Cirrhosis physical examination
|
Cirrhosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case studies |
|
Cirrhosis physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cirrhosis physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cirrhosis physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sudarshana Datta, MD [2]
Overview
Patients with cirrhosis usually present with signs of jaundice, palmar erythema, spider angiomata, gynaecomastia and alteration of mental status arising due to complications of cirrhosis. Abdominal examination may show signs of abdominal distension, caput medusae, splenomegaly and flank dullness on percussion. Other findings on examination include nail changes, presence of Clubbing, dupuytren's contracture(flexion deformities of the fingers) and Asterixis in cases with hepatic encephalopathy.
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with cirrhosis is usually remarkable for: jaundice, spider angiomata, ascites, asterixis, spleenomegaly and palmar erythema.
Appearance of the patient
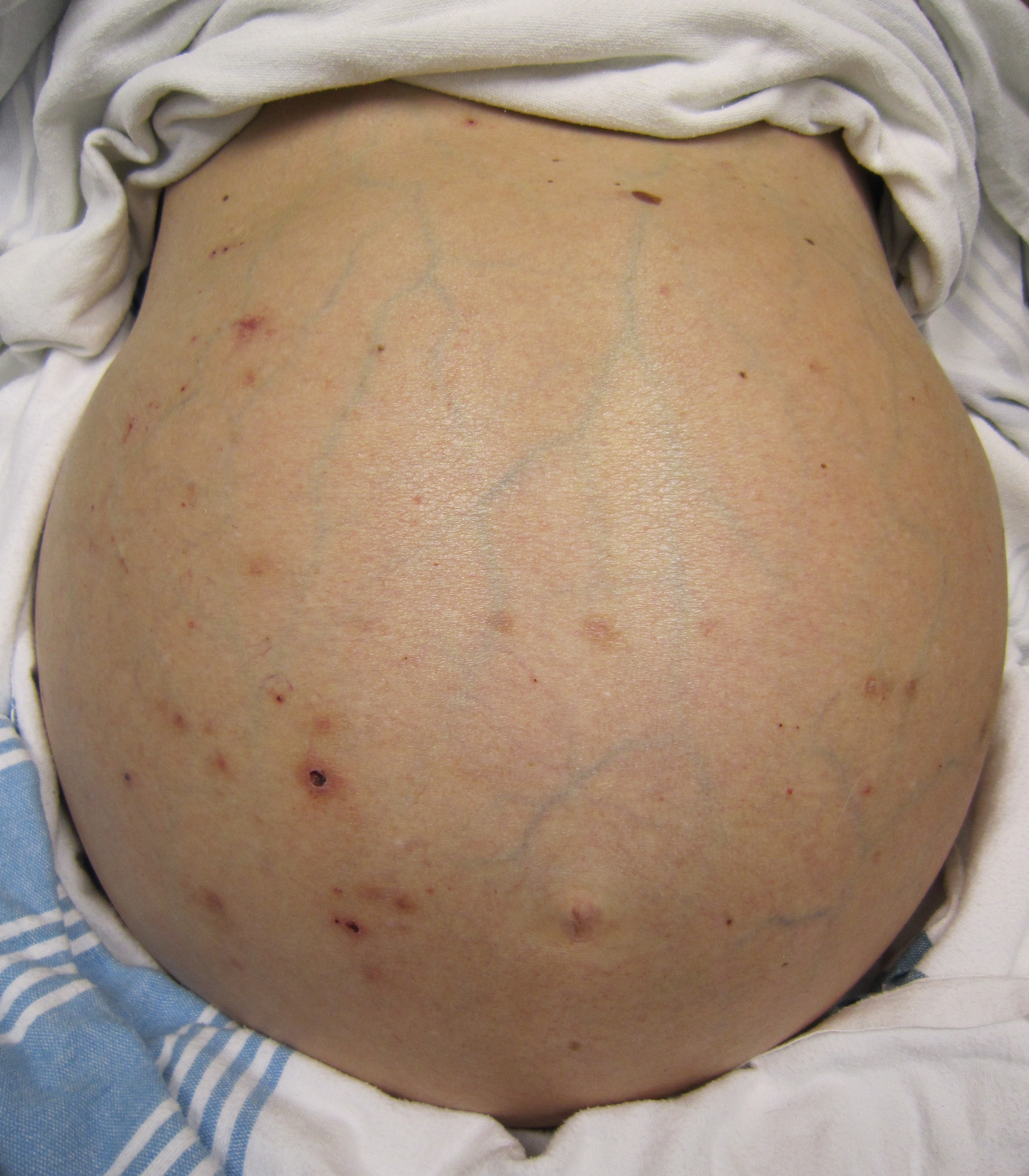
- Patients with cirrhosis usually appear weak due to constitutional symptoms such as weight loss, anorexia and muscle atrophy. Yellowish discoloration of skin and abdominal distension may also be present due to ascites.
