Bone age
|
WikiDoc Resources for Bone age |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Bone age |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Bone age at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Bone age at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Bone age
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Bone age Risk calculators and risk factors for Bone age
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Bone age |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Bone age is a way of describing the degree of maturation of a child's bones. As a person grows from fetal life through childhood, puberty, and finishes growth as a young adult, the bones of the skeleton change in size and shape. These changes can be seen by x-ray. The "bone age" of a child is the average age at which children reach this stage of bone maturation. A child's current height and bone age can be used to predict adult height.
At birth, only the metaphyses of the "long bones" are present. The long bones are those that grow primarily by elongation at an epiphysis at one end of the growing bone. The long bones include the femurs, tibias, and fibulas of the lower limb, the humeri, radii, and ulnas of the upper limb (arm + forearm), and the phalanges of the fingers and toes. The long bones of the leg comprise nearly half of adult height. The other primary skeletal component of height is the spine and skull.
As a child grows the epiphyses become calcified and appear on the x-rays, as do the carpal and tarsal bones of the hands and feet, separated on the x-rays by a layer of invisible cartilage where most of the growth is occurring. As sex steroid levels rise during puberty, bone maturation accelerates. As growth nears conclusion and attainment of adult height, bones begin to approach the size and shape of adult bones. The remaining cartilaginous portions of the epiphyses become thinner. As these cartilaginous zones become obliterated, the epiphyses are said to be "closed" and no further lengthening of the bones will occur. A small amount of spinal growth concludes an adolescent's growth.
