Chlamydia trachomatis: Difference between revisions
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
::*Note (2): Pregnant and lactating women should be treated with [[erythromycin]]. [[Azithromycin]] might prove useful for treatment of LGV in pregnancy, but no published data are available regarding its safety and efficacy. [[Doxycycline]] is contraindicated in pregnant women. | ::*Note (2): Pregnant and lactating women should be treated with [[erythromycin]]. [[Azithromycin]] might prove useful for treatment of LGV in pregnancy, but no published data are available regarding its safety and efficacy. [[Doxycycline]] is contraindicated in pregnant women. | ||
::*Note (3): Persons with both LGV and HIV infection should receive the same regimens as those who are HIV negative. Prolonged therapy might be required, and delay in resolution of symptoms might occur. | ::*Note (3): Persons with both LGV and HIV infection should receive the same regimens as those who are HIV negative. Prolonged therapy might be required, and delay in resolution of symptoms might occur. | ||
::* Note(4): | ::* Note(4): Persons who have had sexual contact with a patient who has LGV within the 60 days before onset of the patient’s symptoms should be examined and tested for urethral, cervical, or rectal chlamydial infection depending on anatomic site of exposure. They should be presumptively treated with a chlamydia regimen [[Azithromycin]] 1 g PO single dose {{or}} [[Doxycycline]] 100 mg PO bid for 7 days). | ||
==Gallery== | ==Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 25 June 2015
| Chlamydia trachomatis | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
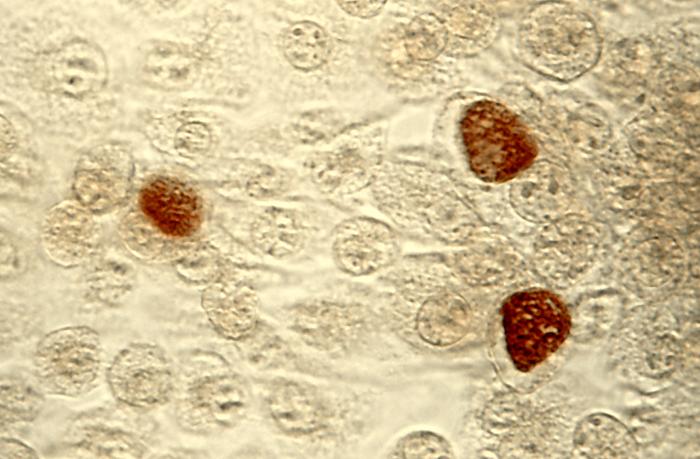 C. trachomatis inclusion bodies (brown) in a McCoy cell culture.
| ||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||
| Chlamydia trachomatis Busacca, 1935 |
Chlamydia trachomatis is one of three bacterial species in the genus Chlamydia, family Chlamydiaceae, class Chlamydiae, phylum Chlamydiae, domain Bacteria. C. trachomatis has only been found living inside the cells of humans, causing the following conditions:
In men
In women
- Cervicitis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Premature birth
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic pain, chronic or acute
- Newborn eye (trachoma) or lung infection
In both sexes
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Urethritis
- Infertility
- Proctitis (rectal disease and bleeding)
- Reactive arthritis
- Trachoma
C. trachomatis has also been detected in some patients with temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disease. It may be treated with any of several antibiotics: azithromycin, erythromycin or doxycycline/tetracycline.
C. trachomatis was the first chlamydial agent discovered in humans. It comprises two human biovars: trachoma and lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV). Many, but not all, C. trachomatis strains have an extrachromosomal plasmid. Chlamydia species are readily identified and distinguished from other chlamydial species using DNA-based tests. Most strains of C. trachomatis are recognized by monoclonal antibodies [mAbs] to epitopes in the VS4 region of MOMP. However, these mAbs may also crossreact with the other two Chlamydia species, Chlamydia suis and Chlamydia muridarum.
Treatment
- Chlaymydial infections [1]
- Chlamydial Infections in Adolescents and Adults
- Preferred regimen : Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days OR Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen (1): Erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days
- Alternative regimen (2): Levofloxacin 500 mg PO qd for 7 days OR Ofloxacin 300 mg PO bid for 7 days.
- Note: Patients should be instructed to refer their sex partners for evaluation, testing, and treatment if they had sexual contact with the patient during the 60 days preceding onset of the patient's symptoms or chlamydia diagnosis.