- Normal/low blood pressure with normal pulse pressure.
Skin
- Jaundice : yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes, and mucus membranes due to increased bilirubin (at least 2-3 mg/dL or 30 mmol/L). Urine may also appear dark.
- Pallor
- Bruises
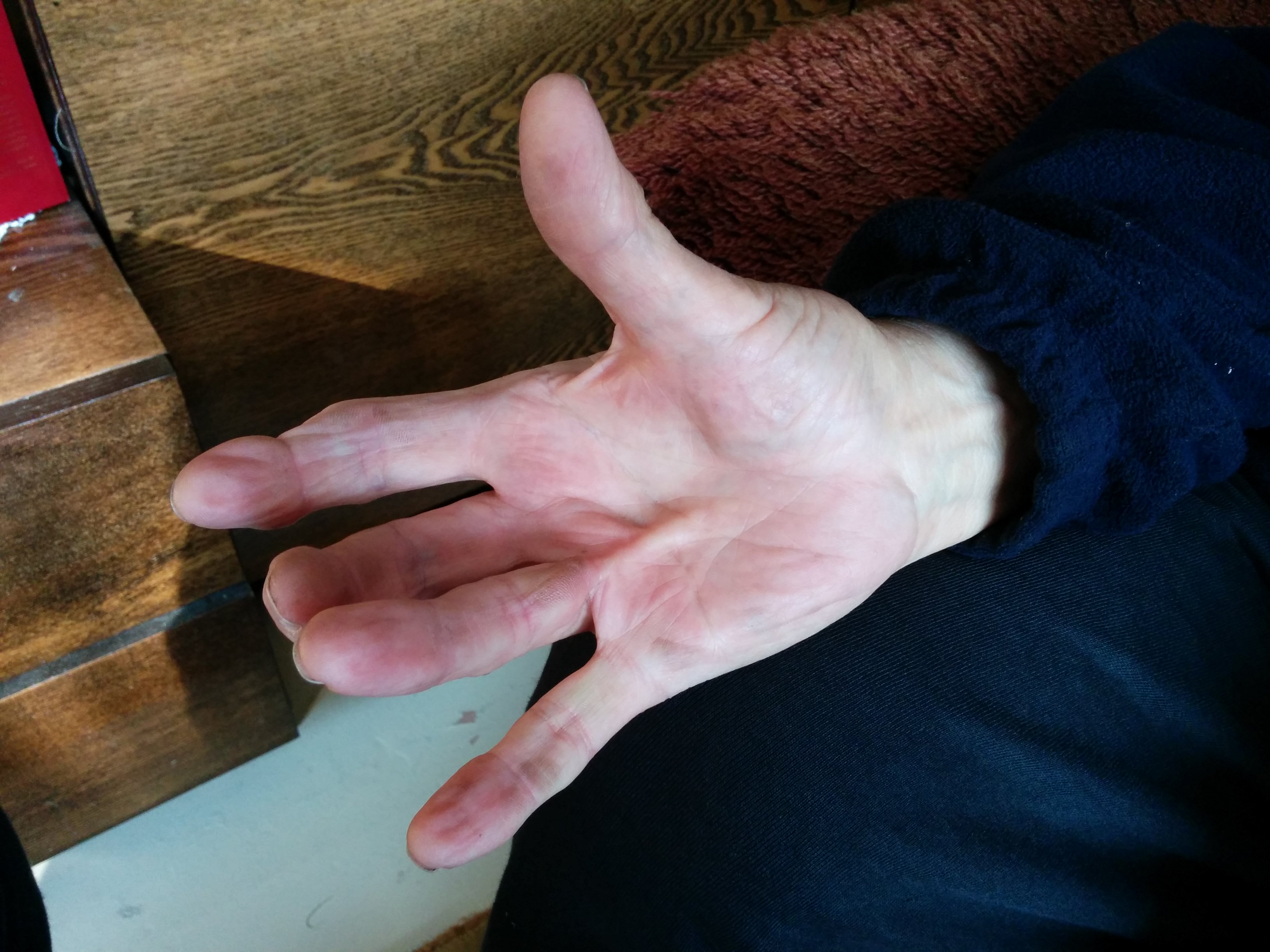
- Palmar erythema on the thenar and hypothenar eminences, due to altered sex hormone metabolism.
