection, USP is effective in the palliative management of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma metastatic to the liver, when given by continuous regional intra-arterial infusion in carefully selected patients who are considered incurable by surgery or other means. Patients with known disease extending beyond an area capable of infusion via a single artery should, except in unusual circumstances, be considered for systemic therapy with other chemotherapeutic agents.
Dosing Information
- Each vial must be reconstituted with 5 mL of sterile water for injection to yield a solution containing approximately 100 mg of floxuridine/mL. The calculated daily dose(s) of the drug is then diluted with 5% dextrose or 0.9% sodium chloride injection to a volume appropriate for the infusion apparatus to be used. The administration of floxuridine is best achieved with the use of an appropriate pump to overcome pressure in large arteries and to ensure a uniform rate of infusion.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
- The recommended therapeutic dosage schedule of floxuridine by continuous arterial infusion is 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg/day. The higher dosage ranges (0.4 to 0.6 mg) are usually employed for hepatic artery infusion because the liver metabolizes the drug, thus reducing the potential for systemic toxicity. Therapy can be given until adverse reactions appear. When these side effects have subsided, therapy may be resumed. The patients should be maintained on therapy as long as response to floxuridine continues.
- Procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs should be considered. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.1-7 There is no general agreement that all of the procedures recommended in the guidelines are necessary or appropriate.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Floxuridine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Floxuridine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Floxuridine in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Floxuridine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Floxuridine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Floxuridine therapy is contraindicated for patients in a poor nutritional state, those with depressed bone marrow function or those with potentially serious infections.
Warnings
BECAUSE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SEVERE TOXIC REACTIONS, ALL PATIENTS SHOULD BE HOSPITALIZED FOR THE FIRST COURSE OF THERAPY.
- Floxuridine should be used with extreme caution in poor risk patients with impaired hepatic or renal function or a history of high-dose pelvic irradiation or previous use of alkylating agents. The drug is not intended as an adjuvant to surgery.
- Floxuridine may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. It has been shown to be teratogenic in the chick embryo, mouse (at doses of 2.5 to 100 mg/kg) and rat (at doses of 75 to 150 mg/kg). Malformations included cleft palates; skeletal defects; and deformed appendages, paws and tails. The dosages which were teratogenic in animals are 4.2 to 125 times the recommended human therapeutic dose.
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with floxuridine in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking (receiving) this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant.
Combination Therapy
- Any form of therapy which adds to the stress of the patient, interferes with nutrition or depresses bone marrow function will increase the toxicity of floxuridine.
Precautions
General
- Floxuridine is a highly toxic drug with a narrow margin of safety. Therefore, patients should be carefully supervised since therapeutic response is unlikely to occur without some evidence of toxicity. Severe hematological toxicity, gastrointestinal hemorrhage and even death may result from the use of floxuridine despite meticulous selection of patients and careful adjustment of dosage. Although severe toxicity is more likely in poor risk patients, fatalities may be encountered occasionally even in patients in relatively good condition.
- Therapy is to be discontinued promptly whenever one of the following signs of toxicity appears:
- Stomatitis or esophagopharyngitis, at the first visible sign
- Leukopenia (WBC under 3500) or a rapidly falling white blood count
- Vomiting, intractable
- Diarrhea, frequent bowel movements or watery stools
- Thrombocytopenia (platelets under 100,000)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Adverse reactions to the arterial infusion of floxuridine are generally related to the procedural complications of regional arterial infusion.
- The more common adverse reactions to the drug are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, enteritis, stomatitis and localized erythema. The more common laboratory abnormalities are anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and elevations of alkaline phosphatase, serum transaminase, serum bilirubin and lactic dehydrogenase.
- Other adverse reactions are:
- Gastrointestinal: duodenal ulcer, duodenitis, gastritis, bleeding, gastroenteritis, glossitis, pharyngitis, anorexia, cramps, abdominal pain; possible intra- and extrahepatic biliary sclerosis, as well as acalculous cholecystitis.
- Dermatologic: alopecia, dermatitis, nonspecific skin toxicity, rash.
- Cardiovascular: myocardial ischemia.
- Laboratory Abnormalities: BSP, prothrombin, total proteins, sedimentation rate and thrombopenia.
- Procedural Complications of Regional Arterial Infusion: arterial aneurysm; arterial ischemia; arterial thrombosis; embolism; fibromyositis; thrombophlebitis; hepatic necrosis; abscesses; infection at catheter site; bleeding at catheter site; catheter blocked, displaced or leaking.
- The following adverse reactions have not been reported with floxuridine but have been noted following the administration of 5-fluorouracil. While the possibility of these occurring following floxuridine therapy is remote because of its regional administration, one should be alert for these reactions following the administration of floxuridine because of the pharmacological similarity of these two drugs: pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, myocardial ischemia, angina, anaphylaxis, generalized allergic reactions, acute cerebellar syndrome, nystagmus, headache, dry skin, fissuring, photosensitivity, pruritic maculopapular rash, increased pigmentation of the skin, vein pigmentation, lacrimal duct stenosis, visual changes, lacrimation, photophobia, disorientation, confusion, euphoria, epistaxis and nail changes, including loss of nails.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Floxuridine in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Floxuridine Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Floxuridine has been shown to be teratogenic in the chick embryo, mouse (at doses of 2.5 to 100 mg/kg) and rat (at doses of 75 to 150 mg/kg). Malformations included cleft palates, skeletal defects and deformed appendages, paws and tails. The dosages which were teratogenic in animals are 3.2 to 125 times the recommended human therapeutic dose.
