Carbenicillin
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Carbenicillin is an antibiotic that is FDA approved for the treatment of infections due to Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Morganella morganii (formerly Proteus morganii), Providencia rettgeri (formerly Proteus rettgeri), Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, Enterococci. Common adverse reactions include nausea, bad taste, diarrhea, vomiting, flatulence, glossitis, abdominal cramps, dry mouth, furry tongue, rectal bleeding, anorexia, hypersensitivity, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
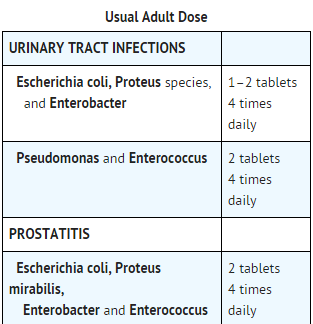
- Geocillin (carbenicillin indanyl sodium) is indicated in the treatment of acute and chronic infections of the upper and lower urinary tract and in asymptomatic bacteriuria due to susceptible strains of the following organisms.
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Morganella morganii (formerly Proteus morganii)
- Providencia rettgeri (formerly Proteus rettgeri)
- Proteus vulgaris
- Pseudomonas
- Enterobacter
- Enterococci
- Geocillin is also indicated in the treatment of prostatitis due to susceptible strains of the following organisms.
- Escherichia coli
- Enterococcus (S. faecalis)
- Proteus mirabilis
- Enterobacter sp.
- WHEN HIGH AND RAPID BLOOD AND URINE LEVELS OF ANTIBIOTIC ARE INDICATED, THERAPY WITH GEOPEN (CARBENICILLIN DISODIUM) SHOULD BE INITIATED BY PARENTERAL ADMINISTRATION FOLLOWED, AT THE PHYSICIAN'S DISCRETION, BY ORAL THERAPY.
- NOTE: Susceptibility testing should be performed prior to and during the course of therapy to detect the possible emergence of resistant organisms which may develop.
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain effectiveness of Geocillin and other antibacterial drugs, Geocillin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Carbenicillin in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Carbenicillin in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Carbenicillin in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Carbenicillin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Carbenicillin in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Geocillin is ordinarily contraindicated in patients who have a known penicillin allergy.
Warnings
- Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients on oral penicillin therapy. Although anaphylaxis is more frequent following parenteral therapy, it has occurred in patients on oral penicillins.
- These reactions are more apt to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens.
- There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe hypersensitivity reactions when treated with a cephalosporin, and vice versa. Before initiating therapy with a penicillin, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. If an allergic reaction occurs, the drug should be discontinued and the appropriate therapy instituted.
- SERIOUS ANAPHYLACTOID REACTIONS REQUIRE IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE. OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS STEROIDS AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, INCLUDING INTUBATION, SHOULD ALSO BE ADMINISTERED AS INDICATED.
- Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including GEOCILLIN(carbenicillin indanyl sodium ), and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
- C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
- If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following adverse reactions have been reported as possibly related to Geocillin administration in controlled studies which include 344 patients receiving Geocillin.
Gastrointestinal
- The most frequent adverse reactions associated with Geocillin therapy are related to the gastrointestinal tract. Nausea, bad taste, diarrhea, vomiting, flatulence, and glossitis were reported. Abdominal cramps, dry mouth, furry tongue, rectal bleeding, anorexia, and unspecified epigastric distress were rarely reported.
Dermatologic
- Hypersensitivity reactions such as skin rash, urticaria, and less frequently pruritus.
Hematologic
- As with other penicillins, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia have infrequently been observed. The clinical significance of these abnormalities is not known.
Miscellaneous
- Other reactions rarely reported were hyperthermia, headache, itchy eyes, vaginitis, and loose stools.
Abnormalities of Hepatic Function Tests
- Mild SGOT elevations have been observed following Geocillin administration.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Reproduction studies have been performed at dose levels of 1000 or 500 mg/kg in rats, 200 mg/kg in mice, and at 500 mg/kg in monkeys with no harm to fetus due to Geocillin. There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Carbenicillin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
- It is not known whether the use of Geocillin in humans during labor or delivery has immediate or delayed adverse effects on the fetus, prolongs the duration of labor, or increases the likelihood that forceps delivery or other obstetrical intervention or resuscitation of the newborn will be necessary.
Nursing Mothers
- Carbenicillin class antibiotics are excreted in milk although the amounts excreted are unknown; therefore, caution should be exercised if administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Since only limited clinical data is available to date in children, the safety of Geocillin administration in this age group has not yet been established.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Carbenicillin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Carbenicillin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Overdosage
- Geocillin is generally nontoxic. Geocillin when taken in excessive amounts may produce mild gastrointestinal irritation. The drug is rapidly excreted in the urine and symptoms are transitory. The usual symptoms of anaphylaxis may occur in hypersensitive individuals.