- Spider angiomata: Increased estradiol levels lead to the formation of vascular lesions consisting of central arterioles surrounded by smaller vessels [1]
- Telangiectasias or spider veins: small dilated blood vessels near the surface of the skin.
-
Telingectasias
Source: Wikimedia commons -
Palmar erythema
Source: Wikimedia commons[2]
{{#ev:youtube|RT-8OzD9j00}}
HEENT
- Abnormalities of the head/hair may include thinning of hair on the scalp due to hyperestrogenism
- Kayser-Fleischer rings: dark rings that appear to encircle the iris of the eye in patients with Wilson's disease[3]
- Parotid gland enlargement
- Fetor hepaticus: severe portal-systemic shunting leads to increased levels of dimethyl sulfide leads to a sweet pungent smell in the breath
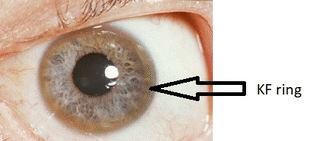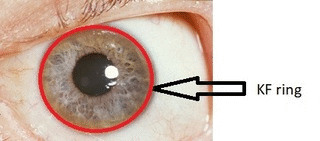
Source: Wikimedia commons
Abdomen
- Inspection:
- Palpation:
- Fluid wave
- Hepatomegaly may be present in initial stages. The liver may also be normal or shrunken.
- Spleenomegaly may be present in patients with cirrhosis from nonalcoholic etiologies, due to portal hypertension
- Percussion:
- Flank dullness may be present due to ascites (needs approximately 1500ml for detection)
- Auscultation:
- Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur: venous hum that may be present in patients with portal hypertension.
- Mechanism: due to collateral connections between remnant of the umbilical vein and the portal system
- Location: Epigastrium
- Exacerbating factors: Valsalva maneuver
- Diminished by: application of pressure on the skin above the umbilicus
- Cruveilhier-Baumgarten murmur: venous hum that may be present in patients with portal hypertension.
-
Abdominal distention, ascites-By James Heilman, MD (Own work)
{{#ev:youtube|8LDUtAAUJBc}} {{#ev:youtube|CHUBTgrU3Oc}}
Genitourinary
- Testicular atrophy
- Inversion of the normal male pubic hair pattern
Neuromuscular
- Hepatic encephalopathy may have signs of:
- Alteration of mental status
- Confusion
- Coma
- Asterixis (bilateral but asynchronous flapping motions of outstretched, dorsiflexed hands) is seen in patients with hepatic encephalopathy.
{{#ev:youtube|Or65nOrcz1A}}
Extremities
- Edema of the lower extremities
- Muscle atrophy
- Nail changes:[6]
- Muehrcke nails: paired horizontal white bands separated by normal color due to hypoalbuminemia [7][8][9][10][11]
- Terry nails: the proximal two-thirds of the nail plate appears white, whereas the distal one-third is red due to hypoalbuminemia
- Clubbing: the angle between the nail plate and proximal nail fold is greater than 180 degrees
- Severe clubbing:
- "Drum stick" appearance of distal fingers
- Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy: chronic proliferative periostitis of the long bones [12][13]
- Dupuytren's contracture may cause flexion deformities of the fingers: This occurs due to shortening and thickening of the palmar fascia, due to collagen deposition and fibroblastic proliferation.[14]
- Asterixis in cases with hepatic encephalopathy[15][16][17]
-
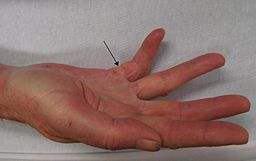
Dupuytren's contracture
Source: Wikimedia commons -
Dupuytren´s Contracture on the ring finger
-
Clubbing: angle between the nail plate and proximal nail fold is greater than 180 degrees
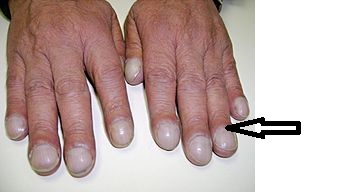
Source: Wikimedia commons -
Muehrcke's nails: paired horizontal white bands separated by normal color
Source:Wikimedia commons [18]
Chest findings
- Gynecomastia: due to increased estradiol levels
- Loss of chest or axillary hair
Other findings
References
- ↑ Li CP, Lee FY, Hwang SJ; et al. (1999). "Spider angiomas in patients with liver cirrhosis: role of alcoholism and impaired liver function". Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 34 (5): 520–3. PMID 10423070.
