Etravirine
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Etravirine is a {{{drugClass}}} that is FDA approved for the treatment of {{{indication}}}. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- INTELENCE®1, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in antiretroviral treatment-experienced patients ages 6 years and older, who have evidence of viral replication and HIV-1 strains resistant to a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and other antiretroviral agents.
- The indication for adult use is based on Week 48 analyses from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of INTELENCE®. Both studies were conducted in clinically advanced, 3-class antiretroviral (NNRTI, N[t]RTI, PI) treatment-experienced adults. The indication for pediatric use is based on 24-week analyses of a single-arm, Phase 2 trial in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric subjects 6 years to less than 18 years of age.
- In treatment-experienced adult and pediatric patients, the following points should be considered when initiating therapy with INTELENCE®:
- Treatment history and resistance testing should guide the use of INTELENCE® due to concerns for potential cross-resistance .
- In patients who have experienced virologic failure on an NNRTI-containing regimen, do not use INTELENCE® in combination with only N[t]RTIs .
- The use of other active antiretroviral agents with INTELENCE® is associated with an increased likelihood of treatment response.
- The safety and efficacy of INTELENCE® have not been established in treatment-naïve adult patients.
Dosage
The recommended oral dose of INTELENCE® tablets is 200 mg (one 200 mg tablet or two 100 mg tablets) taken twice daily following a meal. The type of food does not affect the exposure to etravirine.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
INTELENCE® 25 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 25 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white, oval, scored tablets debossed with "TMC" on one side.
INTELENCE® 100 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 100 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white oval tablets debossed with "TMC125" on one side and "100" on the other side.
INTELENCE® 200 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 200 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white, biconvex, oblong tablets debossed with "T200" on one side.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Etravirine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Etravirine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Indications
- INTELENCE®1, in combination with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in antiretroviral treatment-experienced patients ages 6 years and older, who have evidence of viral replication and HIV-1 strains resistant to a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and other antiretroviral agents.
- The indication for adult use is based on Week 48 analyses from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of INTELENCE®. Both studies were conducted in clinically advanced, 3-class antiretroviral (NNRTI, N[t]RTI, PI) treatment-experienced adults. The indication for pediatric use is based on 24-week analyses of a single-arm, Phase 2 trial in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric subjects 6 years to less than 18 years of age.
- In treatment-experienced pediatric patients, the following points should be considered when initiating therapy with INTELENCE®:
- Treatment history and resistance testing should guide the use of INTELENCE® due to concerns for potential cross-resistance .
- In patients who have experienced virologic failure on an NNRTI-containing regimen, do not use INTELENCE® in combination with only N[t]RTIs .
- The use of other active antiretroviral agents with INTELENCE® is associated with an increased likelihood of treatment response.
- The safety and efficacy of INTELENCE® have not been established in treatment-naïve adult patients.
Dosage
Pediatric Patients (6 years to less than 18 years of age)
The recommended dose of INTELENCE® for pediatric patients 6 years to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 16 kg is based on body weight (see TABLE BELOW) not exceeding the recommended adult dose. INTELENCE® tablet(s) should be taken orally, following a meal. The type of food does not affect the exposure to etravirine.
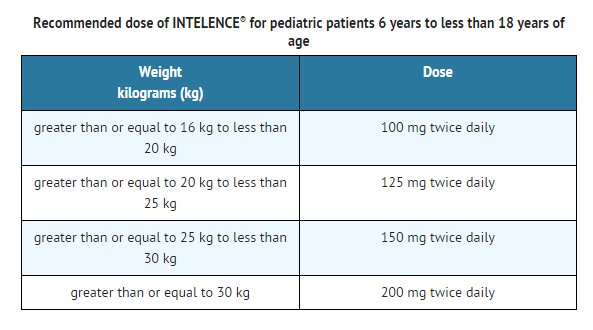
- The safety and efficacy of INTELENCE® have not been established in children less than 6 years of age
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
INTELENCE® 25 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 25 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white, oval, scored tablets debossed with "TMC" on one side.
INTELENCE® 100 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 100 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white oval tablets debossed with "TMC125" on one side and "100" on the other side.
