DVL2
| Dishevelled, dsh homolog 2 (Drosophila) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
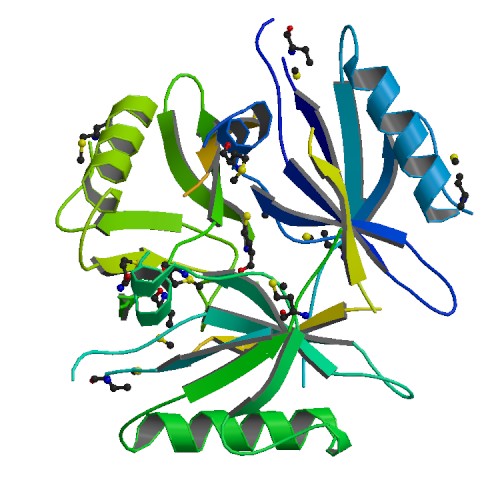 PDB rendering based on 1l6o. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | DVL2 ; | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | Template:OMIM5 Template:MGI HomoloGene: 20927 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Template:GNF Ortholog box | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| UniProt | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||
Dishevelled, dsh homolog 2 (Drosophila), also known as DVL2, is a human gene.[1]
This gene encodes a member of the dishevelled (dsh) protein family. The vertebrate dsh proteins have approximately 40% amino acid sequence similarity with Drosophila dsh. This gene encodes a 90-kD protein that undergoes posttranslational phosphorylation to form a 95-kD cytoplasmic protein, which may play a role in the signal transduction pathway mediated by multiple Wnt proteins. The mechanisms of dishevelled function in Wnt signaling are likely to be conserved among metazoans.[1]
References
Further reading
- Greco TL, Sussman DJ, Camper SA (1997). "Dishevelled-2 maps to human chromosome 17 and distal to Wnt3a and vestigial tail (vt) on mouse chromosome 11". Mamm. Genome. 7 (6): 475–6. PMID 8662242.
- Pizzuti A, Amati F, Calabrese G; et al. (1997). "cDNA characterization and chromosomal mapping of two human homologues of the Drosophila dishevelled polarity gene". Hum. Mol. Genet. 5 (7): 953–8. PMID 8817329.
- Klingensmith J, Yang Y, Axelrod JD; et al. (1997). "Conservation of dishevelled structure and function between flies and mice: isolation and characterization of Dvl2". Mech. Dev. 58 (1–2): 15–26. PMID 8887313.
- Semënov MV, Snyder M (1997). "Human dishevelled genes constitute a DHR-containing multigene family". Genomics. 42 (2): 302–10. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4713. PMID 9192851.
- Strovel ET, Wu D, Sussman DJ (2000). "Protein phosphatase 2Calpha dephosphorylates axin and activates LEF-1-dependent transcription". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (4): 2399–403. PMID 10644691.
- Song DH, Sussman DJ, Seldin DC (2000). "Endogenous protein kinase CK2 participates in Wnt signaling in mammary epithelial cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (31): 23790–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909107199. PMID 10806215.
- Zhang Y, Neo SY, Han J, Lin SC (2000). "Dimerization choices control the ability of axin and dishevelled to activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (32): 25008–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002491200. PMID 10829020.
- Chen W, Hu LA, Semenov MV; et al. (2002). "beta-Arrestin1 modulates lymphoid enhancer factor transcriptional activity through interaction with phosphorylated dishevelled proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98 (26): 14889–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.211572798. PMID 11742073.
- Habas R, Kato Y, He X (2002). "Wnt/Frizzled activation of Rho regulates vertebrate gastrulation and requires a novel Formin homology protein Daam1". Cell. 107 (7): 843–54. PMID 11779461.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Habas R, Dawid IB, He X (2003). "Coactivation of Rac and Rho by Wnt/Frizzled signaling is required for vertebrate gastrulation". Genes Dev. 17 (2): 295–309. doi:10.1101/gad.1022203. PMID 12533515.
- Chen W, ten Berge D, Brown J; et al. (2003). "Dishevelled 2 recruits beta-arrestin 2 to mediate Wnt5A-stimulated endocytosis of Frizzled 4". Science. 301 (5638): 1391–4. doi:10.1126/science.1082808. PMID 12958364.
- Wong CK, Luo W, Deng Y; et al. (2004). "The DIX domain protein coiled-coil-DIX1 inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation by Axin and dishevelled through distinct mechanisms". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (38): 39366–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404598200. PMID 15262978.
- Torban E, Wang HJ, Groulx N, Gros P (2005). "Independent mutations in mouse Vangl2 that cause neural tube defects in looptail mice impair interaction with members of the Dishevelled family". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (50): 52703–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408675200. PMID 15456783.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA; et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T; et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Zhang L, Gao X, Wen J; et al. (2006). "Dapper 1 antagonizes Wnt signaling by promoting dishevelled degradation". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (13): 8607–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600274200. PMID 16446366.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C; et al. (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell. 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |