Dizziness
|
Dizziness Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Dizziness On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Dizziness |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: M.Umer Tariq [2]; Vendhan Ramanujam M.B.B.S; Norina Usman, M.B.B.S[3]
Synonyms and keywords: Disequilibrium; Vertigo; Unsteadiness; Lightheadedness; Disorientation in space; dizzy; floating; giddiness; giddy; reeling; spaced out; swimmy; weak at the knees; wobbliness; wooziness
Overview
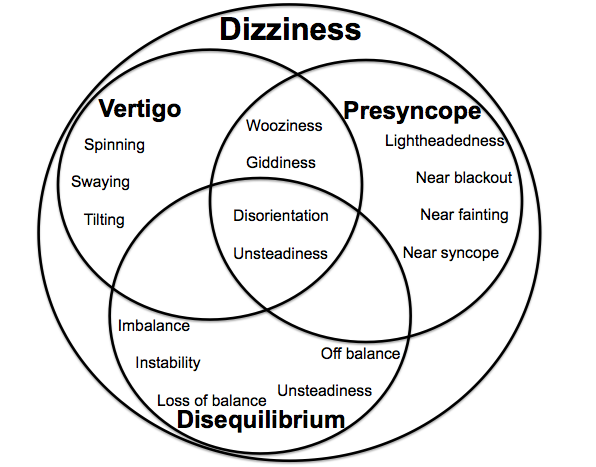
Dizziness is a sensation of postural unsteadiness or deceptive motion. It is one of the most communal presenting complaints that accounts for 5% of primary care practice for individuals aged 65 or older. Dizziness is a nonspecific term mainly used by many people and is classified into different categories: vertigo, spinning, disequilibrium, giddiness, presyncope, faintness, lightheadedness, or feeling woozy.
Definition
Causes
Common causes of dizziness may include[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]:
Medications
Differentiating Dizziness from other Diseases
Vertigo | Presyncope | Disequilibrium | Psychogenic dizziness
Risk Factors
Common risk factors in the development of dizziness include[8][9][10]:
- Family history of thromboembolic factors (diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and rheumatic disease)
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Stroke
- Medication side effect (diuretics, antiepileptic drugs, opioid-based analgesics, antipsychotic drugs, antidepressants, antihypertensive, antifungal, lithium, benzodiazepines, antiarrhythmic, antimalarial and anti-HIV-drugs.
- Multiple sclerosis
- Seizures
- Brain tumors
- Benign positional vertigo
- Labyrinthitis
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
History and Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Electrocardiogram | CT | MRI | Echocardiography | Other Imaging Findings | Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
Medical Therapy | Surgery | Primary Prevention | Secondary Prevention | Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy | Future or Investigational Therapies Template:WH Template:WS
- ↑ Kim AS, Sidney S, Klingman JG, Johnston SC (2012). "Practice variation in neuroimaging to evaluate dizziness in the ED". Am J Emerg Med. 30 (5): 665–72. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2011.02.038. PMC 4560264. PMID 21570240.
- ↑ Keleş A, Demircan A, Kurtoğlu G (2008). "Carbon monoxide poisoning: how many patients do we miss?". Eur J Emerg Med. 15 (3): 154–7. doi:10.1097/MEJ.0b013e3282efd519. PMID 18460956.
- ↑ Lempert T, Olesen J, Furman J, Waterston J, Seemungal B, Carey J; et al. (2012). "Vestibular migraine: diagnostic criteria". J Vestib Res. 22 (4): 167–72. doi:10.3233/VES-2012-0453. PMID 23142830.
- ↑ Gilbert VE (1993). "Immediate orthostatic hypotension: diagnostic value in acutely ill patients". South Med J. 86 (9): 1028–32. PMID 8367748.
- ↑ Lawson J, Johnson I, Bamiou DE, Newton JL (2005). "Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: clinical characteristics of dizzy patients referred to a Falls and Syncope Unit". QJM. 98 (5): 357–64. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hci057. PMID 15820968.
- ↑ Sarasin FP, Louis-Simonet M, Carballo D, Slama S, Junod AF, Unger PF (2002). "Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension among patients presenting with syncope in the ED". Am J Emerg Med. 20 (6): 497–501. doi:10.1053/ajem.2002.34964. PMID 12369019.
- ↑ Newman-Toker DE, Edlow JA (2015). "TiTrATE: A Novel, Evidence-Based Approach to Diagnosing Acute Dizziness and Vertigo". Neurol Clin. 33 (3): 577–99, viii. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2015.04.011. PMC 4522574. PMID 26231273.
- ↑ Rosin C, Bingisser R (2013). "[Not Available]". Ther Umsch. 70 (1): 27–9. doi:10.1024/0040-5930/a000359. PMID 23385126.
- ↑ Chimirri S, Aiello R, Mazzitello C, Mumoli L, Palleria C, Altomonte M; et al. (2013). "Vertigo/dizziness as a Drugs' adverse reaction". J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 4 (Suppl 1): S104–9. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.120969. PMC 3853661. PMID 24347974.
- ↑ Shill HA, Fife TD (2013). "Causes of imbalance and abnormal gait that may be misdiagnosed". Semin Neurol. 33 (3): 270–5. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1354601. PMID 24057830.