Endometrial cancer: Difference between revisions
(Mahshid) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Endometrial cancer}} | {{Endometrial cancer}} | ||
{{CMG}}{{AE}}{{MD}} | {{CMG}}{{AE}}{{MD}} [[Ogechukwu Hannah Nnabude, MD]] | ||
{{SK}} Endometrial adenocarcinoma; adenocarcinoma - endometrium; adenocarcinoma - uterus; cancer - endometrial; uterine corpus cancer; endometrial carcinoma; cancer of the endometrium; cancer of endometrium; Neoplasm of endometrium; Endometrial neoplasm. | {{SK}} Endometrial adenocarcinoma; adenocarcinoma - endometrium; adenocarcinoma - uterus; cancer - endometrial; uterine corpus cancer; endometrial carcinoma; cancer of the endometrium; cancer of endometrium; Neoplasm of endometrium; Endometrial neoplasm. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==[[Endometrial cancer natural history|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ==[[Endometrial cancer natural history|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The definitive diagnosis of endometrial cancer is accomplished by the use of histology. The personal and family history of the patient together with a complete physical examination are instrumental. Intrauterine pregnancy should be considered in women of reproductive age with abnormal uterine bleeding or amenorrhea unless postmenopausal status has been confirmed. If suspicious symptoms, signs, and/or family history are present, basic laboratory evaluation, cervical-vaginal Pap smear, and transvaginal TVU scanning generally are considered. Patients with an abnormal Pap smear should undergo further investigation regardless of age . <ref name="pmid28508342">{{cite journal| author=Tzur T, Kessous R, Weintraub AY| title=Current strategies in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer. | journal=Arch Gynecol Obstet | year= 2017 | volume= 296 | issue= 1 | pages= 5-14 | pmid=28508342 | doi=10.1007/s00404-017-4391-z | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28508342 }} </ref> | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 27 October 2020
For patient information click here
| Endometrial cancer | |
 | |
|---|---|
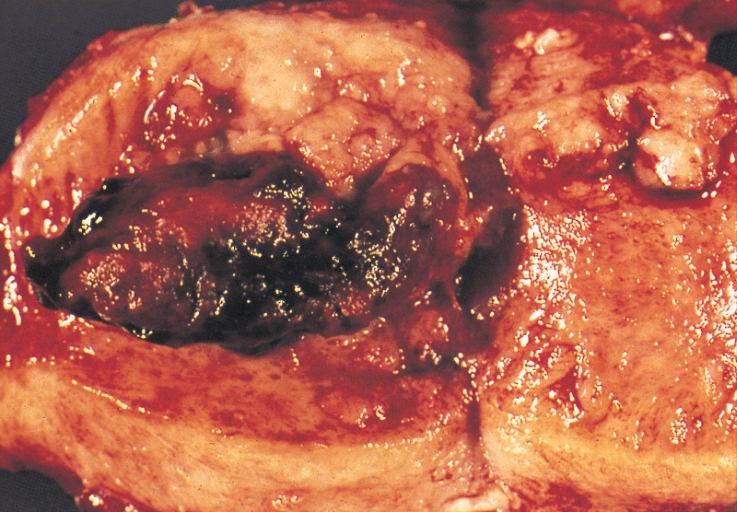
| An endometrial adenocarcinoma invading the uterine muscle |
|
Endometrial cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Endometrial cancer On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Endometrial cancer |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Monalisa Dmello, M.B,B.S., M.D. [2] Ogechukwu Hannah Nnabude, MD
Synonyms and keywords: Endometrial adenocarcinoma; adenocarcinoma - endometrium; adenocarcinoma - uterus; cancer - endometrial; uterine corpus cancer; endometrial carcinoma; cancer of the endometrium; cancer of endometrium; Neoplasm of endometrium; Endometrial neoplasm.
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating Endometrial Cancer from other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
The definitive diagnosis of endometrial cancer is accomplished by the use of histology. The personal and family history of the patient together with a complete physical examination are instrumental. Intrauterine pregnancy should be considered in women of reproductive age with abnormal uterine bleeding or amenorrhea unless postmenopausal status has been confirmed. If suspicious symptoms, signs, and/or family history are present, basic laboratory evaluation, cervical-vaginal Pap smear, and transvaginal TVU scanning generally are considered. Patients with an abnormal Pap smear should undergo further investigation regardless of age . [1]
Treatment
Medical therapy | Surgery | Primary prevention | Secondary prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies
Case Studies
de:Korpuskarzinom no:Livmorkreft
- ↑ Tzur T, Kessous R, Weintraub AY (2017). "Current strategies in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer". Arch Gynecol Obstet. 296 (1): 5–14. doi:10.1007/s00404-017-4391-z. PMID 28508342.