Bursitis MRI
|
Bursitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Bursitis MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Bursitis MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sara Mehrsefat, M.D. [2]
Overview
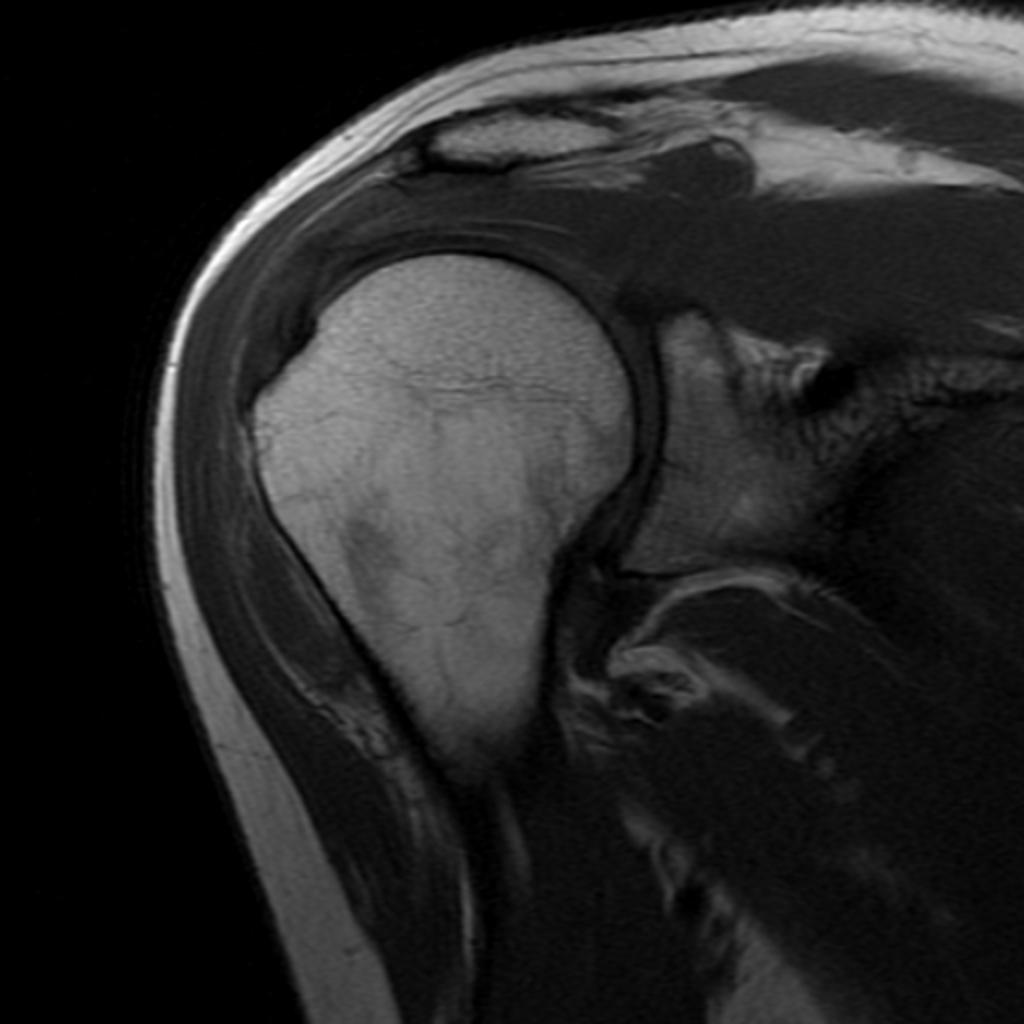
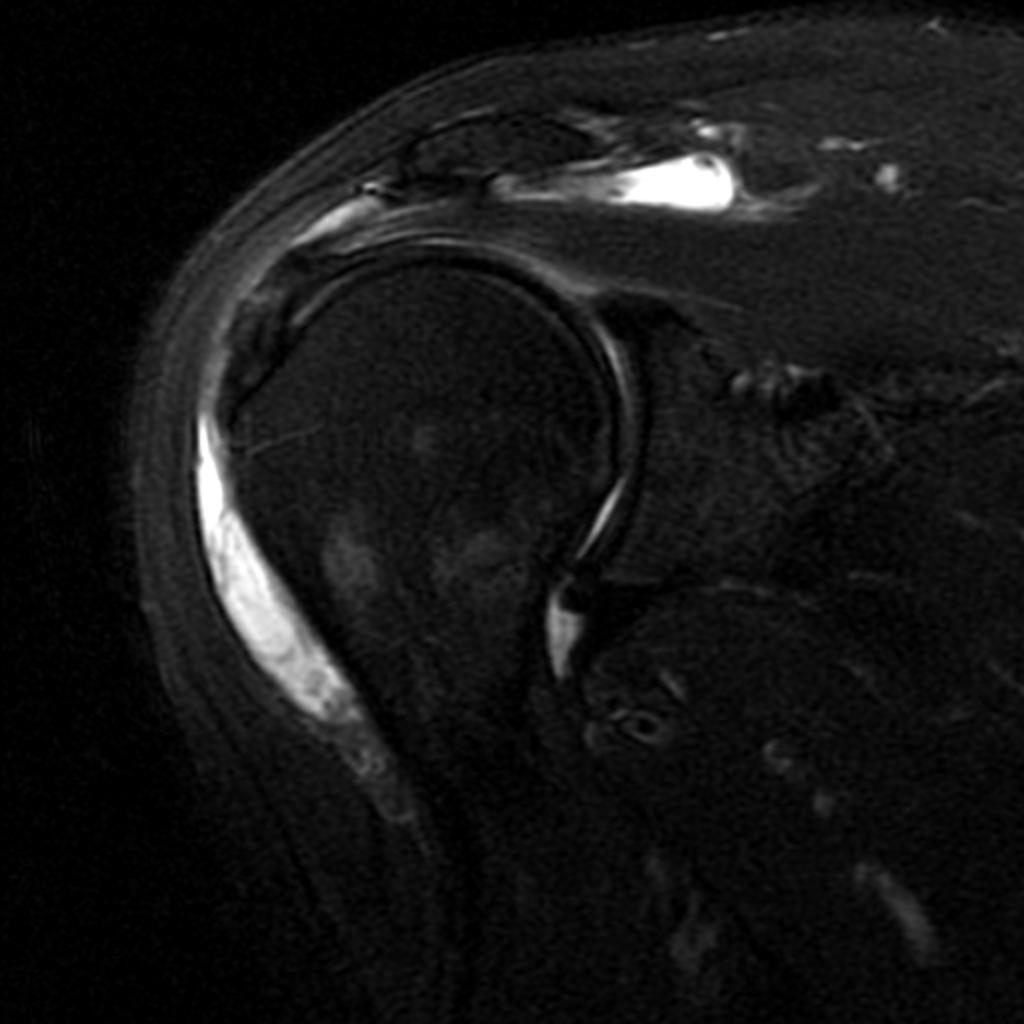