- ↑ "File:Kawasaki symptoms D.jpg - Wikimedia Commons".
- ↑ Sridhar MS, Rangaraju A, Anbarasu K, Reddy SP, Daga S, Jayalakshmi S, Shaik B (2017). "Evaluation of Kayser-Fleischer ring in Wilson disease by anterior segment optical coherence tomography". Indian J Ophthalmol. 65 (5): 354–357. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_400_16. PMC 5565897. PMID 28573989.
- ↑ Kim, SH; Keum, B; Kim, ES; Jeen, YT; Chun, HJ (2014). "Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic: Caput medusae". Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 29 (12): 1952–1952. doi:10.1111/jgh.12802. ISSN 0815-9319.
- ↑ Chandail VS, Jamwal V (2013). "Caput medusae". J Assoc Physicians India. 61 (8): 564. PMID 24818343.
- ↑ MUEHRCKE RC (1956). "The finger-nails in chronic hypoalbuminaemia; a new physical sign". Br Med J. 1 (4979): 1327–8. PMC 1980060. PMID 13316143.
- ↑ Callemeyn J, Van Haecke P, Peetermans WE, Blockmans D (2016). "Clubbing and hypertrophic osteoarthropathy: insights in diagnosis, pathophysiology, and clinical significance". Acta Clin Belg. 71 (3): 123–30. doi:10.1080/17843286.2016.1152672. PMID 27104368.
- ↑ Gibb C, Smith PJ, Miller R (2013). "Clubbing". Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 74 (11): C170–2. PMID 24350360.
- ↑ Morán LM, Ariza A (2013). "Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy associated to liver cirrhosis". Reumatol Clin. 9 (4): 248–9. doi:10.1016/j.reuma.2012.06.010. PMID 23099284.
- ↑ Tully AS, Trayes KP, Studdiford JS (2012). "Evaluation of nail abnormalities". Am Fam Physician. 85 (8): 779–87. PMID 22534387.
- ↑ Salem A, Gamil H, Hamed M, Galal S (2010). "Nail changes in patients with liver disease". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 24 (6): 649–54. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03476.x. PMID 19888943.
- ↑ Yap FY, Skalski MR, Patel DB, Schein AJ, White EA, Tomasian A, Masih S, Matcuk GR (2017). "Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy: Clinical and Imaging Features". Radiographics. 37 (1): 157–195. doi:10.1148/rg.2017160052. PMID 27935768.
- ↑ Pitt P, Mowat A, Williams R, Hamilton E (1994). "Hepatic hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and liver transplantation". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 53 (5): 338–40. PMC 1005335. PMID 8017989.
- ↑ Auld T, Werntz JR (2017). "Dupuytren's disease: How to recognize its early signs". J Fam Pract. 66 (3): E5–E10. PMID 28505213.
- ↑ Butz M, Timmermann L, Gross J, Pollok B, Südmeyer M, Kircheis G, Häussinger D, Schnitzler A (2014). "Cortical activation associated with asterixis in manifest hepatic encephalopathy". Acta Neurol. Scand. 130 (4): 260–7. doi:10.1111/ane.12217. PMID 24372275.
- ↑ Mendizabal M, Silva MO (2010). "Images in clinical medicine. Asterixis". N. Engl. J. Med. 363 (9): e14. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm0911157. PMID 20842766.
- ↑ Schiano TD (2010). "Clinical management of hepatic encephalopathy". Pharmacotherapy. 30 (5 Pt 2): 10S–5S. doi:10.1592/phco.30.pt2.10S. PMID 20412035.
- ↑ "File:Muehrcke's lines.JPG - Wikimedia Commons".
![Palmar erythema Source: Wikimedia commons[2]](/images/8/86/Palmar_erythema_1.jpg)

![Muehrcke's nails: paired horizontal white bands separated by normal color Source:Wikimedia commons [18]](/images/7/77/Nail.gif)