Becker's muscular dystrophy: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
|||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
* [[Genetic testing]] | * [[Genetic testing]] | ||
*A muscle [[biopsy]] ([[immunohistochemistry]] or [[immunoblotting]]) or genetic test ([[blood test]]) confirms the [[diagnosis]]. | *A muscle [[biopsy]] ([[immunohistochemistry]] or [[immunoblotting]]) or genetic test ([[blood test]]) confirms the [[diagnosis]]. | ||
===AHA Scientific Statement: Management of Cardiac Involvement Associated With Neuromuscular Diseases=== | |||
====Cardiac Evaluation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)==== | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:80%" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGreen" |[[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class I]] | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''1.''' All DMD and BMD patients should have an initial cardiac evaluation with examination, ECG, and imaging performed at diagnosis. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |'''"2.''' Asymptomatic DMD/BMD patients with left ventricular dilation or dysfunction or arrhythmia (eg, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular ectopy) should be reevaluated at least annually. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |'''"3.''' Symptomatic DMD/BMD patients should be reevaluated more frequently than annually, with testing and frequency determined by the provider and clinical status. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |'''"4.''' Female DMD/BMD carriers should undergo cardiac evaluation by examination, ECG, and noninvasive imaging in the second to third decade of life, with follow-up evaluations every 3 to 5 years thereafter. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LightGreen" |'''"5.''' Echocardiography should be routinely used in the screening and follow-up care of DMD/ BMD patients. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LemonChiffon" | [[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Classification of Recommendations|Class IIa]] | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LemonChiffon" |<nowiki>"</nowiki>'''1.''' Every-2-year cardiac evaluation by examina- tion, ECG, and noninvasive imaging is rea- sonable in asymptomatic DMD/BMD patients <10 years of age, increasing to annual evalu- ation at 10 years of age. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LemonChiffon" |'''"2.''' It is reasonable to consider periodic use of advanced tissue imaging modalities (eg, CMR with contrast) in the care of DMD/BMD patients for assessment of cardiac function, particularly in patients with poor acoustic windows or for assessment of myocardial fibrosis. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LemonChiffon" |'''"3.''' Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitor- ing for patients with DMD/BMD is reasonable every 1 to 3 years, based on age, EF, and clinical assessment. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: C]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="LemonChiffon" |'''"4.''' In the absence of an implantable cardio- verter-de brillator (ICD) or other arrhythmia monitoring, at least annual ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring is reason- able for patents with DMD/BMD with EF <35% or age ≥17 years. ''([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme#Level of Evidence|Level of Evidence: B]])'' <nowiki>"</nowiki> | |||
|} | |||
==Treatment == | ==Treatment == | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 24 November 2017
For patient information, click here
| Becker's muscular dystrophy | |
| ICD-10 | G71.0 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 359.1 |
| DiseasesDB | 1280 |
| MedlinePlus | 000706 |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Becker's muscular dystrophy (also known as Benign pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy) is an X-linked recessive inherited disorder characterized by slowly progressive muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis.
It is a type of dystrophinopathy, which includes a spectrum of muscle diseases in which there is insufficient dystrophin produced in the muscle cells, resulting in instability in the structure of muscle cell membrane. This is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which encodes the protein dystrophin. Becker's muscular dystrophy is related to Duchenne muscular dystrophy in that both result from a mutation in the dystrophin gene, but in Duchenne muscular dystrophy no functional dystrophin is produced making DMD much more severe than BMD. Both Duchenne and Becker's muscular dystrophy have traditionally been called "X-linked" recessive diseases, but in view of modern molecular biology and identification of the dystrophin gene, it might be more appropriate to say they are X-chromosome recessive diseases.
