Avatrombopag: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 302: | Line 302: | ||
|PK=(Description) | |PK=(Description) | ||
|nonClinToxic=(Description) | |nonClinToxic=(Description) | ||
|clinicalStudies= | |clinicalStudies=*The efficacy of DOPTELET for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure was established in 2 identically-designed multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (ADAPT-1 (NCT01972529) and ADAPT-2 (NCT01976104)). In each study, patients were assigned to the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (˂40 x109L) or the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (≥40 to ˂50 x109 L) based on their platelet count at Baseline. Patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either DOPTELET or placebo. Patients were stratified according to hepatocellular cancer (HCC) status and risk of bleeding associated with the elective procedure (low, moderate, or high). Patients undergoing neurosurgical interventions, thoracotomy, laparotomy or organ resection were not eligible for enrollment. | ||
( | *Patients in the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 60 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days, and patients in the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 40 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days. Eligible patients were scheduled to undergo their procedure (low, moderate, or high bleeding risk) 5 to 8 days after their last dose of treatment. Patient populations were similar between the pooled Low and High Baseline Platelet Count Cohorts and consisted of 66% male and 35% female; median age 58 years and 61% White, 34% Asian, and 3% Black. | ||
*In ADAPT-1, a total of 231 patients were randomized, 149 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 82 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated group was 31.1 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 30.7 x109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 44.9 x109/L. | |||
*In ADAPT-2, a total of 204 patients were randomized, 128 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 76 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated group was 32.7 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 32.5 x109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 44.5 x109/L. | |||
*Across both baseline platelet count cohorts and the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups, patients underwent a broad spectrum of types of scheduled procedures that ranged from low to high bleeding risk. Overall, the majority of patients (60.8% [248/430] subjects) in all treatment groups underwent low bleeding risk procedures, 17.2% [70/430] of patients underwent procedures associated with moderate bleeding risk, and 22.1% [90/430] of subjects underwent procedures associated with high bleeding risk. The proportions of patients undergoing low, moderate, and high-risk procedures were similar between the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups. | |||
*The major efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following an elective procedure. Additional secondary efficacy outcomes were the proportion of patients who achieved platelet counts of >50 x109/L on the day of procedure and the change in platelet count from baseline to procedure day. | |||
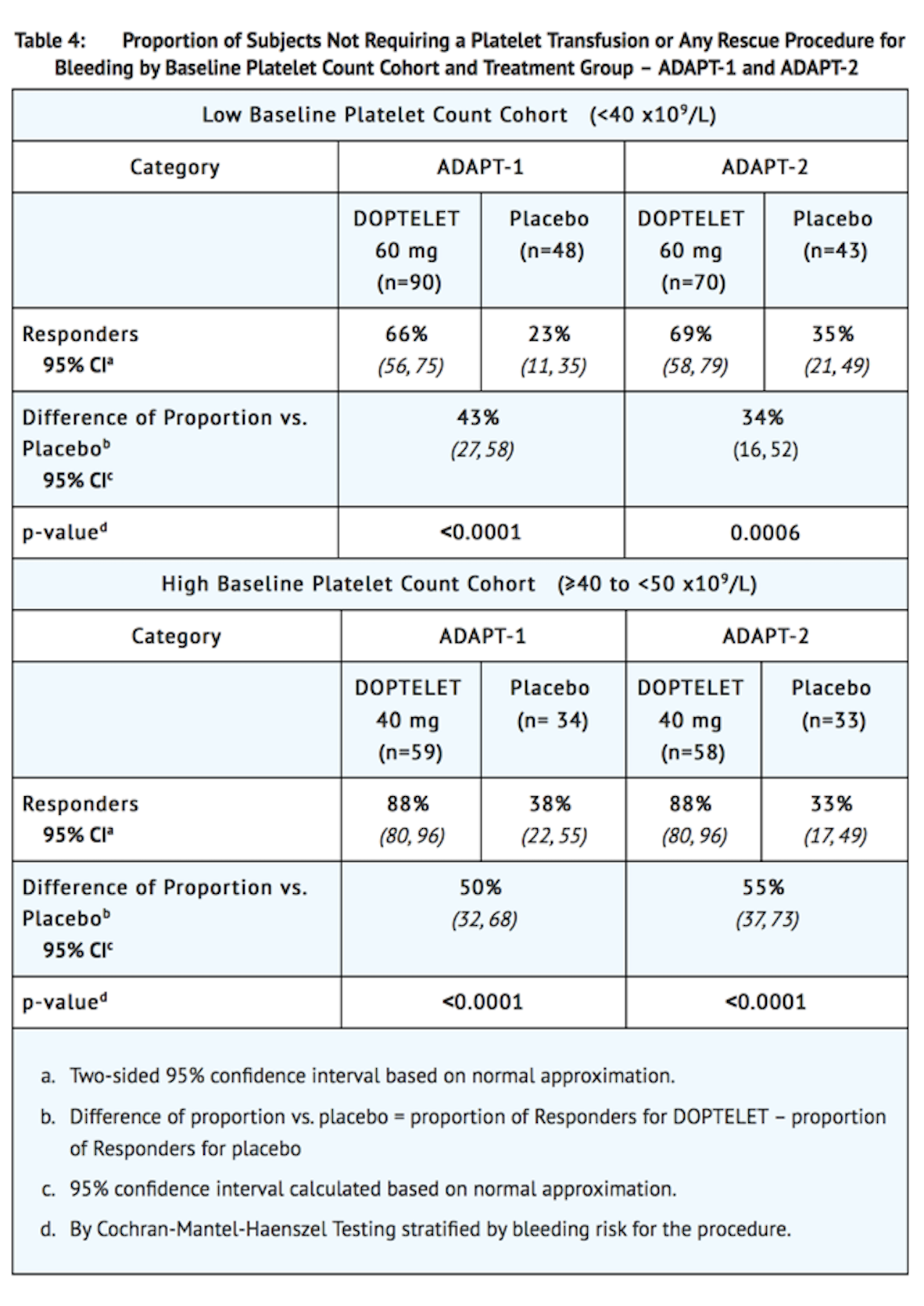
