Ciprofloxacin (otic)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Ciprofloxacin (otic) is an antibiotic that is FDA approved for the treatment of acute otitis externa. Common adverse reactions include site pain, ear pruritus, fungal ear superinfection, and headache.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is a quinolone antimicrobial indicated for the treatment of acute otitis externa due to susceptible isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus.
Dosage
- The contents of one single use container (deliverable volume: 0.25 mL) should be instilled into the affected ear twice daily (approximately 12 hours apart) for 7 days.
- Wash hands before use. The solution should be warmed, by holding the container in the hands for at least 1 minute, to minimize the dizziness that may result from the instillation of a cold solution into the ear canal. The patient should lie with the affected ear upward and then the solution should be instilled. This position should be maintained for at least 1 minute to facilitate penetration of the drops into the ear. Repeat, if necessary, for the opposite ear.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
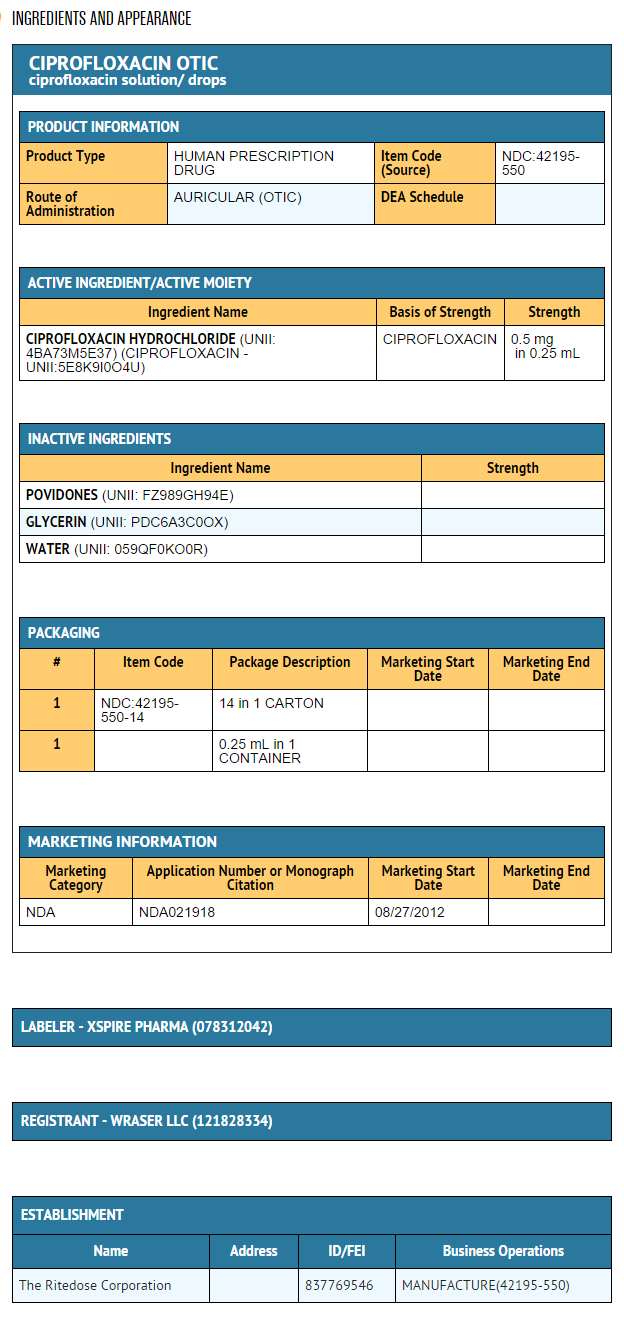
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is a sterile, preservative-free, otic solution of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride equivalent to 0.2 % ciprofloxacin (0.5 mg in 0.25 mL) in each single use container.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is contraindicated in persons with a history of hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin.
Warnings
Otic Use Only
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is for otic use only. It should not be used for injection, for inhalation or for topical ophthalmic use.
Hypersensitivity
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution should be discontinued at the first appearance of a skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Growth of Resistant Organisms with Prolonged Use
- As with other anti-infectives, use of Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including yeast and fungi. If super-infection occurs, discontinue use and institute alternative therapy.
Lack of Clinical Response
- If the infection is not improved after one week of therapy, cultures may help guide further treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse drug reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
- In a randomized, active-controlled clinical trial, approximately 300 patients with clinical signs and symptoms of otitis externa were treated with Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were application site pain, ear pruritus, fungal ear superinfection, and headache, each reported in approximately 2-3% of patients.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Ciprofloxacin (otic) Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Pregnancy Category C.
- Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and mice using oral doses of up to 100 mg/kg and intravenous (IV) doses up to 30 mg/kg and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus as a result of ciprofloxacin. In rabbits, ciprofloxacin (30 and 100 mg/kg orally) produced gastrointestinal disturbances resulting in maternal weight loss and an increased incidence of abortion, but no teratogenicity was observed at either dose. After intravenous administration of doses up to 20 mg/kg, no maternal toxicity was produced in the rabbit, and no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was observed.
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution. No adequate and well-controlled studies have been performed in pregnant women. Caution should be exercised when Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is used by a pregnant woman.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Ciprofloxacin is excreted in human milk with systemic use. It is not known whether ciprofloxacin is excreted in human milk following otic use. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution in infants below one year of age have not been established. The efficacy of Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution in treating otitis externa in pediatric patients one year or older has been demonstrated in controlled clinical trials.
- There is no evidence that the otic administration of quinolones has any effect on weight bearing joints, even though systemic administration of some quinolones has been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals.
Geriatic Use
- No overall differences in safety and effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Drop
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in the drug label.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- The bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin results from interference with the enzyme DNA gyrase, which is needed for the synthesis of bacterial DNA.
Structure
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution 0.2% contains the synthetic antimicrobial agent ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is a sterile, preservative-free solution for otic use. Each single use container of Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution delivers 0.25 mL of solution equivalent to 0.5 mg of ciprofloxacin. The inactive ingredients are povidone, glycerin, and water for injection. Sodium hydroxide and/or lactic acid may be added to adjust pH.
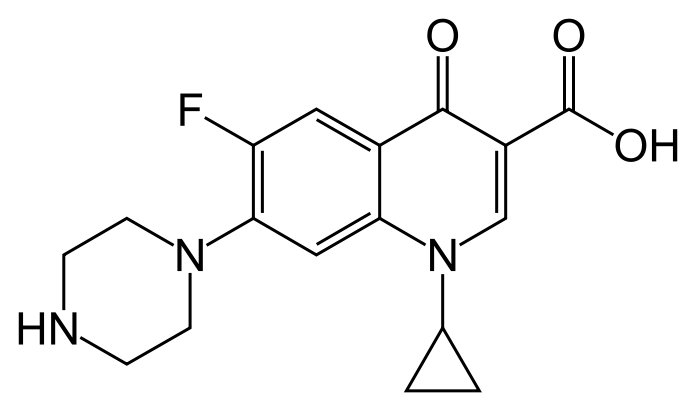
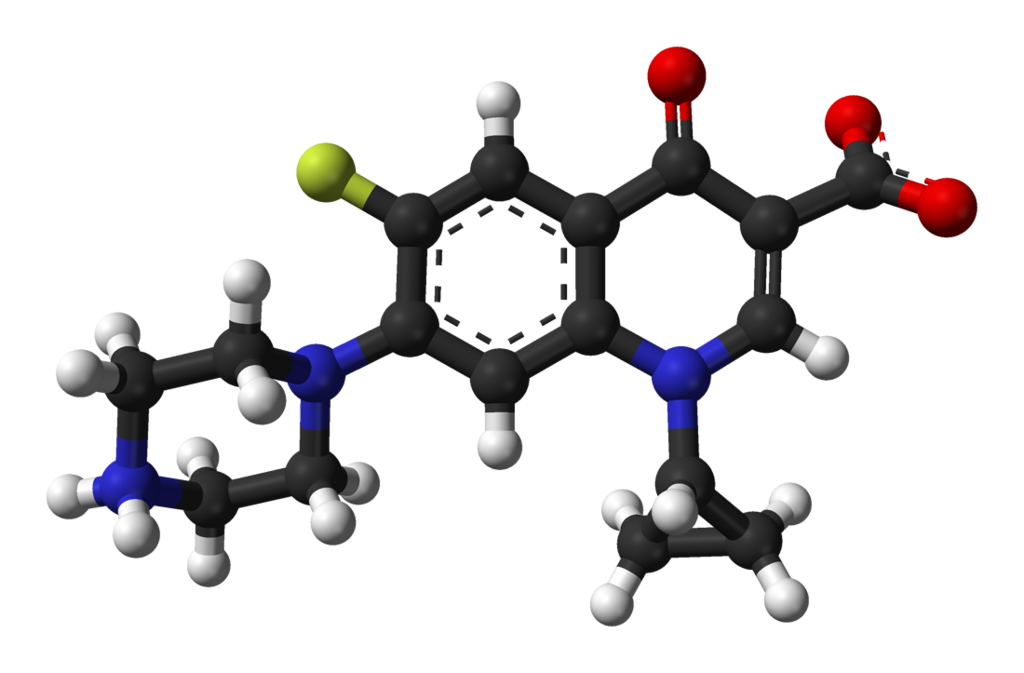
- Ciprofloxacin, a fluroquinolone is available as the monohydrochloride, monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. Its molecular formula is C17H18FN3O3•HCl•H2O, and molecular weight is 385.82.