INTELENCE® 200 mg Tablets
- INTELENCE® 200 mg tablets are supplied as white to off-white, biconvex, oblong tablets debossed with "T200" on one side.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Etravirine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Etravirine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- None
Warnings
Severe Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Severe, potentially life-threatening, and fatal skin reactions have been reported. These include cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme. Hypersensitivity reactions including drug rash with eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) have also been reported and were characterized by rash, constitutional findings, and sometimes organ dysfunction, including hepatic failure. In Phase 3 clinical trials, Grade 3 and 4 rashes were reported in 1.3% of subjects receiving INTELENCE® compared to 0.2% of placebo subjects. A total of 2.2% of HIV-1-infected subjects receiving INTELENCE® discontinued from Phase 3 trials due to rash. Rash occurred most commonly during the first 6 weeks of therapy. The incidence of rash was higher in females.
- Discontinue INTELENCE® immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions develop (including, but not limited to, severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, facial edema, hepatitis, eosinophilia, angioedema). Clinical status including liver transaminases should be monitored and appropriate therapy initiated. Delay in stopping INTELENCE® treatment after the onset of severe rash may result in a life-threatening reaction.
Fat Redistribution
- Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorso cervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
- Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including INTELENCE®. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
- Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections:
- Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions
Clinical Trials Experience: Adults
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- The safety assessment is based on all data from 1203 subjects in the Phase 3 placebo-controlled trials, TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216, conducted in antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult subjects, 599 of whom received INTELENCE® (200 mg twice daily). In these pooled trials, the median exposure for subjects in the INTELENCE® arm and placebo arm was 52.3 and 51.0 weeks, respectively. Discontinuations due to adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were 5.2% in the INTELENCE® arm and 2.6% in the placebo arm.
- The most frequently reported ADR at least Grade 2 in severity was rash (10.0%). Stevens-Johnson syndrome, drug hypersensitivity reaction and erythema multiforme were reported in less than 0.1% of subjects during clinical development with INTELENCE® [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]. A total of 2.2% of HIV-1-infected subjects in Phase 3 trials receiving INTELENCE® discontinued due to rash. In general, in clinical trials, rash was mild to moderate, occurred primarily in the second week of therapy, and was infrequent after Week 4. Rash generally resolved within 1 to 2 weeks on continued therapy. The incidence of rash was higher in women compared to men in the INTELENCE® arm in the Phase 3 trials (rash ≥ Grade 2 was reported in 9/60 [15.0%] women versus 51/539 [9.5%] men; discontinuations due to rash were reported in 3/60 [5.0%] women versus 10/539 [1.9%] men). Patients with a history of NNRTI-related rash did not appear to be at increased risk for the development of INTELENCE®-related rash compared to patients without a history of NNRTI-related rash.
Common Adverse Reactions
- Clinical ADRs of moderate intensity or greater (greater than or equal to Grade 2) and reported in at least 2% of subjects treated with INTELENCE® and occurring at a higher rate compared to placebo (excess of 1%) are presented in Table 1. Laboratory abnormalities considered ADRs are included in Table 2.
