Florfenicol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
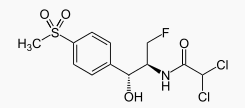
| Synonyms | 2,2-dichloro-N-((1R,2S)-3-fluoro-1-hydroxy-1-(4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)ethanamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | intramuscular, subcutaneous |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14Cl2FNO4S |
| Molar mass | 358.21 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Florfenicol |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Florfenicol Most cited articles on Florfenicol |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Florfenicol |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Florfenicol at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Florfenicol at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Florfenicol
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Florfenicol Discussion groups on Florfenicol Patient Handouts on Florfenicol Directions to Hospitals Treating Florfenicol Risk calculators and risk factors for Florfenicol
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Florfenicol |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Florfenicol (marketed by Schering-Plough Animal Health under the trade name Nuflor) is a fluorinated synthetic analog of thiamphenicol.[1]
In the United States, florfenicol is currently indicated for the treatment of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) associated with Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Haemophilus somnus, for treatment of bovine interdigital phlegmon (foot rot, acute interdigital necrobacillosis, infectious pododermatitis) associated with Fusobacterium necrophorum and Bacteroides melaninogenicus.
Florfenicol is also used in aquaculture, and is licensed for use in the United States for the control of enteric septicemia in catfish.[2]
The use of florfenicol in horses, and likely in other equids, typically causes diarrhea. This has been anecdotally reported to progress to lethal cases of acute colitis. Therefore, use of this antimicrobial in the equine patient should be limited to cases in which other, safer, options are not available. [3]
Contamination
Florfenicol was among the drug contaminants in a brand of supermarket eggs in Taiwan and Iran.[4]
External links
References
- ↑ Syriopoulou VP, Harding AL, Goldmann DA, Smith AL (February 1981). "In vitro antibacterial activity of fluorinated analogs of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 19 (2): 294–7. PMC 181412. PMID 6957162.
- ↑ Gaunt, P. S.; Langston, C.; Wrzesinski, C.; Gao, D.; Adams, P.; Crouch, L.; Sweeney, D.; Endris, R. "Multidose pharmacokinetics of orally administered florfenicol in the channel catfish ( )". Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 36 (5): 502–506. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2885.2012.01426.x.
- ↑ Robinson, N.E.; Sprayberry, K.A. (2009). Current therapy in equine medicine. Saunders Elesevier. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-4160-5475-7. Retrieved March 21, 2011.
- ↑ Lee I-chia (8 January 2013). "Survey suggests certain eggs may be dangerous". Taipei Times. Retrieved 3 November 2014.
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drug
- Amphenicols
- Sulfones
- Phenethylamines
- Alcohols
- Organofluorides
- Acetamides
- Organochlorides