*Responders were defined as patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following a scheduled procedure. The following were considered rescue therapies to manage risk of bleeding associated with a procedure: whole blood transfusion, packed red blood cell (RBC) transfusion, platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or cryoprecipitate administration, Vitamin K, desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid, or surgical or interventional radiology procedures performed to achieve hemostasis and control blood loss. In both baseline platelet count cohorts, patients in the DOPTELET treatment groups had a greater proportion of responders than the corresponding placebo treatment groups that was both clinically meaningful and statistically significant as detailed in Table 4. | |||
[[image:Avatrombopag_Clinical_Studies_Table.png|none|thumb|400px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | |||
*In addition, both trials demonstrated a higher proportion of patients who achieved the target platelet count of ≥ 50 x109/L on the day of the procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 69% vs 4%, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 67% vs 7%, respectively; P <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort- ADAPT-1: 88% vs 21%, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 93% vs 39%, respectively; P <0.0001). | |||
*Further, both trials demonstrated a greater mean change in platelet counts from baseline to the day of the procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 32 x109/L vs 0.8 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 31.3 x109/L vs 3.0 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 37.1 x109/L vs 1.0 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001;ADAPT-2: 44.9 x109/L vs 5.9 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001). | |||
*A measured increase in platelet counts was observed in both DOPTELET treatment groups over time beginning on Day 4 post-dose, that peaked on Day 10-13, decreased 7 days post-procedure, and then returned to near baseline values by Day 35. | |||
|howSupplied=*DOPTELET 20 mg tablets are supplied as round, biconvex, yellow, film-coated tablets, and debossed with “AVA” on one side and “20” on the other side. | |howSupplied=*DOPTELET 20 mg tablets are supplied as round, biconvex, yellow, film-coated tablets, and debossed with “AVA” on one side and “20” on the other side. | ||
Revision as of 02:24, 27 June 2018
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
Warning Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Condition Name: (Content)
|
Overview
Avatrombopag is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Warnings
|
Warning Title
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
Condition Name: (Content)
|
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Avatrombopag in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)g
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Avatrombopag and IV administrations.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Avatrombopag
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
(Description)
Structure
(Description with picture)
Pharmacodynamics
(Description)
Pharmacokinetics
(Description)
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
- The efficacy of DOPTELET for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure was established in 2 identically-designed multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (ADAPT-1 (NCT01972529) and ADAPT-2 (NCT01976104)). In each study, patients were assigned to the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (˂40 x109L) or the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (≥40 to ˂50 x109 L) based on their platelet count at Baseline. Patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either DOPTELET or placebo. Patients were stratified according to hepatocellular cancer (HCC) status and risk of bleeding associated with the elective procedure (low, moderate, or high). Patients undergoing neurosurgical interventions, thoracotomy, laparotomy or organ resection were not eligible for enrollment.