- Carbenicillin blood levels achievable with Geocillin are very low, and toxic reactions as a function of overdosage should not occur systematically. The oral LD50 in mice is 3,600 mg/kg, in rats 2,000 mg/kg, and in dogs is in excess of 500 mg/kg. The lethal human dose is not known.
- Although never reported, the possibility of accumulation of indanyl should be considered when large amounts of Geocillin are ingested. Free indole, which is a phenol derivative, may be potentially toxic. In general 8–15 grams of phenol, and presumably a similar amount of indole, are required orally before toxicity (peripheral vascular collapse) may occur. The metabolic by products of indole are nontoxic. In patients with hepatic failure it may be possible for unmetabolized indole to accumulate.
- The metabolic by-products of Geocillin, indanyl sulfate and glucuronide, as well as free carbenicillin, are dialyzable.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Free carbenicillin is the predominant pharmacologically active fraction of Geocillin. Carbenicillin exerts its antibacterial activity by interference with final cell wall synthesis of susceptible bacteria.
- Geocillin is acid stable, and rapidly absorbed from the small intestine following oral administration. It provides relatively low plasma concentrations of antibiotic and is primarily excreted in the urine. After absorption, Geocillin is rapidly converted to carbenicillin by hydrolysis of the ester linkage.
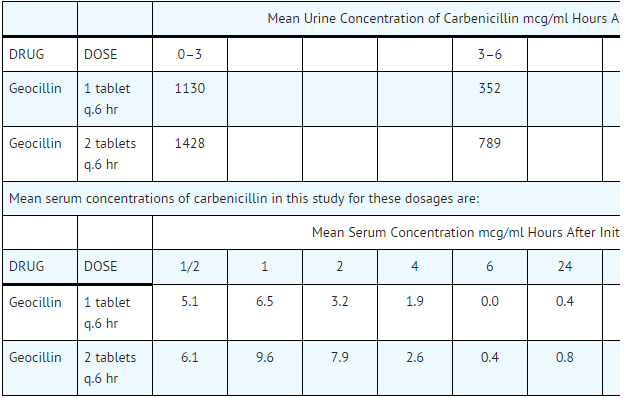
- Following ingestion of a single 500 mg tablet of Geocillin, a peak carbenicillin plasma concentration of approximately 6.5 mcg/ml is reached in 1 hour. About 30% of this dose is excreted in the urine unchanged within 12 hours, with another 6% excreted over the next 12 hours.
- In a multiple dose study utilizing volunteers with normal renal function, the following mean urine and serum levels of carbenicillin were achieved:
Microbiology
- The antibacterial activity of Geocillin is due to its rapid conversion to carbenicillin by hydrolysis after absorption. Though Geocillin provides substantial in vitro activity against a variety of both gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, the most important aspect of its profile is in its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity. Because of the high urine levels obtained following administration, Geocillin has demonstrated clinical efficacy in urinary infections due to susceptible strains of:
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Proteus vulgaris
- Morganella morganii (formerly Proteus morganii)
- Pseudomonas species
- Providencia rettgeri (formerly Proteus rettgeri)
- Enterobacter species
- Enterococci (S. faecalis)
- In addition, in vitro data, not substantiated by clinical studies, indicate the following pathogens to be usually susceptible to Geocillin:
- Staphylococcus species (nonpenicillinase producing)
- Streptococcus species
Resistance
- Most Klebsiella species are usually resistant to the action of Geocillin. Some strains of Pseudomonas species have developed resistance to carbenicillin.
Susceptibility Testing
- Geopen (carbenicillin disodium) Susceptibility Powder or 100 µg Geopen Susceptibility Discs may be used to determine microbial susceptibility to Geocillin using one of the following standard methods recommended by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards:
- M2-A3, "Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests"
- M7-A, "Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically"
- M11-A, "Reference Agar Dilution Procedure for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria"
- M17-P, "Alternative Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria"
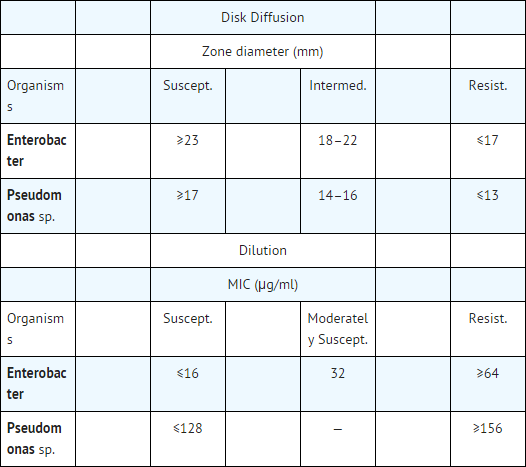
- Tests should be interpreted by the following criteria:
- Interpretations of susceptible, intermediate, and resistant correlate zone size diameters with MIC values. A laboratory report of "susceptible" indicates that the suspected causative microorganism most likely will respond to therapy with carbenicillin. A laboratory report of "resistant" indicates that the infecting microorganism most likely will not respond to therapy. A laboratory report of "moderately susceptible" indicates that the microorganism is most likely susceptible if a high dosage of carbenicillin is used, or if the infection is such that high levels of carbenicillin may be attained as in urine. A report of "intermediate" using the disk diffusion method may be considered an equivocal result, and dilution tests may be indicated.