Eponym
Becker's is named after the German doctor Peter Emil Becker. [1][2][3]
Genetics
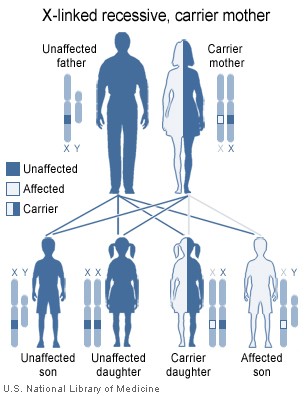
The disorder is inherited with an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. The gene is located on the X chromosome. Since women have two X chromosomes, if one X chromosome has the non-working gene, the second X chromosome will have a working copy of the gene to compensate. In these cases, some women have much milder symptoms because of this ability to compensate. For example, carrier females of mutations are at increased risk for dilated cardiomyopathy. Since men have an X and a Y chromosome and because they don't have another X to compensate for the defective gene, they will develop symptoms if they inherit the non-working gene.
All dystrophinopathes are inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. The risk to the siblings of an affected individual depends upon the carrier status of the mother. Carrier females have a 50% chance of passing the DMD mutation in each pregnancy. Sons who inherit the mutation will be affected; daughters who inherit the mutation will be carriers. Men who have Becker's muscular dystrophy can have children, and all their daughters are carriers, but none of the sons will inherit their father's mutation. Prenatal testing through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) for pregnancies at risk is possible if the DMD mutation is found in a family member or if informative linked markers have been identified.
Becker's muscular dystrophy occurs in approximately 3 to 6 in 100,000 male births. Symptoms usually appear in men at about ages 8-25, but may sometimes begin later. The average age of becoming unable to walk is 25-70. Women rarely develop symptoms.
Genetic counseling is indicated for individuals or families who may carry this condition.
Symptoms
- Muscle weakness, slowly progressive (Difficulty running, hopping, jumping; Progressive difficulty walking)
- Ability to walk may continue into adulthood (up to age 80)
- Frequent falls
- Difficulty breathing
- Non progressive cognitive dysfunction only in rare cases: not as common as in duchenne because the brain only needs small amounts of dystrophin
- Skeletal deformities, chest and back (scoliosis)
- Muscle deformities (contractions of heels, legs; Pseudohypertrophy of calf muscles)
- Fatigue
- Heart disease
People with this disorder typically experience progressive muscle weakness of the leg and pelvis muscles, which is associated with a loss of muscle mass (wasting). Muscle weakness also occurs in the arms, neck, and other areas, but not as noticeably severe as in the lower half of the body.
Calf muscles initially enlarge during the ages of 5-15 (an attempt by the body to compensate for loss of muscle strength), but the enlarged muscle tissue is eventually replaced by fat and connective tissue (pseudohypertrophy) as the legs become less used (use of wheelchair).
Muscle contractions occur in the legs and heels, causing inability to use the muscles because of shortening of muscle fibers and fibrosis of connective tissue. Bones may develop abnormally, causing skeletal deformities of the chest and other areas.
Cardiomyopathy (damage to the heart) does not occur as commonly with this disorder as it does with Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Cognitive problems may accompany the disorder, but they are not inevitable and do not worsen as the disorder progresses.
Signs and tests
The pattern of symptom development resembles that of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy, but with a later, and much slower rate of progression. Noticeable signs of Muscular Dystrophy also include the lack of pectroral and upper arm muscles, especially when the disease is unnoticed through the early teen years. Muscle wasting begins in the legs and pelvis (or core), then progresses to the muscles of the shoulders and neck, followed by loss of arm muscles and respiratory muscles. Calf muscle enlargement (pseudohypertrophy) is quite obvious. Cardiomyopathy may occur, but the development of congestive heart failure or arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) is rare.
- The ability to walk may continue to age 40 or older.
- Creatine kinase (CPK) levels may be elevated.
- An electromyography (EMG) shows that weakness is caused by destruction of muscle tissue rather than by damage to nerves.
- Genetic testing
- A muscle biopsy (immunohistochemistry or immunoblotting) or genetic test (blood test) confirms the diagnosis.