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with floxuridine in pregnant women. While there is no evidence of teratogenicity in humans due to floxuridine, it should be kept in mind that other drugs which inhibit DNA synthesis (eg, methotrexate and aminopterin) have been reported to be teratogenic in humans. Floxuridine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
- Floxuridine has not been studied in animals for its effects on peri- and postnatal development. However, compounds which inhibit DNA, RNA and protein synthesis might be expected to have adverse effects on peri- and postnatal development.
- There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Floxuridine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Floxuridine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether floxuridine is excreted in human milk. Because floxuridine inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis, mothers should not nurse while receiving this drug.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Floxuridine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Floxuridine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Intra arterial
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Floxuridine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Floxuridine in the drug label.
Overdosage
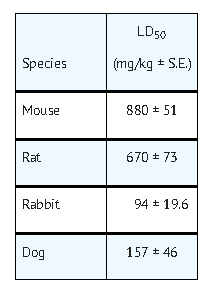
- The possibility of overdosage with floxuridine is unlikely in view of the mode of administration. Nevertheless, the anticipated manifestations would be nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal ulceration and bleeding, bone marrow depression (including thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and agranulocytosis). No specific antidotal therapy exists. Patients who have been exposed to an overdosage of floxuridine should be monitored hematologically for at least 4 weeks. Should abnormalities appear, appropriate therapy should be utilized. The acute intravenous toxicity of floxuridine is as follows:
Pharmacology

Mechanism of Action
- When floxuridine is given by rapid intra-arterial injection it is apparently rapidly catabolized to 5-fluorouracil. Thus, rapid injection of floxuridine produces the same toxic and antimetabolic effects as does 5-fluorouracil. The primary effect is to interfere with the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and to a lesser extent inhibit the formation of ribonucleic acid (RNA). However, when floxuridine is given by continuous intra-arterial infusion its direct anabolism to floxuridine-monophosphate is enhanced, thus increasing the inhibition of DNA.
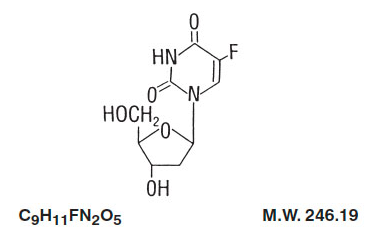
Structure
- Floxuridine for Injection, USP, an antineoplastic antimetabolite, is available as a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized powder for reconstitution. Each vial contains 500 mg of floxuridine which is to be reconstituted with 5 mL of sterile water for injection. An appropriate amount of reconstituted solution is then diluted with a parenteral solution for intra-arterial infusion.
- Floxuridine is a fluorinated pyrimidine. Chemically, floxuridine is 2’-deoxy-5-fluorouridine. It is a white to off-white odorless solid which is freely soluble in water. The 2% aqueous solution has a pH of between 4.0 and 5.5.
The structural formula is:
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Floxuridine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- Floxuridine is metabolized in the liver. The drug is excreted intact and as urea, fluorouracil, α-fluoro-β-ureidopropionic acid, dihydrofluorouracil, α-fluoro-β-guanidopropionic acid and α-fluoro-β-alanine in the urine; it is also expired as respiratory carbon dioxide. Pharmacokinetic data on intra-arterial infusion of floxuridine are not available.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
- Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of floxuridine have not been conducted. On the basis of the available data, no evaluation can be made of the carcinogenic risk of floxuridine to humans.
Mutagenesis
- Oncogenic transformation of fibroblasts from mouse embryo has been induced in vitro by floxuridine, but the relationship between oncogenicity and mutagenicity is not clear. Floxuridine has also been shown to be mutagenic in human leukocytes in vitro and in the Drosophila test system. In addition, 5-fluorouracil, to which floxuridine is catabolized when given by intraarterial injection, has been shown to be mutagenic in in vitro tests.
Impairment of Fertility
- The effects of floxuridine on fertility and general reproductive performance have not been studied in animals. However, because floxuridine is catabolized to 5-fluorouracil, it should be noted that 5-fluorouracil has been shown to induce chromosomal aberrations and changes in chromosome organization of spermatogonia in rats at doses of 125 or 250 mg/kg, administered intraperitoneally.
- Spermatogonial differentiation was also inhibited by fluorouracil, resulting in transient infertility. In female rats, fluorouracil, administered intraperitoneally at doses of 25 or 50 mg/kg during the preovulatory phase of oogenesis, significantly reduced the incidence of fertile matings, delayed the development of pre- and post-implantation embryos, increased the incidence of preimplantation lethality and induced chromosomal anomalies in these embryos. Compounds such as floxuridine, which interfere with DNA, RNA and protein synthesis, might be expected to have adverse effects on gametogenesis.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Floxuridine in the drug label.
How Supplied
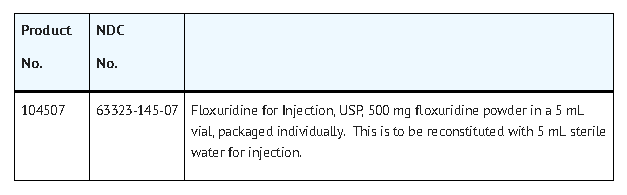
- Vial stoppers do not contain natural rubber latex.
The sterile powder should be stored at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Reconstituted vials should be stored under refrigeration 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) for not more than 2 weeks.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Floxuridine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Floxuridine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Floxuridine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Floxuridine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Floxuridine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Floxuridine Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Floxuridine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Floxuridine
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Floxuridine |Label Name=Floxuridine04.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Floxuridine |Label Name=Floxuridine05.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Floxuridine |Label Name=Floxuridine06.png
}}