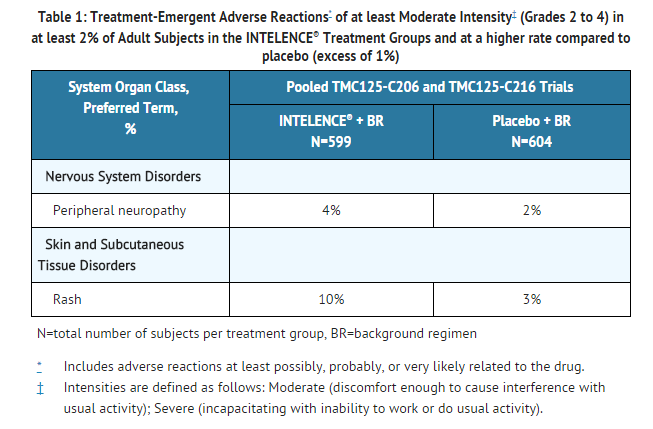
Less Common Adverse Reactions
- Treatment-emergent ADRs occurring in less than 2% of subjects (599 subjects) receiving INTELENCE® and of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) are listed below by body system:
- Cardiac Disorders: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation
- Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: vertigo
- Eye Disorders: blurred vision
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: gastroesophageal reflux disease, flatulence, gastritis, abdominal distension, pancreatitis, constipation, dry mouth, hematemesis, retching, stomatitis
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: sluggishness
- Hematologic Disorders: hemolytic anemia
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatic failure, hepatomegaly, cytolytic hepatitis, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis
- Immune System Disorders: drug hypersensitivity, immune reconstitution syndrome
- Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: diabetes mellitus, anorexia, dyslipidemia
- Nervous System Disorders: paraesthesia, somnolence, convulsion, hypoesthesia, amnesia, syncope, disturbance in attention, hypersomnia, tremor
- Psychiatric Disorders: anxiety, sleep disorders, abnormal dreams, confusional state, disorientation, nervousness, nightmares
- Renal and Urinary Disorders: acute renal failure
- Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: gynecomastia
- Respiratory,Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: exertional dyspnea, bronchospasm
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: night sweats, lipohypertrophy, prurigo, hyperhidrosis, dry skin, swelling face
- Additional ADRs of at least moderate intensity observed in other trials were acquired lipodystrophy, angioneurotic edema, erythema multiforme and haemorrhagic stroke, each reported in no more than 0.5% of subjects.
Laboratory Abnormalities in Treatment-Experienced Patients
Selected Grade 2 to Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline observed in adult subjects treated with INTELENCE® are presented in Table 2.
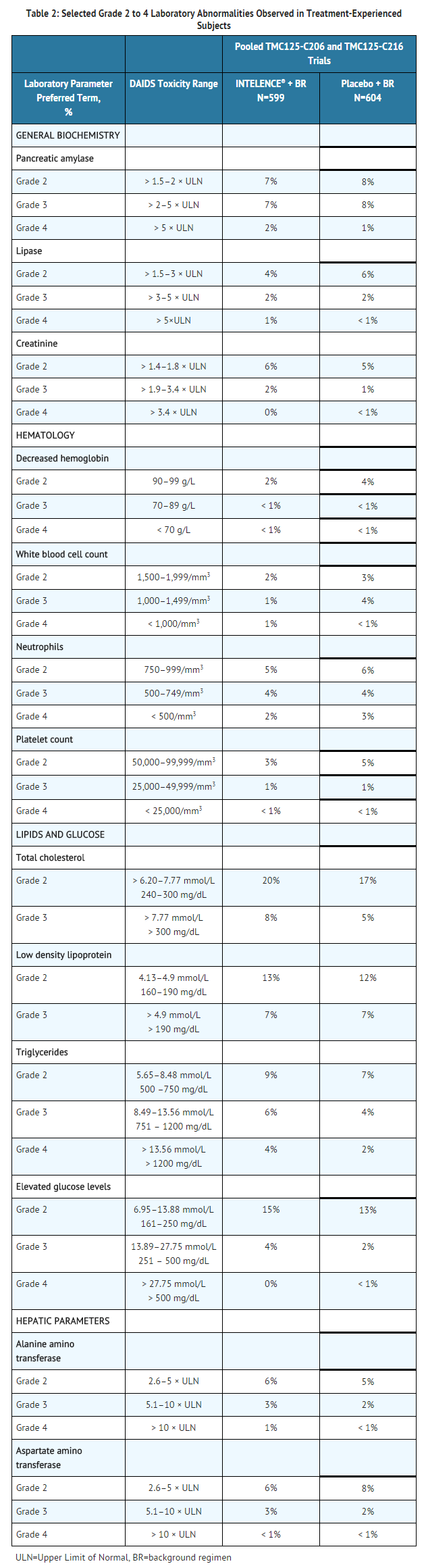
Patients co-infected with hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus
- In Phase 3 trials TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216, 139 subjects (12.3%) with chronic hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infection out of 1129 subjects were permitted to enroll. AST and ALT abnormalities occurred more frequently in hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infected subjects for both treatment groups. Grade 2 or higher laboratory abnormalities that represent a worsening from baseline of AST, ALT or total bilirubin occurred in 27.8%, 25.0% and 7.1% respectively, of INTELENCE®-treated co-infected subjects as compared to 6.7%, 7.5% and 1.8% of non-co-infected INTELENCE®-treated subjects. In general, adverse events reported by INTELENCE®-treated subjects with hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infection were similar to INTELENCE®-treated subjects without hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infection.