AHA Scientific Statement: Management of Cardiac Involvement Associated With Neuromuscular Diseases
Cardiac Evaluation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)
| Class I |
| "1. All DMD and BMD patients should have an initial cardiac evaluation with examination, ECG, and imaging performed at diagnosis. (Level of Evidence: B) " |
| "2. Asymptomatic DMD/BMD patients with left ventricular dilation or dysfunction or arrhythmia (eg, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular ectopy) should be reevaluated at least annually. (Level of Evidence: C) " |
| "3. Symptomatic DMD/BMD patients should be reevaluated more frequently than annually, with testing and frequency determined by the provider and clinical status. (Level of Evidence: C) " |
| "4. Female DMD/BMD carriers should undergo cardiac evaluation by examination, ECG, and noninvasive imaging in the second to third decade of life, with follow-up evaluations every 3 to 5 years thereafter. (Level of Evidence: C) " |
| "5. Echocardiography should be routinely used in the screening and follow-up care of DMD/ BMD patients. (Level of Evidence: B) " |
| Class IIa |
| "1. Every-2-year cardiac evaluation by examina- tion, ECG, and noninvasive imaging is rea- sonable in asymptomatic DMD/BMD patients <10 years of age, increasing to annual evalu- ation at 10 years of age. (Level of Evidence: B) " |
| "2. It is reasonable to consider periodic use of advanced tissue imaging modalities (eg, CMR with contrast) in the care of DMD/BMD patients for assessment of cardiac function, particularly in patients with poor acoustic windows or for assessment of myocardial fibrosis. (Level of Evidence: B) " |
| "3. Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitor- ing for patients with DMD/BMD is reasonable every 1 to 3 years, based on age, EF, and clinical assessment. (Level of Evidence: C) " |
| "4. In the absence of an implantable cardio- verter-de brillator (ICD) or other arrhythmia monitoring, at least annual ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring is reason- able for patents with DMD/BMD with EF <35% or age ≥17 years. (Level of Evidence: B) " |
Treatment
There is no known cure for Becker's muscular dystrophy. Treatment is aimed at control of symptoms to maximize the quality of life.
Activity is encouraged. Inactivity (such as bed rest) can worsen the muscle disease. Physical therapy may be helpful to maintain muscle strength. Orthopedic appliances such as braces and wheelchairs may improve mobility and self-care.
Genetic counseling may be advisable. Sons of a man with Becker's muscular dystrophy do not develop the disorder, but daughters will be carriers. The daughters' sons may develop the disorder.
Immunosuppressant steroids like Prednisone have been known to help slow the progression of Becker Muscular Dystrophy. The drug contributes to an increased production of the protein Utrophin which closely resembles Dystrophin, the protein that is defective in BMD.
MY0-029
MYO-029 is an experimental myostatin inhibiting drug developed by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of muscular dystrophy. Myostatin is a protein that inhibits the growth of muscle tissue, MYO-029 is a recombinant human antibody designed to bind and inhibit the activity of myostatin.
A 2005/2006 study, which included participants afflicted with Becker's, was completed by Wyeth in Collegeville, PA.
Prognosis
Becker's muscular dystrophy results in slowly progressive disability. Death can occur in the fifth decade but some patients live to an advanced age of 68 or later.
Complications
- Deformities
- Permanent, progressive disability manifested as decreased mobility or decreased ability to care for self
- Mental impairment
- Cardiomyopathy
- Pneumonia or other respiratory infections
- Respiratory failure
Quality of Life
The quality of life for patients with Becker's muscular dystrophy need not be impacted by the symptoms of the disorder. With assistive devices, independence can be maintained indefinitely. People affected by Becker's muscular dystrophy can still drive, work, own businesses, and maintain active lifestyles. Those affected by the disorder can also still participate in sports for the disabled, such as wheelchair tennis or Power Soccer.
References
- ↑ Template:WhoNamedIt
- ↑ P. E. Becker, F. Kiener. Eine neue x-chromosomale Muskeldystrophie. Archiv für Psychiatrie und Nervenkrankheiten, Berlin, 1955, 193: 427-448.
- ↑ P. E. Becker. Neue Ergebnisse der Genetik der Muskeldystrophien. Acta genetica et statistica medica, 1957, 7: 303-310.
Template:Muscular Dystrophy it:Distrofia muscolare di Becker nl:Becker spierdystrofie no:Beckers muskeldystrofi fi:Beckerin lihasdystrofia