Chronic stable angina electrocardiography: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Electrocardiography (ECG) at Rest== | ==Electrocardiography (ECG) at Rest== | ||
The ECG is critical not only to add support to the clinical suspicion of CAD but also to provide prognostic information based on the pattern and magnitude of the abnormalities. | *The ECG is critical not only to add support to the clinical suspicion of [[CAD]] but also to provide prognostic information based on the pattern and magnitude of the abnormalities. | ||
It is in normal range in approximately half of patients with chronic stable angina without a history of previous [[myocardial infarction]]. In the others, a variety of ECG finding may suggest an [[ischemic heart disease]]. | *It is in normal range in approximately half of patients with chronic stable angina without a history of previous [[myocardial infarction]]. In the others, a variety of ECG finding may suggest an [[ischemic heart disease]]. | ||
'''Q waves''' may suggest prior myocardial infarction, but in the absence of a clinical history of previous [[myocardial infarction]] or [[CAD]], Q waves may also be caused by other conditions, including [[hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]], [[left ventricular hypertrophy]], dilated non ischemic cardiomyopathy and accessory conduction pathways. Isolated Q waves in lead III or QS pattern in V1 and V2 are nonspecific for diagnosis. | *'''Q waves''' may suggest prior [[myocardial infarction]], but in the absence of a clinical history of previous [[myocardial infarction]] or [[CAD]], | ||
:*Q waves may also be caused by other conditions, including [[hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]], [[left ventricular hypertrophy]], dilated non ischemic cardiomyopathy and accessory conduction pathways. | |||
:*Isolated Q waves in lead III or QS pattern in V1 and V2 are nonspecific for diagnosis. | |||
The occurrence of | *The occurrence of '''ST segment depression''' and '''[[T wave inversion]]''' in the resting [[ECG]], and signs of [[left ventricular hypertrophy]], [[left bundle branch block]] (LBBB) and left anterior hemiblock [[LAH]] are compatible with, favors to, but are not specific for [[CAD]]. | ||
:*A physician should consider these abnormal ECG findings as indications for further evaluation. | |||
:*'''Giant T-wave inversion''' in precordial leads is sometimes an important indicator of severe Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery stenosis. | |||
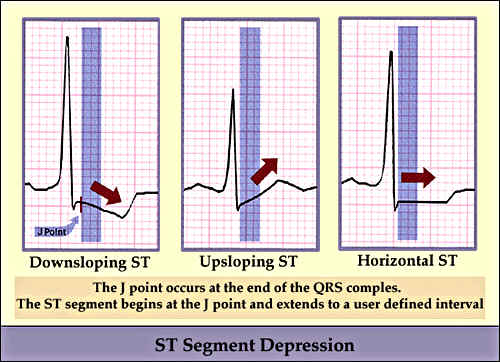
ST segment changes in angina can be seen as '''downsloping, upsloping or horizontal ST | |||
*ST segment changes in [[angina]] can be seen as '''downsloping, upsloping or horizontal [[ST segment depression]]'''. | |||
[[Image:ST_depression.jpg]] | [[Image:ST_depression.jpg]] | ||
==ACC / AHA Guidelines- ECG(DO NOT EDIT)<ref name=" | |||
==ACC / AHA Guidelines- Resting ECG(DO NOT EDIT)<ref name="pmid10351980">Gibbons RJ, Chatterjee K, Daley J, Douglas JS, Fihn SD, Gardin JM et al. (1999) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10351980 ACC/AHA/ACP-ASIM guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina: executive summary and recommendations. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Management of Patients with Chronic Stable Angina).] ''Circulation'' 99 (21):2829-48. PMID: [http://pubmed.gov/10351980 10351980]</ref>== | |||
{{cquote| | {{cquote| | ||
===Class I=== | ===Class I=== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 27: | ||
2. Rest [[ECG]] during an episode of [[chest pain]]. ''(Level of Evidence: B)''}} | 2. Rest [[ECG]] during an episode of [[chest pain]]. ''(Level of Evidence: B)''}} | ||
==ESC Guidelines- Resting ECG for Initial diagnostic assessment of angina (DO NOT EDIT)<ref name="pmid16735367">{{cite journal| author=Fox K, Garcia MA, Ardissino D, Buszman P, Camici PG, Crea F et al.| title=Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: executive summary: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology. | journal=Eur Heart J | year= 2006 | volume= 27 | issue= 11 | pages= 1341-81 | pmid=16735367 | doi=10.1093/eurheartj/ehl001 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16735367 }} </ref>== | |||
{{cquote| | |||
===Class I (in all patients)=== | |||
'''1.''' Resting [[ECG]] while pain free. ''(Level of Evidence: C)'' | |||