- The chemical structure of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride is:

Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Ciprofloxacin (otic) in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- The plasma concentrations of ciprofloxacin were not measured following administration of 0.25 mL Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution (total dose: 0.5 mg ciprofloxacin). However, the maximum plasma concentration of ciprofloxacin is anticipated to be less than 5 ng/mL.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
- Long-term carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats have been completed for ciprofloxacin. After daily oral doses of 750 mg/kg (mice) and 250 mg/kg (rats) were administered for up to 2 years, there was no evidence that ciprofloxacin had any carcinogenic or tumorigenic effects in these species. No long-term studies of Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution have been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential.
- Eight in vitro mutagenicity tests have been conducted with ciprofloxacin, and the test results are listed below:
- Salmonella/Microsome Test (Negative)
- Escherichia coli DNA Repair Assay (Negative)
- Mouse Lymphoma Cell Forward Mutation Assay (Positive)
- Chinese Hamster V79 Cell HGPRT Test (Negative)
- Syrian Hamster Embryo Cell Transformation Assay (Negative)
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae Point Mutation Assay (Negative)
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitotic Crossover and Gene Conversion Assay (Negative)
- Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay (Positive).
- Two of the 8 in vitro tests were positive, but results of the following 3 in vivo test systems gave negative results:
- Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay
- Micronucleus Test (Mice)
- Dominant Lethal Test (Mice).
- Fertility studies performed in rats at oral doses of ciprofloxacin up to 100 mg/kg/day revealed no evidence of impairment. This would be over 100 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of ototopical ciprofloxacin based upon body surface area, assuming total absorption of ciprofloxacin from the ear of a patient treated with Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution twice per day.
Clinical Studies
- In a randomized, multi-center, evaluator-blinded study of patients with acute otitis externa, patients were treated with either Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution twice daily or neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and hydrocortisone otic solution (PNH) three times daily for 7 days.
- In the per protocol population, clinical cure was achieved at the end of a 7-day treatment in 70% (173/247) for the Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution treated group versus 60% (147/243) for the control treated group.
How Supplied
- Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is a clear, colorless, sterile, preservative-free solution. Ciprofloxacin Otic Solution is supplied as a 0.2% otic solution in a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) single use container. Each single use container delivers 0.25 mL of solution equivalent to 0.5 mg of ciprofloxacin; 14 single use containers are packaged in a foil overwrap pouch in a carton (NDC 42195-550-14).
Storage
- Store at 15ºC to 25ºC (59ºF to 77ºF). Discard used containers. Store unused containers in pouch to protect from light.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Ciprofloxacin (otic) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

{{#ask: Label Page::Ciprofloxacin (otic) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information

Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Ciprofloxacin (otic) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- CIPROFLOXACIN OTIC®[2]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Ciprofloxacin (otic) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Drusano GL, Standiford HC, Plaisance K, Forrest A, Leslie J, Caldwell J, GL (September 1986). "Absolute oral bioavailability of ciprofloxacin". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 30 (3): 444–6. doi:10.1128/aac.30.3.444. ISSN 0066-4804. PMC 180577. PMID 3777908.
|first2=missing|last2=in Authors list (help);|first3=missing|last3=in Authors list (help);|first4=missing|last4=in Authors list (help);|first5=missing|last5=in Authors list (help);|first6=missing|last6=in Authors list (help) - ↑ "ciprofloxacin hydrochloride solution/ drops".
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Ciprofloxacin (otic)
|Pill Name=No image.jpg
|Drug Name=
|Pill Ingred=|+sep=;
|Pill Imprint=
|Pill Dosage={{{dosageValue}}} {{{dosageUnit}}}
|Pill Color=|+sep=;
|Pill Shape=
|Pill Size (mm)=
|Pill Scoring=
|Pill Image=
|Drug Author=
|NDC=
}}