Pediatric endocrinologists are the physicians who most commonly order and interpret bone age x-rays and evaluate children for advanced or delayed growth and physical development.
Methods
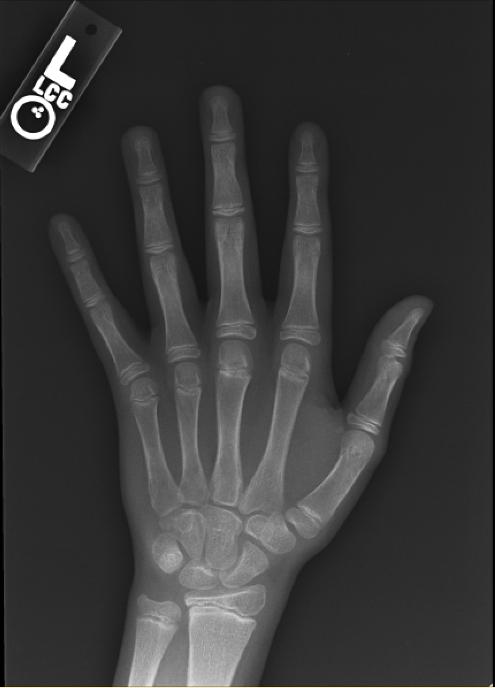
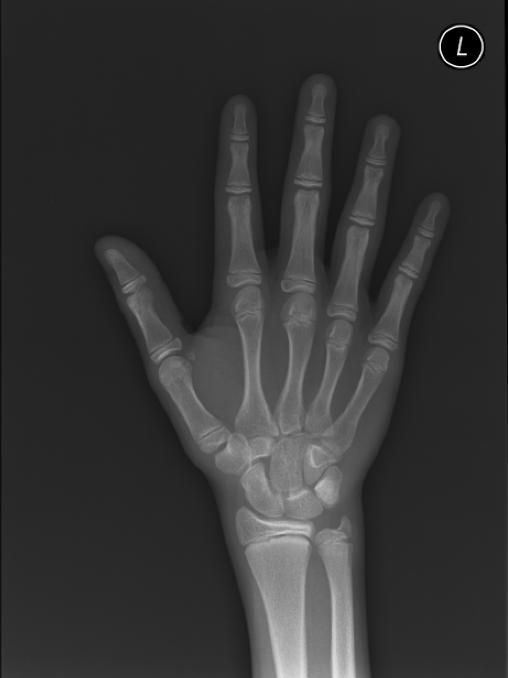
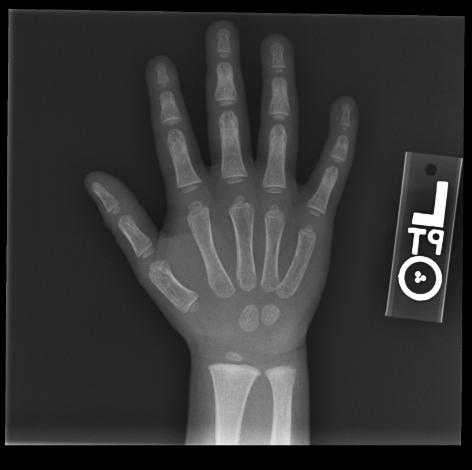
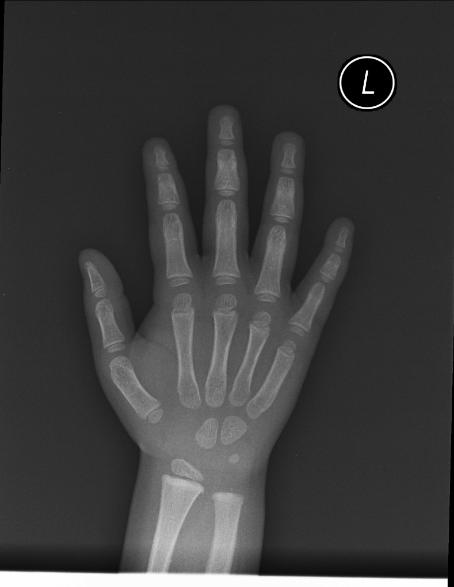
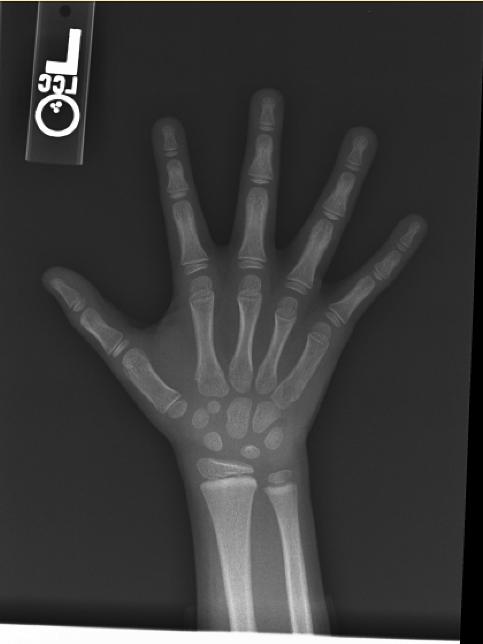
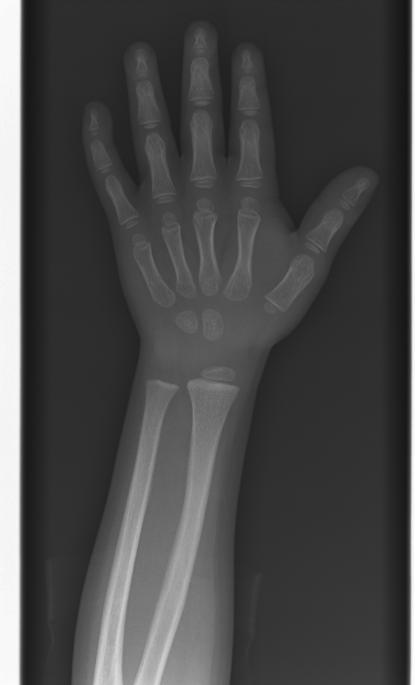
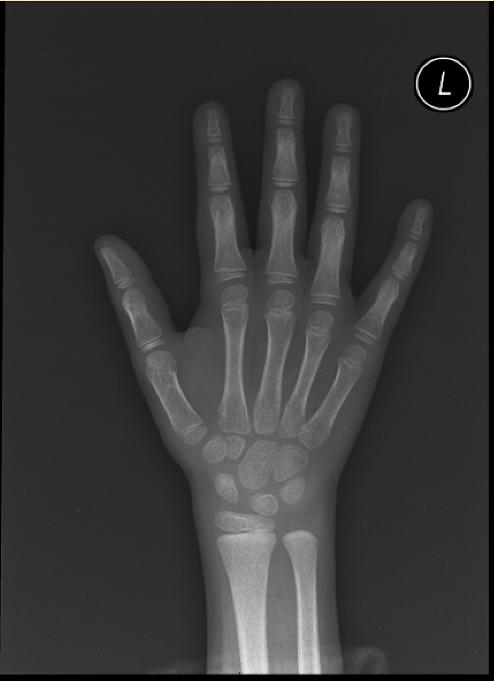
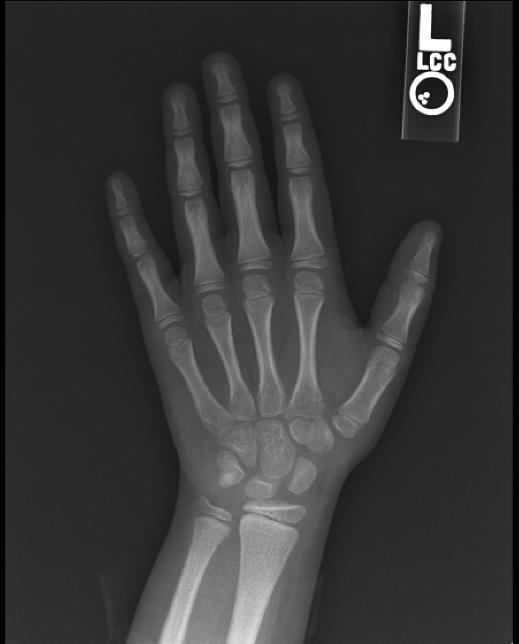
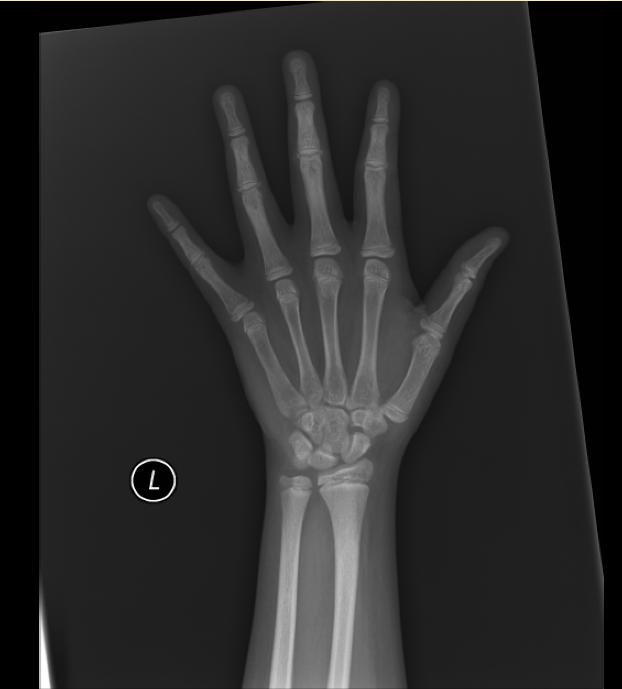
The most commonly used method is based on a single x-ray of the fingers, hand, and wrist. A hand is easily x-rayed with minimal radiation and shows many bones in a single view. The bones in the x-ray are compared to the bones of a standard atlas, usually Greulich and Pyle [1]
Male
-
4y 6m
-
11y 6m
-
13y
-
13y 6m
-
14y
Female
-
2y 6m
-
3yImage:
-
4y 2m
-
4y 6m
-
5y
-
6y 12m
-
8y 10m
-
11y
-
12y
A more complex method also based on hand x-rays is the "TW2" method [2] An atlas based on knee maturation has also been compiled.
The hands of infants do not change much in the first year of life and if precise bone age assessment is desired, an x-ray of approximately half of the skeleton (a "hemiskeleton" view) may be obtained to assess some of the areas such as shoulders and pelvis which change more in infancy.
Height prediction
Statistics have been compiled to indicate the percentage of height growth remaining at a given bone age. By simple arithmetic, a predicted adult height can be computed from a child's height and bone age. Separate tables are used for boys and girls because of the sex difference in timing of puberty, and slightly different percentages are used for children with unusually advanced or delayed bone maturation. These tables, the Bayley-Pinneau tables, are included as an appendix in the Greulich and Pyle atlas.