- Patients in the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 60 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days, and patients in the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 40 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days. Eligible patients were scheduled to undergo their procedure (low, moderate, or high bleeding risk) 5 to 8 days after their last dose of treatment. Patient populations were similar between the pooled Low and High Baseline Platelet Count Cohorts and consisted of 66% male and 35% female; median age 58 years and 61% White, 34% Asian, and 3% Black.
- In ADAPT-1, a total of 231 patients were randomized, 149 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 82 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated group was 31.1 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 30.7 x109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 44.9 x109/L.
- In ADAPT-2, a total of 204 patients were randomized, 128 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 76 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated group was 32.7 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 32.5 x109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean Baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3 x109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 44.5 x109/L.
- Across both baseline platelet count cohorts and the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups, patients underwent a broad spectrum of types of scheduled procedures that ranged from low to high bleeding risk. Overall, the majority of patients (60.8% [248/430] subjects) in all treatment groups underwent low bleeding risk procedures, 17.2% [70/430] of patients underwent procedures associated with moderate bleeding risk, and 22.1% [90/430] of subjects underwent procedures associated with high bleeding risk. The proportions of patients undergoing low, moderate, and high-risk procedures were similar between the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups.
- The major efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following an elective procedure. Additional secondary efficacy outcomes were the proportion of patients who achieved platelet counts of >50 x109/L on the day of procedure and the change in platelet count from baseline to procedure day.
- Responders were defined as patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following a scheduled procedure. The following were considered rescue therapies to manage risk of bleeding associated with a procedure: whole blood transfusion, packed red blood cell (RBC) transfusion, platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or cryoprecipitate administration, Vitamin K, desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid, or surgical or interventional radiology procedures performed to achieve hemostasis and control blood loss. In both baseline platelet count cohorts, patients in the DOPTELET treatment groups had a greater proportion of responders than the corresponding placebo treatment groups that was both clinically meaningful and statistically significant as detailed in Table 4.
- In addition, both trials demonstrated a higher proportion of patients who achieved the target platelet count of ≥ 50 x109/L on the day of the procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 69% vs 4%, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 67% vs 7%, respectively; P <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort- ADAPT-1: 88% vs 21%, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 93% vs 39%, respectively; P <0.0001).
- Further, both trials demonstrated a greater mean change in platelet counts from baseline to the day of the procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 32 x109/L vs 0.8 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 31.3 x109/L vs 3.0 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort-ADAPT-1: 37.1 x109/L vs 1.0 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001;ADAPT-2: 44.9 x109/L vs 5.9 x109/L, respectively; P <0.0001).
- A measured increase in platelet counts was observed in both DOPTELET treatment groups over time beginning on Day 4 post-dose, that peaked on Day 10-13, decreased 7 days post-procedure, and then returned to near baseline values by Day 35.
How Supplied
- DOPTELET 20 mg tablets are supplied as round, biconvex, yellow, film-coated tablets, and debossed with “AVA” on one side and “20” on the other side.
- NDC 71369-020-10: carton with one blister card of ten 20 mg tablets.
- NDC 71369-020-11: one blister card with ten 20 mg tablets.
- NDC 71369-020-15: carton with one blister card of fifteen 20 mg tablets.
- NDC 71369-020-16: one blister card of fifteen 20 mg tablets.
Storage
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store tablets in original package.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Avatrombopag |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

{{#ask: Label Page::Avatrombopag |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Risks
Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
- DOPTELET is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist and TPO receptor agonists have been associated with thrombotic and thromboembolic complications in patients with chronic liver disease. Portal vein thrombosis has been reported in patients with chronic liver disease treated with TPO receptor agonists.
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their prescriber of a known or suspected pregnancy.
Lactation
- Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with DOPTELET and for at least 2 weeks after the final dose.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Avatrombopag interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Doptelet
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Avatrombopag Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.