Clinical Trials Experience: Pediatric Subjects (6 years to less than 18 years of age)
- The safety assessment in children and adolescents is based on the Week 24 analysis of the single-arm, Phase 2 trial TMC125-C213 in which 101 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1 infected subjects 6 years to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 16 kg received INTELENCE® in combination with other antiretroviral agents. The frequency, type and severity of adverse drug reactions in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adult subjects, except for rash which was observed more frequently in pediatric subjects. The most common adverse drug reactions in at least 2% of pediatric subjects were rash and diarrhea. Rash was reported more frequently in female subjects than in male subjects (rash ≥ Grade 2 was reported in 13/64 [20.3%] females versus 2/37 [5.4%] males; discontinuations due to rash were reported in 4/64 [6.3%] females versus 0/37 [0%] males). Rash (greater than or equal to Grade 2) occurred in 15% of pediatric subjects. In the majority of cases, rash was mild to moderate, of macular/papular type, and occurred in the second week of therapy. Rash was self-limiting and generally resolved within 1 week on continued therapy. The safety profile for subjects who completed 48 weeks of treatment was similar to the safety profile for subjects who completed 24 weeks of treatment.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following events have been identified during postmarketing use of INTELENCE®. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Immune System Disorders: Severe hypersensitivity reactions including DRESS and cases of hepatic failure have been reported.
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: rhabdomyolysis
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Fatal cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported.
Drug Interactions
- Etravirine is a substrate of CYP3A, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. Therefore, co-administration of INTELENCE® with drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 may alter the therapeutic effect or adverse reaction profile of INTELENCE® (see TABLE 3).
- Etravirine is an inducer of CYP3A and inhibitor of CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and P-glycoprotein. Therefore, co-administration of drugs that are substrates of CYP3A, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 or are transported by P-glycoprotein with INTELENCE® may alter the therapeutic effect or adverse reaction profile of the co-administered drug(s) (see TABLE 3).
- Table 3 shows the established and other potentially significant drug interactions based on which, alterations in dose or regimen of INTELENCE® and/or co-administered drug may be recommended. Drugs that are not recommended for co-administration with INTELENCE® are also included in Table 3.
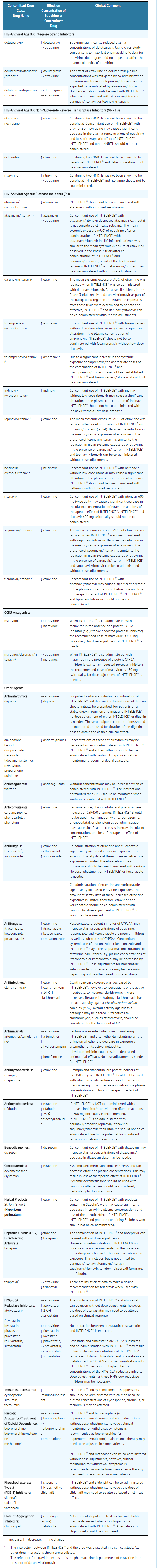
- In addition to the drugs included in Table 3, the interaction between INTELENCE® and the following drugs were evaluated in clinical studies and no dose adjustment is needed for either drug: didanosine, enfuvirtide (ENF),ethinylestradiol/norethindrone, omeprazole, paroxetine, raltegravir, ranitidine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Pregnancy Category B
- No adequate and well-controlled studies of INTELENCE® use in pregnant women have been conducted. In addition, no pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted in pregnant patients. INTELENCE® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry
- To monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to INTELENCE®, an Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263.