'''2.''' Resting [[ECG]] during episode of [[angina]]. ''(Level of Evidence: B)''}} | |||
==ESC Guidelines- Resting ECG for Routine reassessment in patients with chronic stable angina (DO NOT EDIT)<ref name="pmid16735367">{{cite journal| author=Fox K, Garcia MA, Ardissino D, Buszman P, Camici PG, Crea F et al.| title=Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: executive summary: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology. | journal=Eur Heart J | year= 2006 | volume= 27 | issue= 11 | pages= 1341-81 | pmid=16735367 | doi=10.1093/eurheartj/ehl001 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16735367 }} </ref>== | |||
{{cquote| | |||
===Class IIb=== | |||
'''1.''' Routine periodic [[ECG]] in the absence of clinical change. ''(Level of Evidence: C)''}} | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 44: | ||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
* | *Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology <ref name="pmid16735367">{{cite journal| author=Fox K, Garcia MA, Ardissino D, Buszman P, Camici PG, Crea F et al.| title=Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: executive summary: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology. | journal=Eur Heart J | year= 2006 | volume= 27 | issue= 11 | pages= 1341-81 | pmid=16735367 | doi=10.1093/eurheartj/ehl001 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16735367 }} </ref> | ||
*The ACC/AHA/ACP–ASIM Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina <ref name="pmid10351980">Gibbons RJ, Chatterjee K, Daley J, Douglas JS, Fihn SD, Gardin JM et al. (1999) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10351980 ACC/AHA/ACP-ASIM guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina: executive summary and recommendations. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Management of Patients with Chronic Stable Angina).] ''Circulation'' 99 (21):2829-48. PMID: [http://pubmed.gov/10351980 10351980]</ref> | |||
* | *TheACC/AHA 2002 Guideline Update for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina <ref name="pmid12515758">Gibbons RJ, Abrams J, Chatterjee K, Daley J, Deedwania PC, Douglas JS et al. (2003) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12515758 ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for the management of patients with chronic stable angina--summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina).] ''Circulation'' 107 (1):149-58. PMID: [http://pubmed.gov/12515758 12515758]</ref> | ||
*The 2007 Chronic Angina Focused Update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina <ref name=" | *The 2007 Chronic Angina Focused Update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina <ref name="pmid17998462">Fraker TD, Fihn SD, Gibbons RJ, Abrams J, Chatterjee K, Daley J et al. (2007) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17998462 2007 chronic angina focused update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Writing Group to develop the focused update of the 2002 Guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina.] ''Circulation'' 116 (23):2762-72. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187930 DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187930] PMID: [http://pubmed.gov/17998462 17998462]</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Disease state]] | [[Category: Disease state]] | ||
[[Category:Ischemic heart diseases]] | [[Category: Ischemic heart diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category: Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category: Emergency medicine]] | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
Revision as of 04:36, 19 July 2011
|
Chronic stable angina Microchapters | ||
|
Classification | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| ||
|
Differentiating Chronic Stable Angina from Acute Coronary Syndromes | ||
|
Diagnosis | ||
|
Alternative Therapies for Refractory Angina | ||
|
Discharge Care | ||
|
Guidelines for Asymptomatic Patients | ||
|
Case Studies | ||
|
Chronic stable angina electrocardiography On the Web | ||
|
to Hospitals Treating Chronic stable angina electrocardiography | ||
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Chronic stable angina electrocardiography | ||
Editors-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Phone:617-632-7753; Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]; Associate Editor-in-Chief: Smita Kohli, M.D.