- Chlamydial Infections in patients with HIV Infection
- Preferred regimen : Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days OR Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen (1): Erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days
- Alternative regimen (2): Levofloxacin 500 mg PO qd for 7 days OR Ofloxacin 300 mg PO bid for 7 days.
- Pregancy
- Preferred regimen :Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Alternative regimen (1):Amoxicillin 500 mg PO tid for 7 days
- Alternative regimen (2):Erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycinbase 250 mg PO qid for 14 days
- Alternative regimen (3):Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg PO qid for 7 days OR Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 400 mg PO four qid for 14days
- Note:Doxycycline, Ofloxacin, and Levofloxacin are contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Chlamydial infection among neonates
- Ophthalmia Neonatorumcaused by C. trachomatis
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate ,PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Alternative regimen : Azithromycin suspension, PO 20 mg/kg /day qd for 3 days
- Note: The mothers of infants who have chlamydial infection and the sex partners of these women should be evaluated and treated.
- Infant Pneumonia
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Alternative regimen : Azithromycin suspension, PO 20 mg/kg /day qd for 3 days
- Chlamydial infection among infants and childern
- Infants and childern who weigh < 45 kg
- Preferred regimen :Erythromycin base or ethylsuccinate PO 50 mg/kg/ day divided into 4 doses daily for 14 days
- Infants and childern who weigh >45 kg but who are aged <8 years
- Preferred regimen :Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose
- Infants and childern aged >8 years
- Preferred regimen :Azithromycin 1 g PO in a single dose OR Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) is caused by C. trachomatis serovars L1, L2, or L3
- Preferred regimen : Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 21 days
- Alternative regimen: Erythromycin base 500 mg PO qid for 21 days
- Note (1): azithromycin 1 g orally once weekly for 3 weeks is probably effective based on its chlamydial antimicrobial activity. Fluoroquinolone-based treatments might also be effective, but extended treatment intervals are likely required.
- Note (2): Patients should be followed clinically until signs and symptoms have resolved.
- Note (2): Pregnant and lactating women should be treated with erythromycin. Azithromycin might prove useful for treatment of LGV in pregnancy, but no published data are available regarding its safety and efficacy. Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnant women.
- Note (3): Persons with both LGV and HIV infection should receive the same regimens as those who are HIV negative. Prolonged therapy might be required, and delay in resolution of symptoms might occur.
- Note(4): Persons who have had sexual contact with a patient who has LGV within the 60 days before onset of the patient’s symptoms should be examined and tested for urethral, cervical, or rectal chlamydial infection depending on anatomic site of exposure. They should be presumptively treated with a chlamydia regimen Azithromycin 1 g PO single dose OR Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid for 7 days).
Gallery
-
Photomicrograph of Chlamydia trachomatis taken from a urethral scrape. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
McCoy cell monolayers with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (200X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
McCoy cell monolayers with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (50X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Photomicrograph depicts HeLa cells infected with Type-A Chlamydia trachomatis (400X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
-
Patient’s left eye with the upper lid retracted in order to reveal the inflamed conjunctival membrane lining the inside of both the upper and lower lids, due to what was determined to be a case of inclusion conjunctivitis caused by the bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]
External links
- Chlamydiae.com [1]
- Template:GPnotebook
- article at reuters.com
ar:تراخوما da:Klamydia de:Chlamydia trachomatis nl:Chlamydia trachomatis no:Chlamydia trachomatis uk:Chlamydia trachomatis
![Photomicrograph of Chlamydia trachomatis taken from a urethral scrape. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/2/21/Chlamydia15.jpeg)
![McCoy cell monolayers with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (200X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/8/88/Chlamydia11.jpeg)
![McCoy cell monolayers with Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies (50X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/e/e2/Chlamydia10.jpeg)
![Photomicrograph depicts HeLa cells infected with Type-A Chlamydia trachomatis (400X mag). From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/2/29/Chlamydia09.jpeg)
![Patient’s left eye with the upper lid retracted in order to reveal the inflamed conjunctival membrane lining the inside of both the upper and lower lids, due to what was determined to be a case of inclusion conjunctivitis caused by the bacterium, Chlamydia trachomatis. From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/3/3c/Chlamydia03.jpeg)
![From Public Health Image Library (PHIL). [2]](/images/0/01/Chlamydia04.jpeg)