Bursitis
| Bursitis | |
 | |
|---|---|
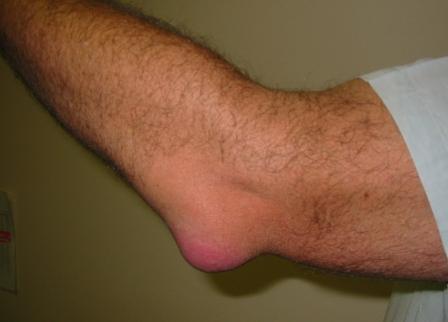
| Bursitis of the Elbow | |
| ICD-10 | M70-M71 |
| ICD-9 | 727.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 31623 |
| MedlinePlus | 000419 |
| eMedicine | emerg/74 |
| MeSH | D002062 |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Bursitis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Bursitis |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Bursitis at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Bursitis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Bursitis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Bursitis Risk calculators and risk factors for Bursitis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Bursitis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Please Join in Editing This Page and Apply to be an Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [3] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Overview
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae, or small sacs of synovial fluid, in the body. Bursae rest at the points where internal functionaries, like muscles and tendons, slide across bone. Healthy bursae create a smooth and almost frictionless gliding surface. With hundreds of them throughout the body they provide this surface for all motion, making movement normally painless. When bursitis takes hold, however, movement that relies on the inflamed bursa becomes rough and painful. Movement of tendons and muscles over the inflamed bursa causes it to become more inflamed, perpetuating the problem.
Pathophysiology & Etiology
Bursitis is commonly caused by repetition of movement or excessive pressure. Elbows and knees are the most commonly affected because they are rested upon more than many parts of the body with bursae and they also get the most repetitive use. Inflammation of bursae can also be caused by other inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Scoliosis can also be a cause of bursitis of the shoulders although this is rare. Shoulder bursitis is more commonly due to overuse of the shoulder joint and muscles. [1]
The other main cause of bursitis is traumatic injury, which can cause swelling of the bursae. The swelling itself causes irritation because the sac will no longer fit in the small area between the bone and the functionary. When the bone begins to increase pressure on the bursa, bursitis ensues.
Diagnosis
The most common examples of this condition are Prepatellar bursitis, Trochanteric bursitis, Olecranon bursitis and Subacromial bursitis.
History and Symptoms
Symptoms can vary from an ache and stiffness in the local area of the joint, to a burning that surrounds the whole joint around the inflamed bursa. With this condition, the pain is usually worse during and after activity, and the bursa and surrounding joint area can become stiffer the following day.
References
External links
- Bursitis information and treatment from NHS Direct
- General Bursitis Information
- Information from the Mayo Clinic
Template:Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue Template:SIB
cs:Bursitida de:Bursitis it:Borsite nl:Slijmbeursontsteking