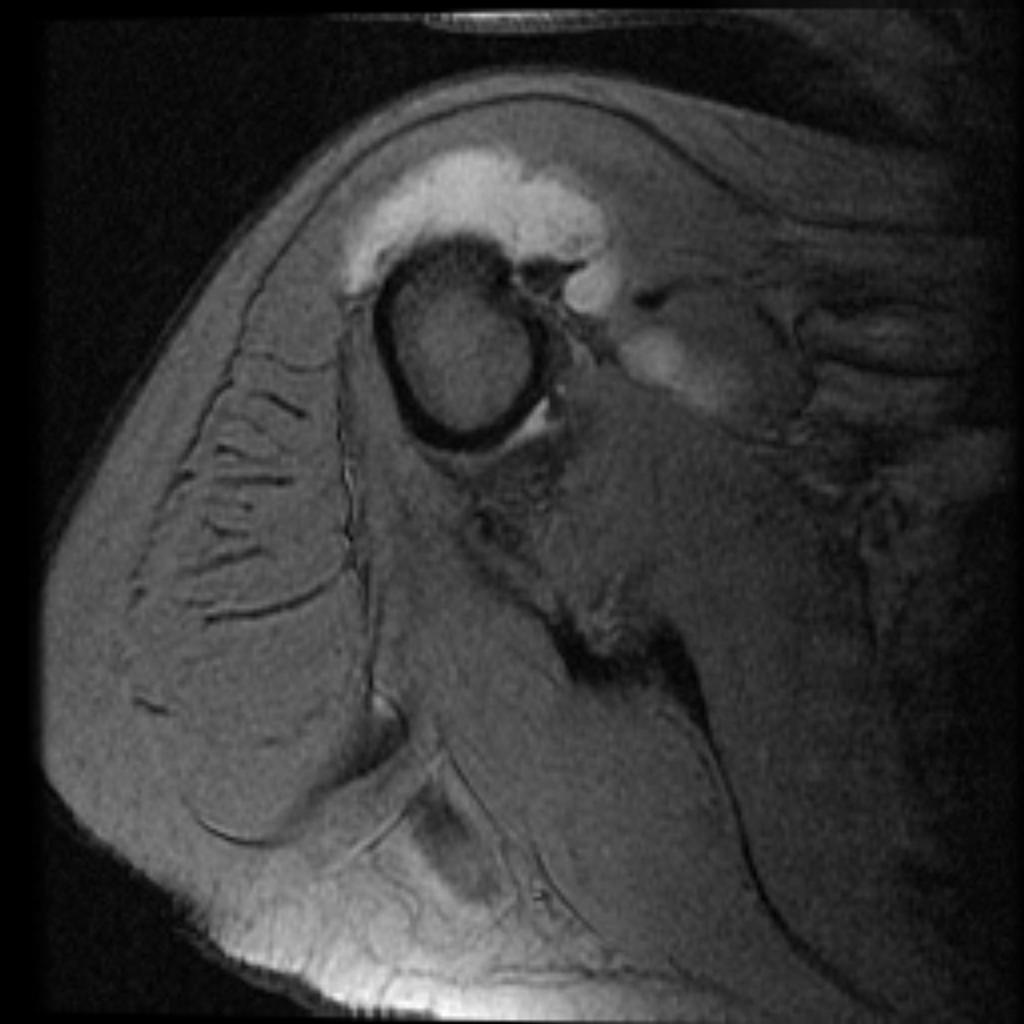
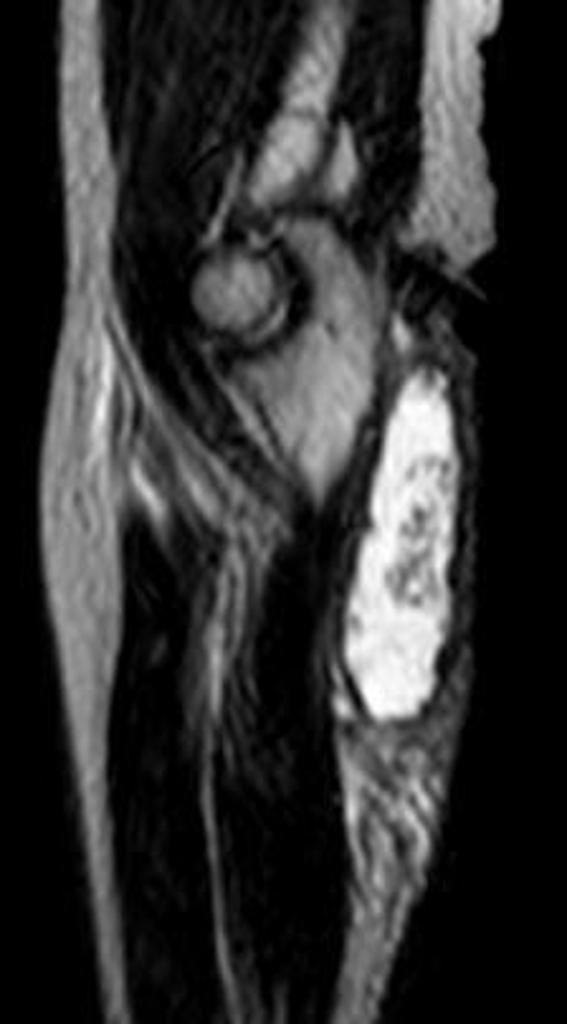
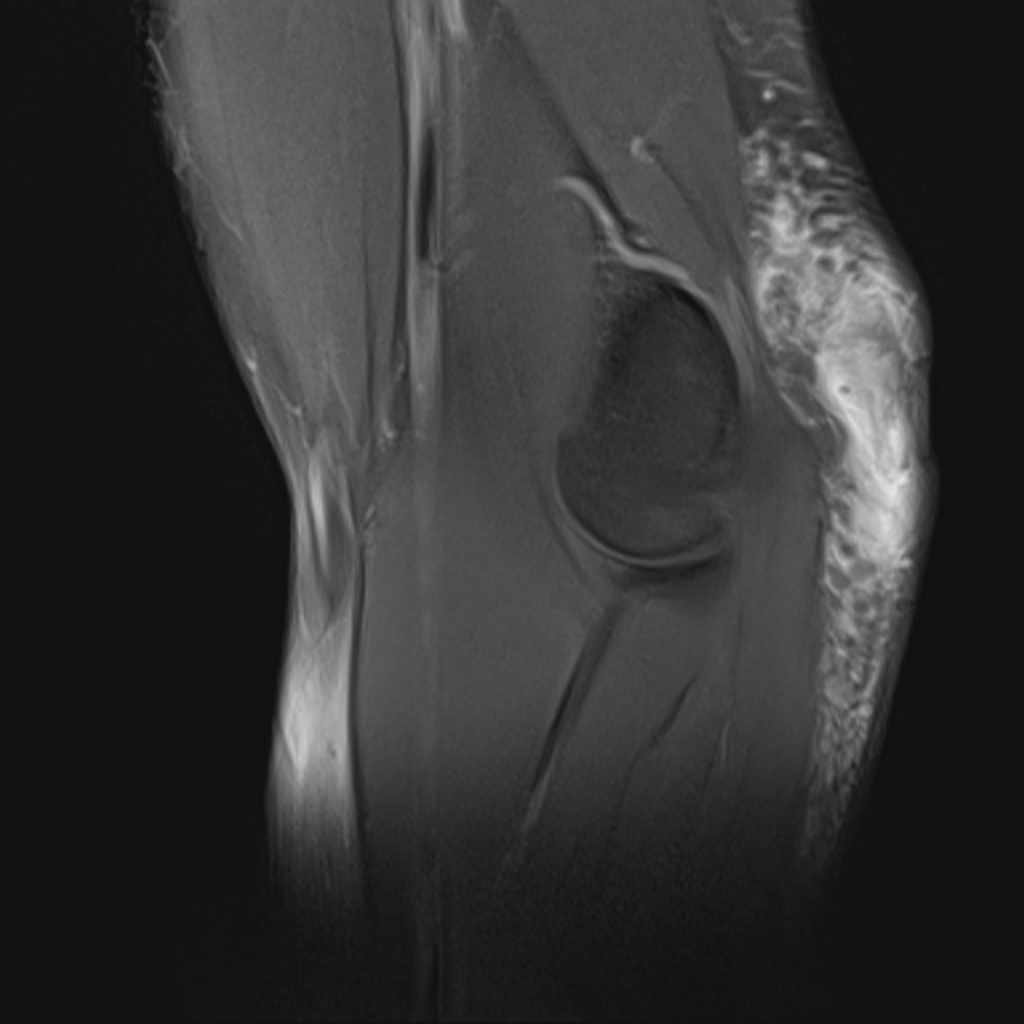
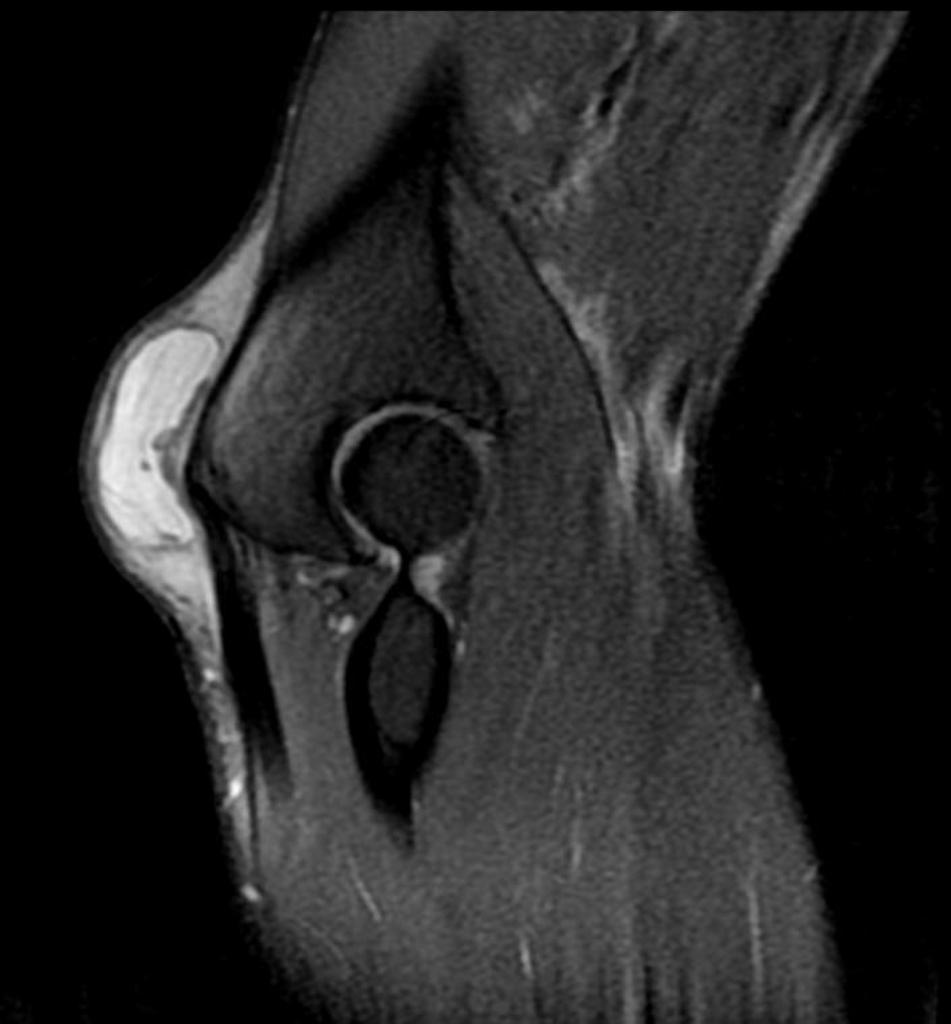
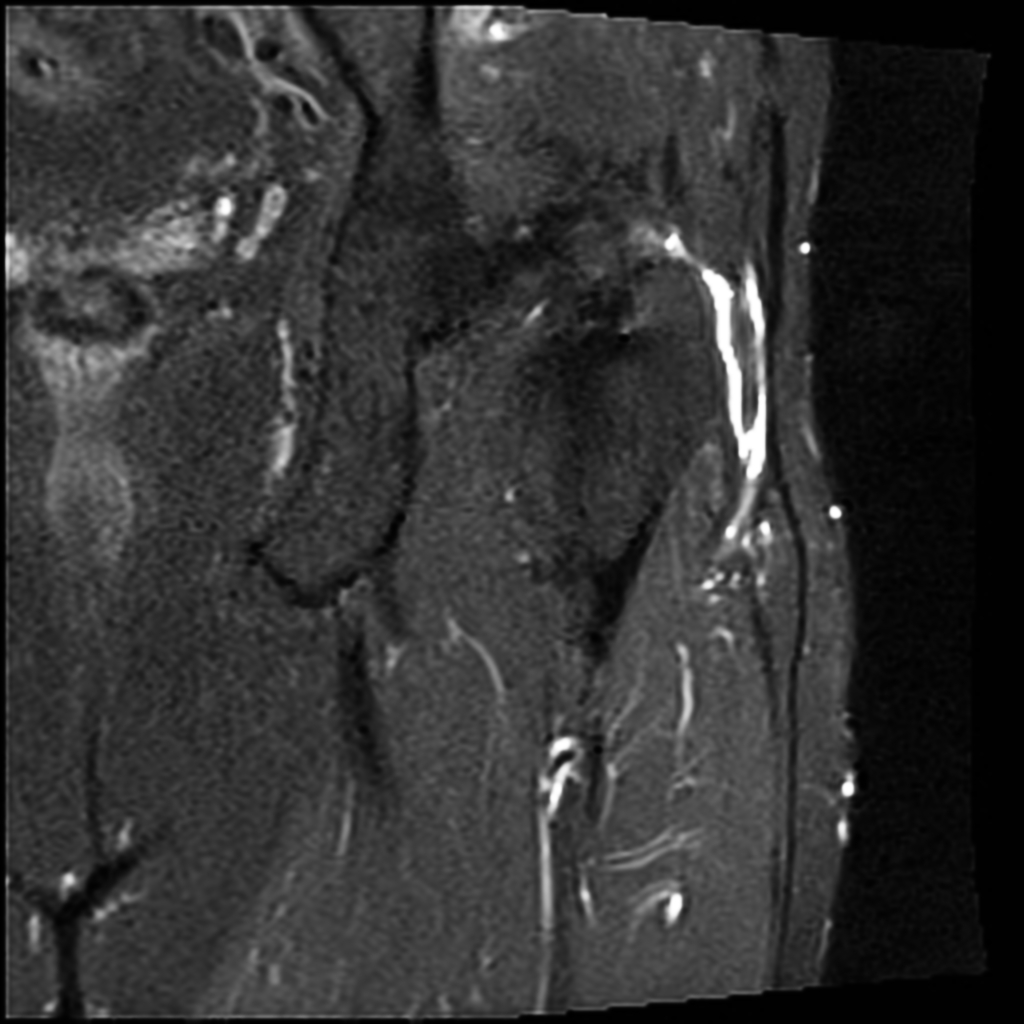
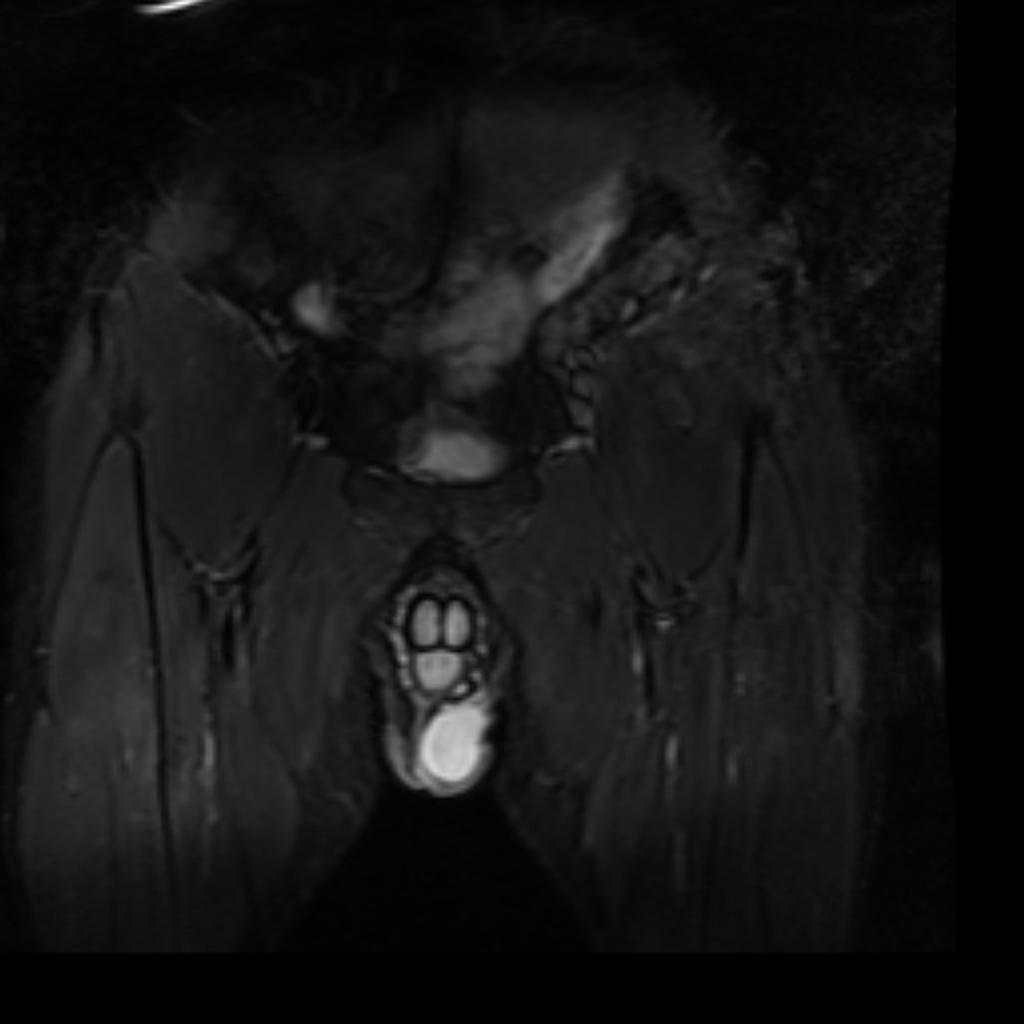
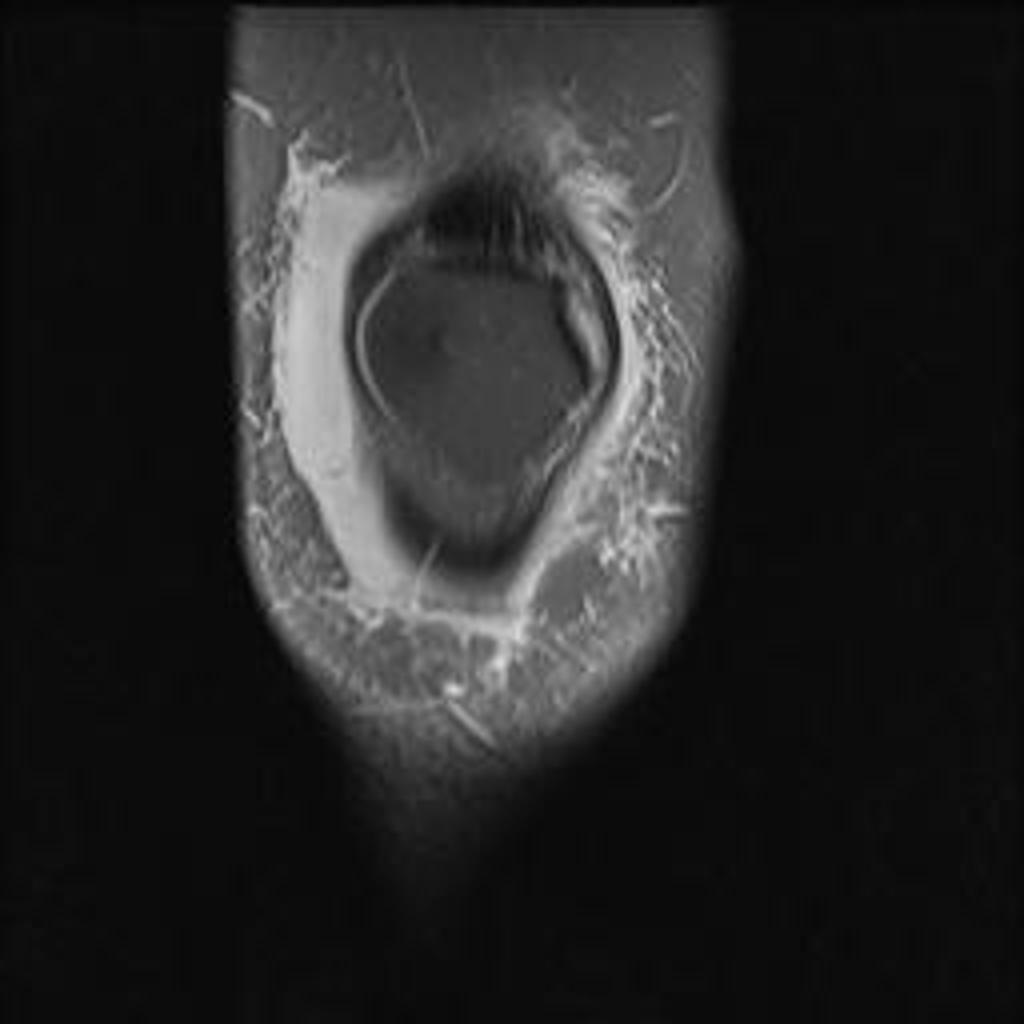
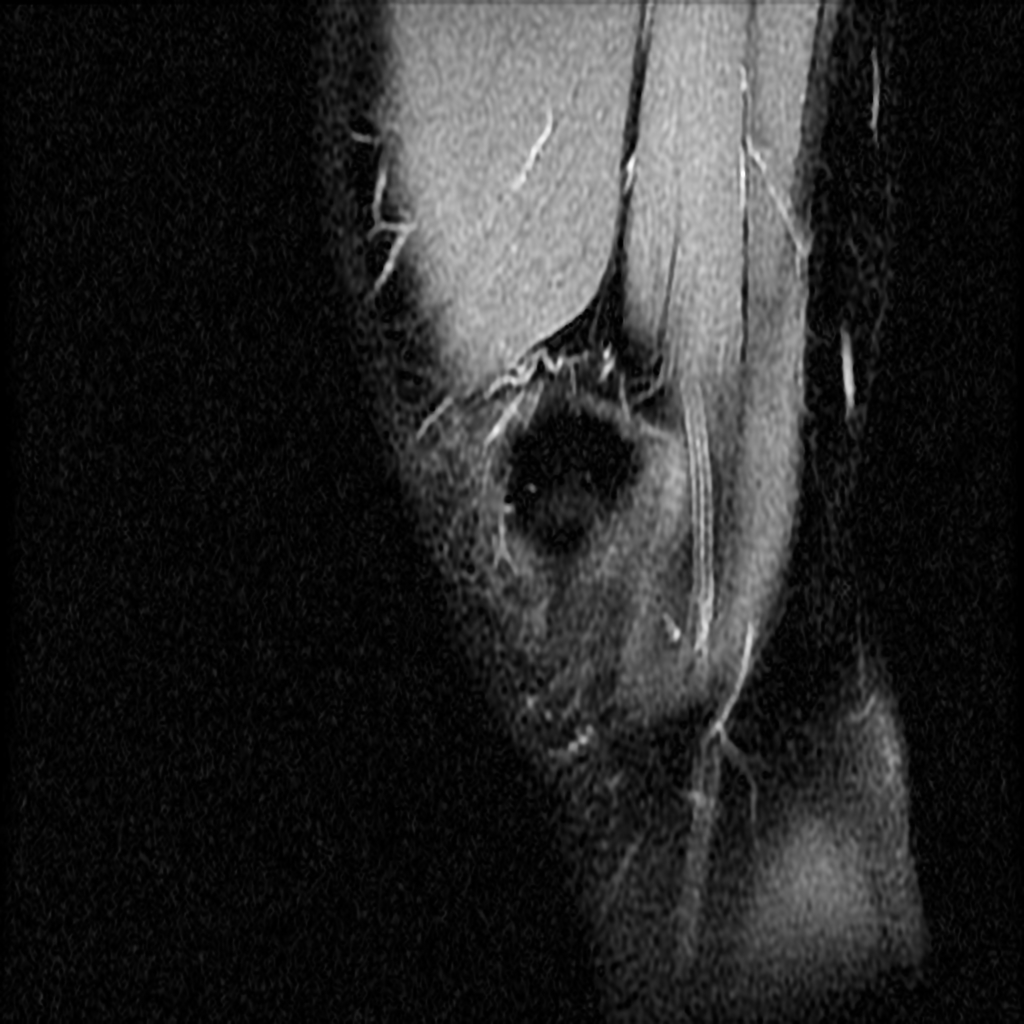