Electrocardiography (ECG) at Rest
- The ECG is critical not only to add support to the clinical suspicion of CAD but also to provide prognostic information based on the pattern and magnitude of the abnormalities.
- It is in normal range in approximately half of patients with chronic stable angina without a history of previous myocardial infarction. In the others, a variety of ECG finding may suggest an ischemic heart disease.
- Q waves may suggest prior myocardial infarction, but in the absence of a clinical history of previous myocardial infarction or CAD,
- Q waves may also be caused by other conditions, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular hypertrophy, dilated non ischemic cardiomyopathy and accessory conduction pathways.
- Isolated Q waves in lead III or QS pattern in V1 and V2 are nonspecific for diagnosis.
- The occurrence of ST segment depression and T wave inversion in the resting ECG, and signs of left ventricular hypertrophy, left bundle branch block (LBBB) and left anterior hemiblock LAH are compatible with, favors to, but are not specific for CAD.
- A physician should consider these abnormal ECG findings as indications for further evaluation.
- Giant T-wave inversion in precordial leads is sometimes an important indicator of severe Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery stenosis.
- ST segment changes in angina can be seen as downsloping, upsloping or horizontal ST segment depression.
ACC / AHA Guidelines- Resting ECG(DO NOT EDIT)[1]
| “ |
Class I1. Rest ECG in patients without an obvious noncardiac cause of chest pain. (Level of Evidence: B) 2. Rest ECG during an episode of chest pain. (Level of Evidence: B) |
” |
ESC Guidelines- Resting ECG for Initial diagnostic assessment of angina (DO NOT EDIT)[2]
| “ |
Class I (in all patients)1. Resting ECG while pain free. (Level of Evidence: C) 2. Resting ECG during episode of angina. (Level of Evidence: B) |
” |
ESC Guidelines- Resting ECG for Routine reassessment in patients with chronic stable angina (DO NOT EDIT)[2]
| “ |
Class IIb1. Routine periodic ECG in the absence of clinical change. (Level of Evidence: C) |
” |
See Also
Sources
- Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology [2]
- The ACC/AHA/ACP–ASIM Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina [1]
- TheACC/AHA 2002 Guideline Update for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina [3]
- The 2007 Chronic Angina Focused Update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina [4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gibbons RJ, Chatterjee K, Daley J, Douglas JS, Fihn SD, Gardin JM et al. (1999) ACC/AHA/ACP-ASIM guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina: executive summary and recommendations. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on Management of Patients with Chronic Stable Angina). Circulation 99 (21):2829-48. PMID: 10351980
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Fox K, Garcia MA, Ardissino D, Buszman P, Camici PG, Crea F; et al. (2006). "Guidelines on the management of stable angina pectoris: executive summary: The Task Force on the Management of Stable Angina Pectoris of the European Society of Cardiology". Eur Heart J. 27 (11): 1341–81. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl001. PMID 16735367.
- ↑ Gibbons RJ, Abrams J, Chatterjee K, Daley J, Deedwania PC, Douglas JS et al. (2003) ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for the management of patients with chronic stable angina--summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on the Management of Patients With Chronic Stable Angina). Circulation 107 (1):149-58. PMID: 12515758
- ↑ Fraker TD, Fihn SD, Gibbons RJ, Abrams J, Chatterjee K, Daley J et al. (2007) 2007 chronic angina focused update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Writing Group to develop the focused update of the 2002 Guidelines for the management of patients with chronic stable angina. Circulation 116 (23):2762-72. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187930 PMID: 17998462