In a number of conditions involving atypical growth, bone age height predictions are less accurate. For example, in children born small for gestational age who remain short after birth, the bone age is a poor predictor of adult height.
Clinical application of bone age readings
An advanced or delayed bone age does not always indicate disease or "pathologic" growth. Conversely, the bone age may be normal in some conditions of abnormal growth. Children do not mature at exactly the same tempo. Just as there is wide variation among the normal population in age of losing teeth or experiencing the first menstrual period, the bone age of a healthy child may be a year or two advanced or delayed.
An advanced bone age is common when a child has had prolonged elevation of sex steroid levels, as in precocious puberty or congenital adrenal hyperplasia. The bone age is often marginally advanced with premature adrenarche, when a child is overweight from a young age or when a child has lipodystrophy. Bone age may be significantly advanced in genetic overgrowth syndromes, such as Sotos syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Marshall-Smith syndrome.
Bone maturation is delayed with the variation of normal development termed constitutional delay of growth and puberty, but delay also accompanies growth failure due to growth hormone deficiency and hypothyroidism.
See also
External links
- A fuller description of the use of bone age films from the University of Utrecht.
- Bone Age - Free MacOS X software to assist in radiographic assessment using G&P standards.
- Central Precocious Puberty support for families.
References
- ↑ Greulich WW, Pyle SI: Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist, 2nd edition. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 1959.
- ↑ Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH, Marshall WA, et al.: Assessment of Skeletal Maturity and Prediction of Adult Height (TW2 Method). New York: Academic Press, 1975.