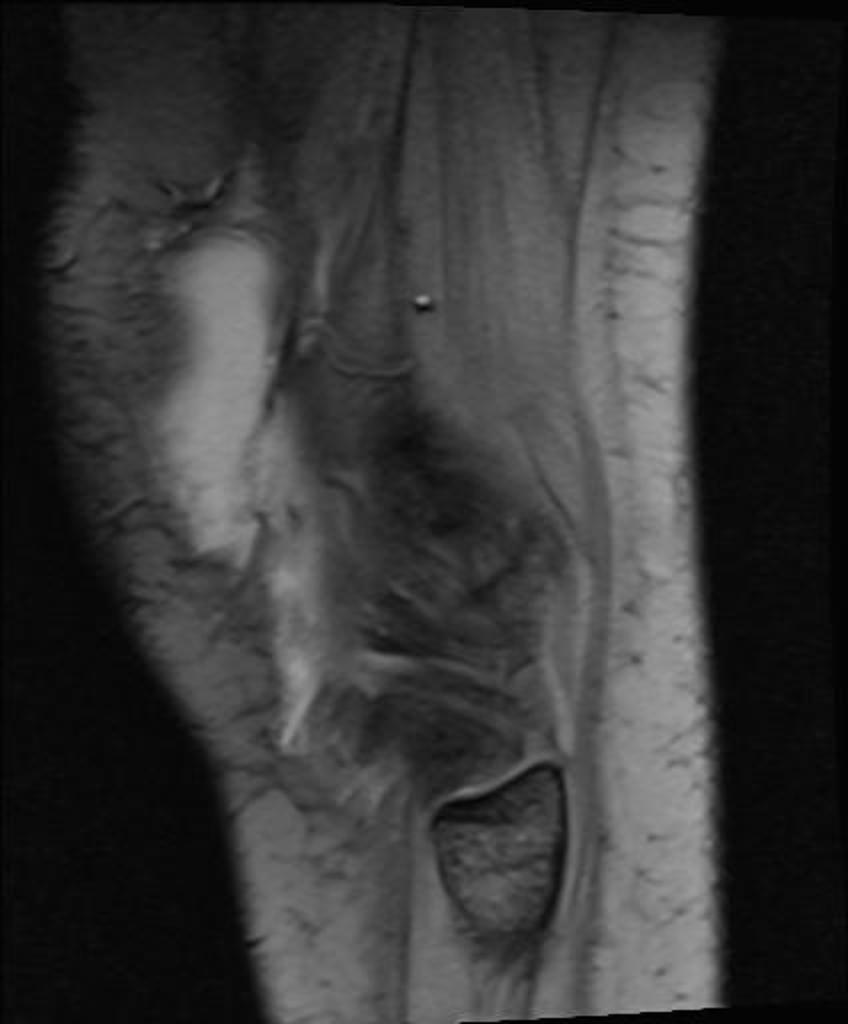
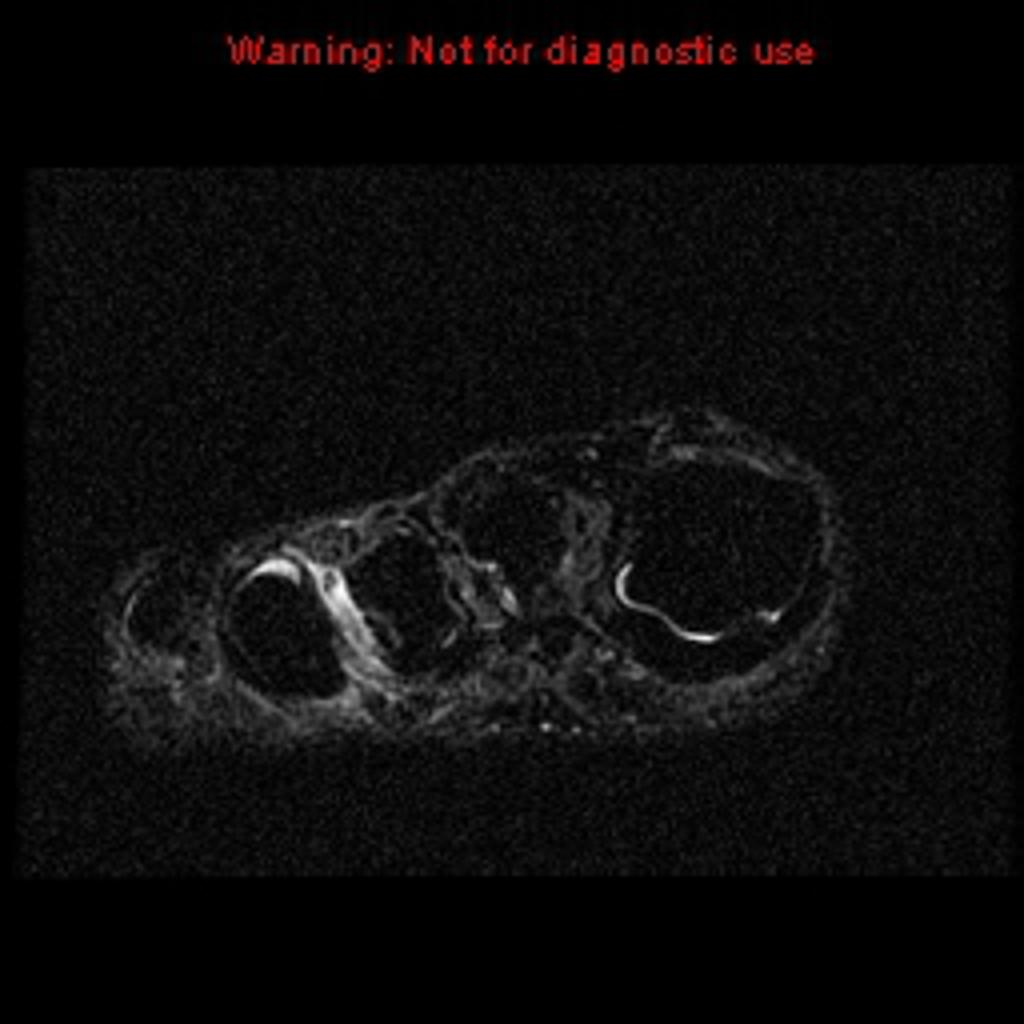
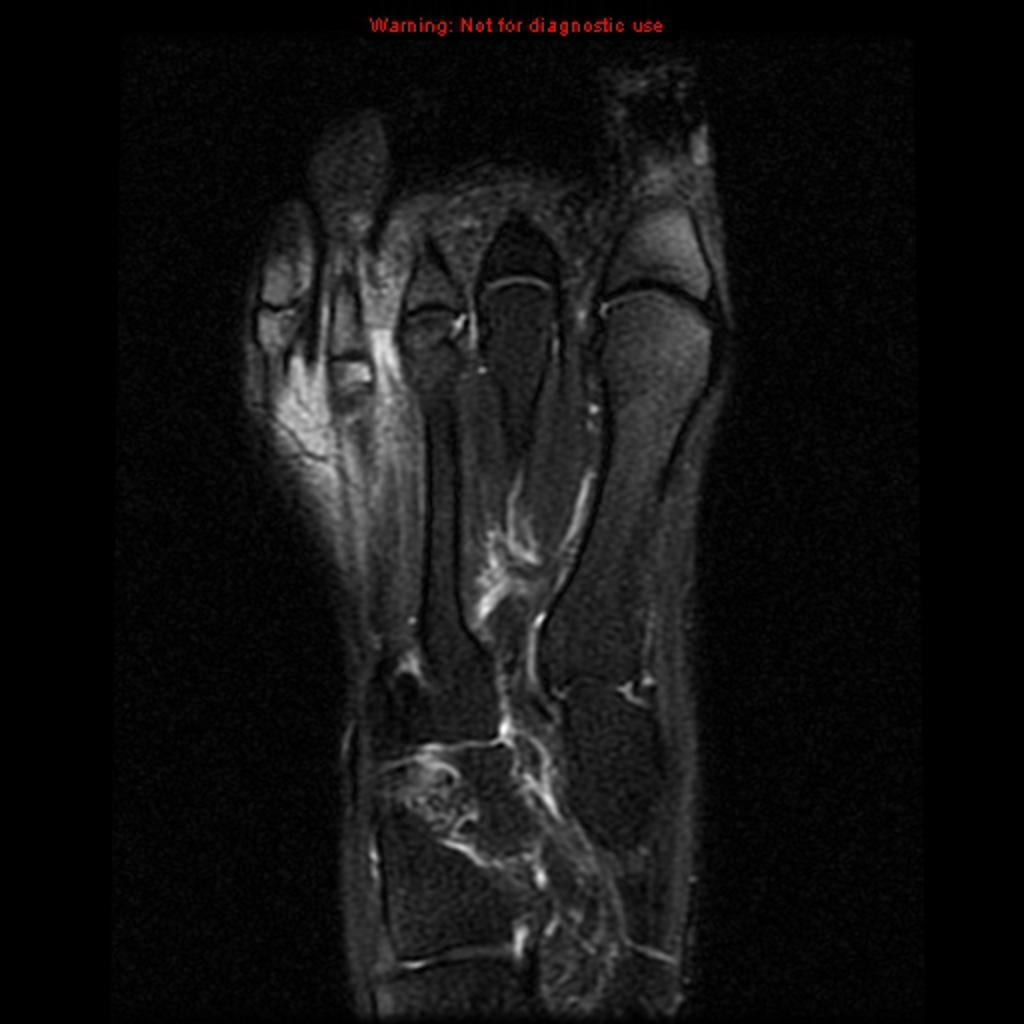
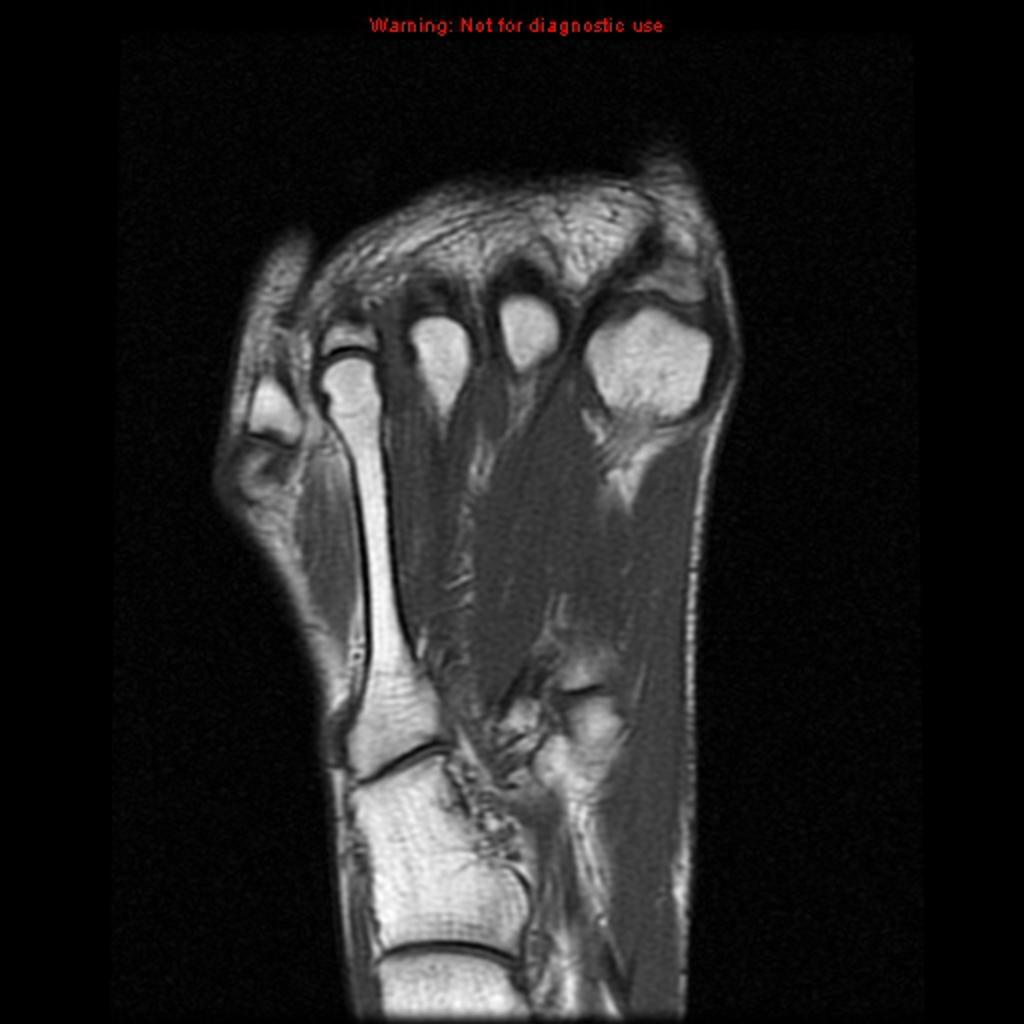
MRI is not often required in patients with bursitis. Due to the requisite cost and time input, the use of MRI is limited compared to ultrasound. MRI is often reserved