EIF2C1
| Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C, 1 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 PDB rendering based on 1si2. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | EIF2C1 ; AGO1; DKFZp686M13167; EIF2C; GERP95; Q99 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 81826 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
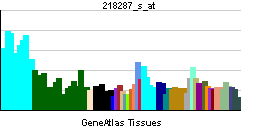 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2C, 1, also known as EIF2C1, is a human gene.[1]
This gene encodes a member of the Argonaute family of proteins which play a role in RNA interference. The encoded protein is highly basic, and contains a PAZ domain and a PIWI domain. It may interact with dicer1 and play a role in short-interfering-RNA-mediated gene silencing. This gene is located on chromosome 1 in a cluster of closely related family members including argonaute 3, and argonaute 4.[1]
References
Further reading
- Carmell MA, Xuan Z, Zhang MQ, Hannon GJ (2002). "The Argonaute family: tentacles that reach into RNAi, developmental control, stem cell maintenance, and tumorigenesis". Genes Dev. 16 (21): 2733–42. doi:10.1101/gad.1026102. PMID 12414724.
- Reddy PH, Stockburger E, Gillevet P, Tagle DA (1998). "Mapping and characterization of novel (CAG)n repeat cDNAs from adult human brain derived by the oligo capture method". Genomics. 46 (2): 174–82. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5044. PMID 9417904.
- Cikaluk DE, Tahbaz N, Hendricks LC; et al. (1999). "GERp95, a membrane-associated protein that belongs to a family of proteins involved in stem cell differentiation". Mol. Biol. Cell. 10 (10): 3357–72. PMID 10512872.
- Koesters R, Adams V, Betts D; et al. (1999). "Human eukaryotic initiation factor EIF2C1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic organization, localization to chromosomal bands 1p34-p35, and expression". Genomics. 61 (2): 210–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5951. PMID 10534406.
- Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Urlaub H; et al. (2003). "Single-stranded antisense siRNAs guide target RNA cleavage in RNAi". Cell. 110 (5): 563–74. PMID 12230974.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Doi N, Zenno S, Ueda R; et al. (2003). "Short-interfering-RNA-mediated gene silencing in mammalian cells requires Dicer and eIF2C translation initiation factors". Curr. Biol. 13 (1): 41–6. PMID 12526743.
- Sasaki T, Shiohama A, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (2004). "Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family in the human genome small star, filled". Genomics. 82 (3): 323–30. PMID 12906857.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T; et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Ma JB, Ye K, Patel DJ (2004). "Structural basis for overhang-specific small interfering RNA recognition by the PAZ domain". Nature. 429 (6989): 318–22. doi:10.1038/nature02519. PMID 15152257.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA; et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- Sen GL, Blau HM (2005). "Argonaute 2/RISC resides in sites of mammalian mRNA decay known as cytoplasmic bodies". Nat. Cell Biol. 7 (6): 633–6. doi:10.1038/ncb1265. PMID 15908945.
- Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ, Parker R (2005). "MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies". Nat. Cell Biol. 7 (7): 719–23. doi:10.1038/ncb1274. PMID 15937477.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE; et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Chu CY, Rana TM (2006). "Translation repression in human cells by microRNA-induced gene silencing requires RCK/p54". PLoS Biol. 4 (7): e210. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040210. PMID 16756390.
- Kim DH, Villeneuve LM, Morris KV, Rossi JJ (2006). "Argonaute-1 directs siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 (9): 793–7. doi:10.1038/nsmb1142. PMID 16936726.
- Janowski BA, Huffman KE, Schwartz JC; et al. (2006). "Involvement of AGO1 and AGO2 in mammalian transcriptional silencing". Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13 (9): 787–92. doi:10.1038/nsmb1140. PMID 16936728.
- Sasaki T, Shimizu N (2007). "Evolutionary conservation of a unique amino acid sequence in human DICER protein essential for binding to Argonaute family proteins". Gene. 396 (2): 312–20. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2007.04.001. PMID 17482383.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |