Daunorubicin
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aparna Vuppala, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Overview
Daunorubicin is a {{{drugClass}}} that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of {{{indication}}}. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include .
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition1
Daunorubicin hydrochloride injection in combination with other approved anticancer drugs is indicated for remission induction in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia (myelogenous, monocytic, erythroid) of adults and for remission induction in acute lymphocytic leukemia of children and adults.
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition3
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition4
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Daunorubicin in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Daunorubicin in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Daunorubicin in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Daunorubicin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Daunorubicin in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients who have shown a hypersensitivity to it.
Warnings
|
WARNINGS
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Bone Marrow
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride is a potent bone marrow suppressant. Suppression will occur in all patients given a therapeutic dose of this drug. Therapy with daunorubicin hydrochloride should not be started in patients with preexisting drug-induced bone marrow suppression unless the benefit from such treatment warrants the risk. Persistent, severe myelosuppression may result in superinfection or hemorrhage.
Cardiac Effects
- Special attention must be given to the potential cardiac toxicity of daunorubicin hydrochloride, particularly in infants and children. Preexisting heart disease and previous therapy with doxorubicin are co-factors of increased risk of daunorubicin-induced cardiac toxicity and the benefit-to-risk ratio of daunorubicin hydrochloride therapy in such patients should be weighed before starting daunorubicin hydrochloride. In adults, at total cumulative doses less than 550 mg/m2, acute congestive heart failure is seldom encountered. However, rare instances of pericarditis-myocarditis, not dose-related, have been reported.
- In adults, at cumulative doses exceeding 550 mg/m2, there is an increased incidence of drug-induced congestive heart failure. Based on prior clinical experience with doxorubicin, this limit appears lower, namely 400 mg/m2, in patients who received radiation therapy that encompassed the heart.
- In infants and children, there appears to be a greater susceptibility to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity compared to that in adults, which is more clearly dose-related. Anthracycline therapy (including daunorubicin) in pediatric patients has been reported to produce impaired left ventricular systolic performance, reduced contractility, congestive heart failure or death. These conditions may occur months to years following cessation of chemotherapy. This appears to be dose-dependent and aggravated by thoracic irradiation. Long-term periodic evaluation of cardiac function in such patients should, thus, be performed. *In both children and adults, the total dose of daunorubicin hydrochloride administered should also take into account any previous or concomitant therapy with other potentially cardiotoxic agents or related compounds such as doxorubicin.
- There is no absolutely reliable method of predicting the patients in whom acute congestive heart failure will develop as a result of the cardiac toxic effect of daunorubicin hydrochloride. However, certain changes in the electrocardiogram and a decrease in the systolic ejection fraction from pretreatment baseline may help to recognize those patients at greatest risk to develop congestive heart failure. On the basis of the electrocardiogram, a decrease equal to or greater than 30% in limb lead QRS voltage has been associated with a significant risk of drug-induced cardiomyopathy. Therefore, an electrocardiogram and/or determination of systolic ejection fraction should be performed before each course of daunorubicin hydrochloride. In the event that one or the other of these predictive parameters should occur, the benefit of continued therapy must be weighed against the risk of producing cardiac damage.
- Early clinical diagnosis of drug-induced congestive heart failure appears to be essential for successful treatment.
Secondary Leukemias
- There have been reports of secondary leukemias in patients exposed to topoisomerase II inhibitors when used in combination with other antineoplastic agents or radiation therapy.
Extravasation at Injection Site
- Extravasation of daunorubicin hydrochloride at the site of intravenous administration can cause severe local tissue necrosis
Precautions
General
- Therapy with daunorubicin hydrochloride requires close patient observation and frequent complete blood-count determinations. Cardiac, renal, and hepatic function should be evaluated prior to each course of treatment.
- Appropriate measures must be taken to control any systemic infection before beginning therapy with daunorubicin hydrochloride.
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride may transiently impart a red coloration to the urine after administration, and patients should be advised to expect this.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Daunorubicin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Daunorubicin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Daunorubicin with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
- Although appropriate studies with daunorubicin hydrochloride have not been performed in the pediatric population, cardiotoxicity may be more frequent and occur at lower cumulative doses in children.
Geriatic Use
- Although appropriate studies with daunorubicin hydrochloride have not been performed in the geriatric population, cardiotoxicity may be more frequent in the elderly. Caution should also be used in patients who have inadequate bone marrow reserves due to old age. In addition, elderly patients are more likely to have age-related renal function impairment, which may require reduction of dosage in patients receiving daunorubicin hydrochloride.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Daunorubicin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Daunorubicin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- Doses of daunorubicin hydrochloride should be reduced in patients with renal impairment. Patients with serum creatinine concentrations of greater than 3 mg/dL should receive 50% of the usual daily dose
Hepatic Impairment
- Doses of daunorubicin hydrochloride should be reduced in patients with hepatic impairment. Patients with serum bilirubin concentrations of 1.2 to 3 mg/dL should receive 75% of the usual daily dose and patients with serum bilirubin concentrations greater than 3 mg/dL should receive 50% of the usual daily dose.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Daunorubicin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Daunorubicin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Daunorubicin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Daunorubicin has antimitotic and cytotoxic activity through a number of proposed mechanisms of action. Daunorubicin forms complexes with DNA by intercalation between base pairs. It inhibits topoisomerase II activity by stabilizing the DNA-topoisomerase II complex, preventing the religation portion of the ligation-religation reaction that topoisomerase II catalyzes. Single strand and double strand DNA breaks result.
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride may also inhibit polymerase activity, affect regulation of gene expression, and produce free radical damage to DNA.
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride possesses an antitumor effect against a wide spectrum of animal tumors, either grafted or spontaneous.
Structure
- Daunorubicin Hydrochloride Injection consists of the hydrochloride salt of an anthracycline cytotoxic antibiotic produced by a strain of Streptomyces coeruleorubidus. It is provided as a deep red sterile liquid in vials for intravenous administration only. Each mL contains daunorubicin hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 5 mg of daunorubicin, 9 mg sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), and water for injection, q.s. It has the following structural formula which may be described with the chemical name of (1S,3S)-3-Acetyl-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1-naphthacenyl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride.
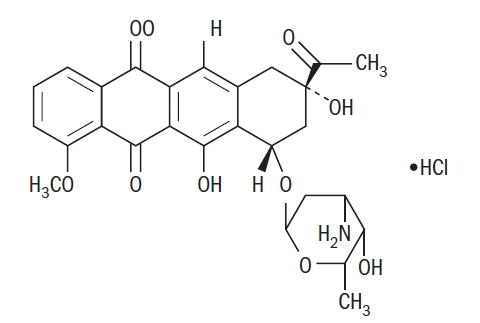
C27H29NO10•HCl M.W. 563.99
It is a hygroscopic crystalline powder. The pH of a 5 mg/mL aqueous solution is 3 to 4.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
General
- Following intravenous injection of daunorubicin hydrochloride, plasma levels of daunorubicin decline rapidly, indicating rapid tissue uptake and concentration. Thereafter, plasma levels decline slowly with a half-life of 45 minutes in the initial phase and 18.5 hours in the terminal phase. By 1 hour after drug administration, the predominant plasma species is daunorubicinol, an active metabolite, which disappears with a half-life of 26.7 hours.
Distribution
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride is rapidly and widely distributed in tissues, with highest levels in the spleen, kidneys, liver, lungs, and heart. The drug binds to many cellular components, particularly nucleic acids. There is no evidence that daunorubicin crosses the blood-brain barrier, but the drug apparently crosses the placenta.
Metabolism and Elimination
- Daunorubicin hydrochloride is extensively metabolized in the liver and other tissues, mainly by cytoplasmic aldo-keto reductases, producing daunorubicinol, the major metabolite which has antineoplastic activity. Approximately 40% of the drug in the plasma is present as daunorubicinol within 30 minutes and 60% in 4 hours after a dose of daunorubicin. Further metabolism via reduction cleavage of the glycosidic bond, 4-O demethylation, and conjugation with both sulfate and glucuronide have been demonstrated. Simple glycosidic cleavage of daunorubicin or daunorubicinol is not a significant metabolic pathway in man. *Twenty-five percent of an administered dose of daunorubicin hydrochloride is eliminated in an active form by urinary excretion and an estimated 40% by biliary excretion.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
- In the treatment of adult acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, daunorubicin hydrochloride, used as a single agent, has produced complete remission rates of 40 to 50%, and in combination with cytarabine, has produced complete remission rates of 53 to 65%.
- The addition of daunorubicin hydrochloride to the two-drug induction regimen of vincristine-prednisone in the treatment of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia does not increase the rate of complete remission. In children receiving identical CNS prophylaxis and maintenance therapy (without consolidation), there is prolongation of complete remission duration (statistically significant, p < 0.02) in those children induced with the three drug (daunorubicin-vincristine-prednisone) regimen as compared to two drugs. There is no evidence of any impact of daunorubicin hydrochloride on the duration of complete remission when a consolidation (intensification) phase is employed as part of a total treatment program.
- In adult acute lymphocytic leukemia, in contrast to childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia, daunorubicin hydrochloride during induction significantly increases the rate of complete remission, but not remission duration, compared to that obtained with vincristine, prednisone, and L-asparaginase alone. The use of daunorubicin hydrochloride in combination with vincristine, prednisone, and L-asparaginase has produced complete remission rates of 83% in contrast to a 47% remission in patients not receiving daunorubicin hydrochloride.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Daunorubicin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Daunorubicin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Daunorubicin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Daunorubicin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Daunorubicin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Daunorubicin
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Daunorubicin |Label Name=Daunorubicin11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Daunorubicin |Label Name=Daunorubicin11.png
}}