for patients for whom there is reason to suspect the presence of other medical conditions such as tumors, ligamentous injures, and tendon injuries. On MRI, bursitis is characterized by bursal fluid collection, subcutaneous edema, and joint effusion.[1][2]
MRI
MRI is not often required in patients with bursitis. MRI is usually reserved for patients for whom there is reason to suspect the presence of other medical conditions such as tumors, ligament injures, and tendon injuries.
On MRI, bursitis is characterized by:[1][2]
- Bursal fluid collection
- Hypointense on T1
- Hyperintense on T2
- Enhancement of bursal margins on (Gd)
- Subcutaneous edema
- Joint effusion
| Type of Bursitis | MRI Images |
|---|---|
| Subacromial bursitis[3] |
|
| Olecranon bursitis[1] |
|
| Trochanteric bursitis [4] |
|
| Prepatellar bursitis[2] |
|
| Intermetatarsal bursitis[5] |
|
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Radiopedia. Olecranon Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/olecranon-bursitis Accessed on August 23, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Radiopedia. Prepatellar Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/cases/prepatellar-bursitis-1 Accessed on August 23, 2016
- ↑ Radiopedia. Shoulder Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/cases/shoulder-bursitis Accessed on August 23, 2016
- ↑ Radiopedia. Trochontreic Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/cases/trochanteric-bursitis Accessed on August 23, 2016
- ↑ Radiopedia. Intermetatarsal Bursitis. http://radiopaedia.org/cases/intermetatarsal-bursitis Accessed on August 23, 2016