Structure
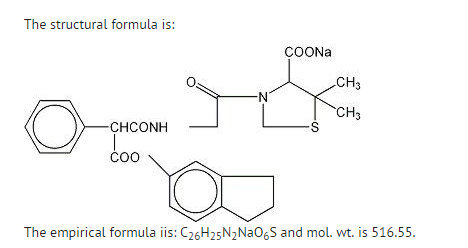
- Geocillin, a semisynthetic penicillin, is the sodium salt of the indanyl ester of Geopen® (carbenicillin disodium). The chemical name is: 1-(5-Indanyl)-N-(2-carboxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] hept-6-yl)-2-phenylmalonamate monosodium salt.
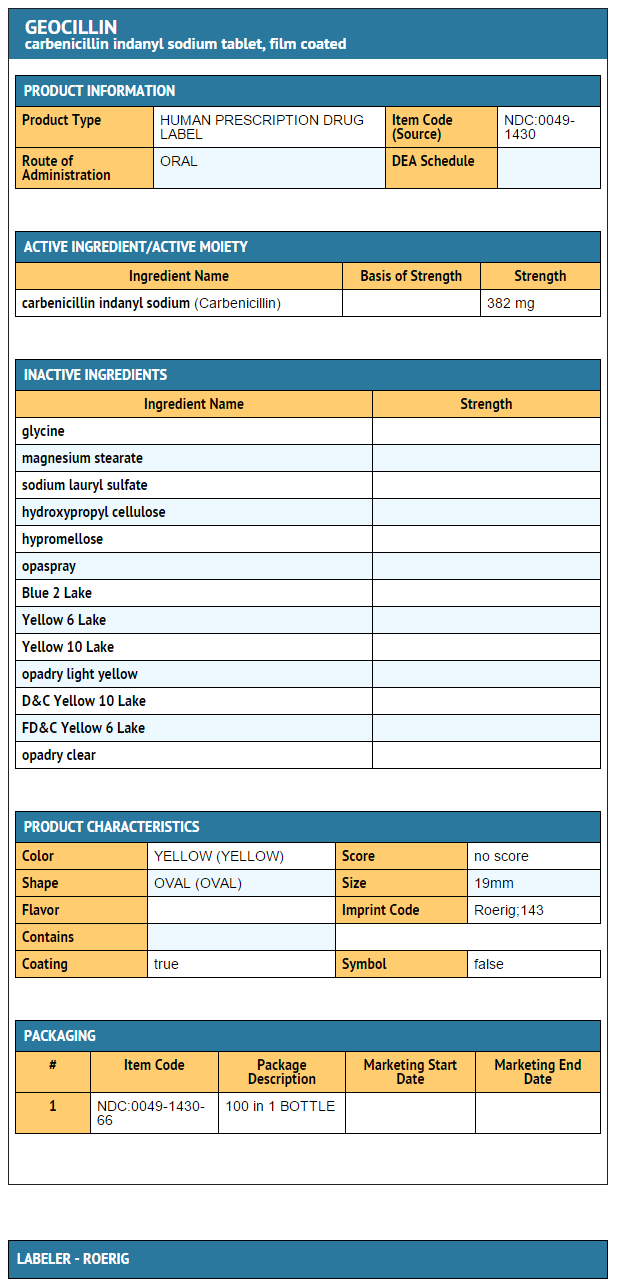
- Geocillin tablets are yellow, capsule-shaped and film-coated, made of a white crystalline solid. Carbenicillin is freely soluble in water. Each Geocillin tablet contains 382 mg of carbenicillin, 118 mg of indanyl sodium ester. Each Geocillin tablet contains 23 mg of sodium.
- Inert ingredients are: glycine; magnesium stearate and sodium lauryl sulfate. May also include the following: hydroxypropyl cellulose; hypromellose; opaspray (which may include Blue 2 Lake, Yellow 6 Lake, Yellow 10 Lake, and other inert ingredients); opadry light yellow (which may contain D&C Yellow 10 Lake, FD&C Yellow 6 Lake and other inert ingredients); opadry clear (which may contain other inert ingredients).
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Geocillin is available as film-coated tablets in bottles of 100's (NDC-0049-1430-66). Each tablet contains carbenicillin indanyl sodium equivalent to 382 mg of carbenicillin.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Carbenicillin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Carbenicillin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Carbenicillin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Carbenicillin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- GEOCILLIN ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Carbenicillin Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Carbenicillin |Label Name=DailyMed - GEOCILLIN- carbenicillin indanyl sodium tablet, film coated .png
}}