EVAR
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss EVAR further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Template:WikiDoc Cardiology News Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
EVAR which stands for Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (or Endovascular Aortic Repair), is a type of Endovascular surgery used to treat an abdominal aortic aneurysm or AAA.
Patient Screening
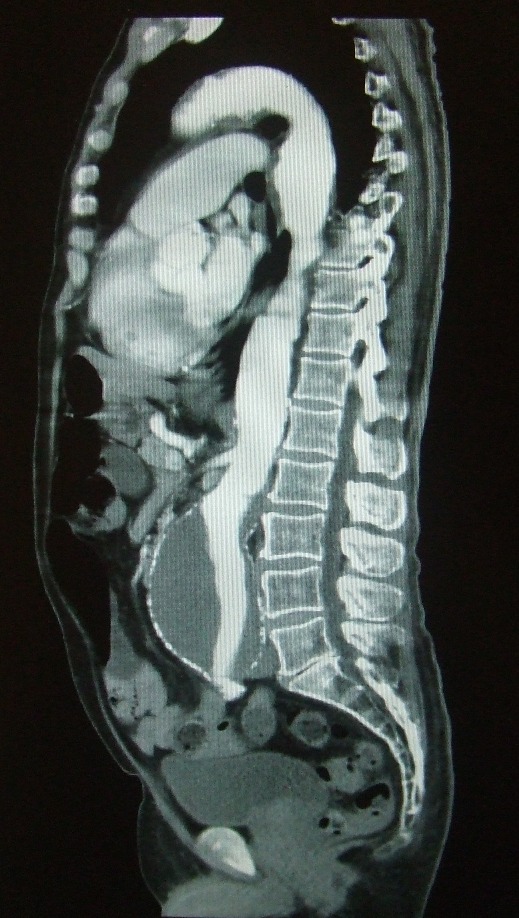
Before patients are deemed to be a suitable candidate for this treatment, they have to go through a rigorous set of tests. These include a CT scan of the aorta and blood tests. The CT scan gives precise measurements of the aneurysm and the surrounding anatomy. In particular the calibre/tortuosity of the iliac arteries and the relationship of the neck of the aneurysm to the renal arteries are important determinants of whether the aneurysm is amenable to endoluminal repair.
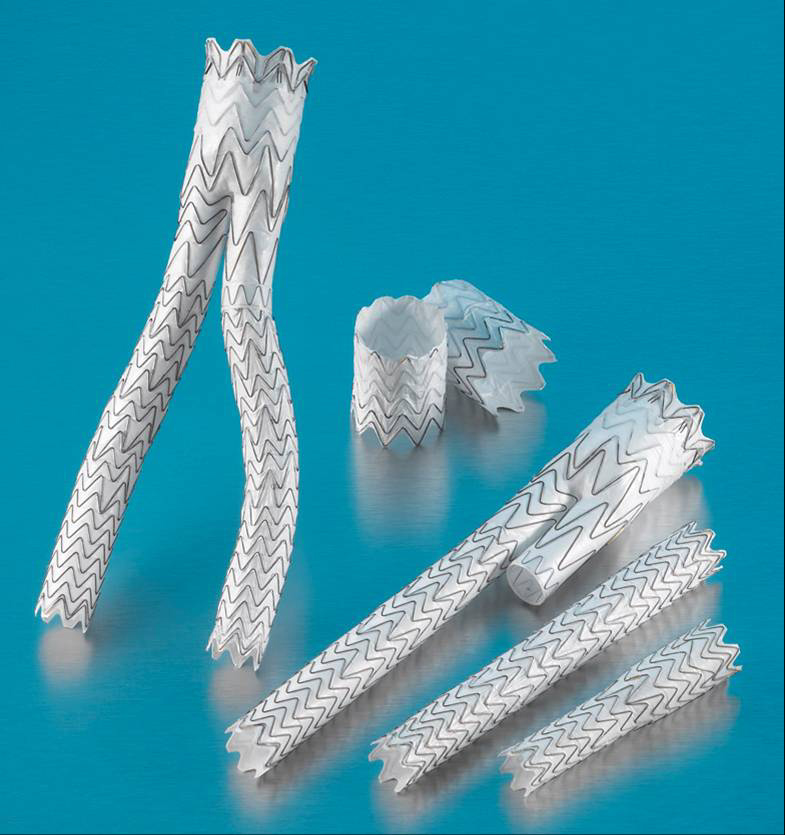

The Procedure
The procedure is carried out in a sterile environment, usually a theatre, under x-ray fluoroscopic guidance. It is carried out by a vascular surgeon or an Interventional Radiologist who collaborate on most cases. The patient is either given a full GA (general anaestheic) or an epidural.
Vascular 'sheaths' are introduced into the patient's femoral arteries, through which the guidewires, catheters and eventually, the Stent Graft is passed.
Diagnostic angiography images or 'runs' are captured of the aorta to determine the location on the patient's renal arteries, so the stent can be deployed below these. The main 'body' of the stent graft is placed first, with the 'limbs' which join on to the main body and sit in the iliacs, placed later.
The idea is that the covered stent, once in place acts as a false lumen for blood to travel down, and not into the surrounding aneurysm sac. This therefore immediately takes the pressure off the aneurysm, which itself will thrombose in time.
Complications
Systemic
MI, CHF, arrhythmias, respiratory failure, renal failure
Dissection, malpositioning, renal failure, thromboembolizaton, ischemic colitis, groin hematoma, wound infection
Migration, detachment, rupture, stenosis, kinking
Endoleaks
Type I,II, III and IV
- Type I - Perigraft (persistent flow at proximal or distal attachment sites)
- Type II - Retrograde flow from collateral branches
- Type III - Fabric tears / graft disconnection
- Type IV - Graft wall porosity