Animal Data
- Reproductive and developmental toxicity studies were performed in rabbits (at oral doses up to 375 mg per kg per day) and rats (at oral doses up to 1000 mg per kg per day). In both species, no treatment-related embryo-fetal effects including malformations were observed. In addition, no treatment-related effects were observed in a separate pre- and postnatal study performed in rats at oral doses up to 500 mg per kg per day. The systemic drug exposures achieved in these animal studies were equivalent to those at the recommended human dose (400 mg per day).
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Etravirine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Etravirine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. It is not known whether etravirine is secreted in human milk. Because of both the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breastfeed if they are receiving INTELENCE®.
Pediatric Use
- Treatment with INTELENCE® is not recommended in children less than 6 years of age. The pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability and efficacy of INTELENCE® in children less than 6 years of age have not been established.
- The safety, pharmacokinetic profile, and virologic and immunologic responses of INTELENCE® were evaluated in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 6 years to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 16 kg. Frequency, type, and severity of adverse drug reactions in pediatric subjects were comparable to those observed in adults, except for rash.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical studies of INTELENCE® did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Etravirine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Etravirine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- Since the renal clearance of etravirine is negligible (less than 1.2%), a decrease in total body clearance is not expected in patients with renal impairment. No dose adjustments are required in patients with renal impairment. As etravirine is highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that it will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment of INTELENCE® is required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of INTELENCE® have not been evaluated in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C).
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Etravirine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Etravirine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Etravirine in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Etravirine in the drug label.
Overdosage
- There is no specific antidote for overdose with INTELENCE®. Human experience of overdose with INTELENCE® is limited. The highest dose studied in healthy volunteers was 400 mg once daily. Treatment of overdose with INTELENCE® consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed active substance is to be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage. Administration of activated charcoal may also be used to aid in removal of unabsorbed active substance. Because etravirine is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to result in significant removal of the active substance.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Etravirine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
- INTELENCE® (etravirine) is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1).
- The chemical name for etravirine is 4-[[6-amino-5-bromo-2-(4-cyanophenyl)amino-4-pyrimidinyl]oxy]]-3,5-dimethylbenzonitrile. Its molecular formula is C20H15BrN6O and its molecular weight is 435.28. Etravirine has the following structural formula:
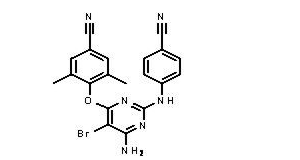
- Etravirine is a white to slightly yellowish brown powder. Etravirine is practically insoluble in water over a wide pH range. It is very slightly soluble in propylene glycol and slightly soluble in ethanol. Etravirine is soluble in polyethylene glycol (PEG)400 and freely soluble in some organic solvents (e.g., N,N-dimethylformamide and tetrahydrofuran).
- INTELENCE® 25 mg tablets are available as white to off-white, oval scored tablets for oral administration. Each 25 mg tablet contains 25 mg of etravirine and the inactive ingredients hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate and lactose monohydrate.
- INTELENCE® 100 mg tablets are available as white to off-white, oval tablets for oral administration. Each 100 mg tablet contains 100 mg of etravirine and the inactive ingredients hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate and lactose monohydrate.
- INTELENCE® 200 mg tablets are available as white to off-white, biconvex, oblong tablets for oral administration. Each 200 mg tablet contains 200 mg of etravirine and the inactive ingredients hypromellose, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate.
Pharmacodynamics
Effects on Electrocardiogram
- In a randomized, double-blind, active, and placebo-controlled crossover study, 41 healthy subjects were administered INTELENCE® 200 mg twice daily, INTELENCE® 400 mg once daily, placebo, and moxifloxacin 400 mg. After 8 days of dosing, etravirine did not prolong the QT interval. The maximum mean (upper 1-sided 95% CI) baseline and placebo-adjusted QTcF were 0.6 ms (3.3 ms) for 200 mg twice daily and -1.0 ms (2.5 ms) for 400 mg once daily dosing regimens.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics in Adults
- The pharmacokinetic properties of INTELENCE® were determined in healthy adult subjects and in treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected adult and pediatric subjects. The systemic exposures (AUC) to etravirine were lower in HIV-1-infected subjects than in healthy subjects.

- Note: The median protein binding adjusted EC50 for MT4 cells infected with HIV-1/IIIB in vitro equals 4 ng per mL.
Absorption and Bioavailability
- Following oral administration, etravirine was absorbed with a Tmax of about 2.5 to 4 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of INTELENCE® is unknown.
- In healthy subjects, the absorption of etravirine is not affected by co-administration of oral ranitidine or omeprazole, drugs that increase gastric pH.
Effects of Food on Oral Absorption
- The systemic exposure (AUC) to etravirine was decreased by about 50% when INTELENCE® was administered under fasting conditions, as compared to when INTELENCE® was administered following a meal. Therefore, INTELENCE® should always be taken following a meal. Within the range of meals studied, the systemic exposures to etravirine were similar. The total caloric content of the various meals evaluated ranged from 345 kilocalories (17 grams fat) to 1160 kilocalories (70 grams fat).
Distribution
- Etravirine is about 99.9% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin (99.6%) and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (97.66% to 99.02%) in vitro. The distribution of etravirine into compartments other than plasma (e.g., cerebrospinal fluid, genital tract secretions) has not been evaluated in humans.
Metabolism
- In vitro experiments with human liver microsomes (HLMs) indicate that etravirine primarily undergoes metabolism by CYP3A, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 enzymes. The major metabolites, formed by methyl hydroxylation of the dimethylbenzonitrile moiety, were at least 90% less active than etravirine against wild-type HIV in cell culture.
Elimination
- After single dose oral administration of 800 mg 14C-etravirine, 93.7% and 1.2% of the administered dose of 14C-etravirine was recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged etravirine accounted for 81.2% to 86.4% of the administered dose in feces. Unchanged etravirine was not detected in urine. The mean (± standard deviation) terminal elimination half-life of etravirine was about 41 (± 20) hours.
Special Populations
Hepatic Impairment
- Etravirine is primarily metabolized by the liver. The steady state pharmacokinetic parameters of etravirine were similar after multiple dose administration of INTELENCE® to subjects with normal hepatic function (16 subjects), mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, 8 subjects), and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, 8 subjects). The effect of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of etravirine has not been evaluated.
Hepatitis B and/or Hepatitis C Virus Co-infection
- Population pharmacokinetic analysis of the TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216 trials showed reduced clearance for etravirine in HIV-1-infected subjects with hepatitis B and/or C virus co-infection. Based upon the safety profile of INTELENCE®, no dose adjustment is necessary in patients co-infected with hepatitis B and/or C virus.
Renal Impairment
- The pharmacokinetics of etravirine have not been studied in patients with renal impairment. The results from a mass balance study with 14C-etravirine showed that less than 1.2% of the administered dose of etravirine is excreted in the urine as metabolites. No unchanged drug was detected in the urine. As etravirine is highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that it will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Gender
- No significant pharmacokinetic differences have been observed between males and females.
Race
- Population pharmacokinetic analysis of etravirine in HIV-infected subjects did not show an effect of race on exposure to etravirine.
Geriatric Patients
- Population pharmacokinetic analysis in HIV-infected subjects showed that etravirine pharmacokinetics are not considerably different within the age range (18 to 77 years) evaluated.
Pediatric Patients
- The pharmacokinetics of etravirine in 101 treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects, 6 years to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 16 kg showed that the administered weight-based dosages (approximately 5.2 mg per kg twice daily up to the adult recommended doses) resulted in etravirine exposure comparable to that in adults receiving INTELENCE® 200 mg twice daily when administered at a dose corresponding to 5.2 mg per kg twice daily. The population pharmacokinetic estimates for etravirine AUC12h and C0h are summarized in the table below.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Etravirine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Etravirine in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Etravirine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Etravirine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Etravirine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Etravirine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Etravirine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Etravirine
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Etravirine |Label Name=Etravirine11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Etravirine |Label Name=Etravirine11.png
}}