Aortic intramural hematoma
| Aortic intramural hematoma | |
 | |
|---|---|
| [1] |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Synonyms and keywords:: IMH
Overview
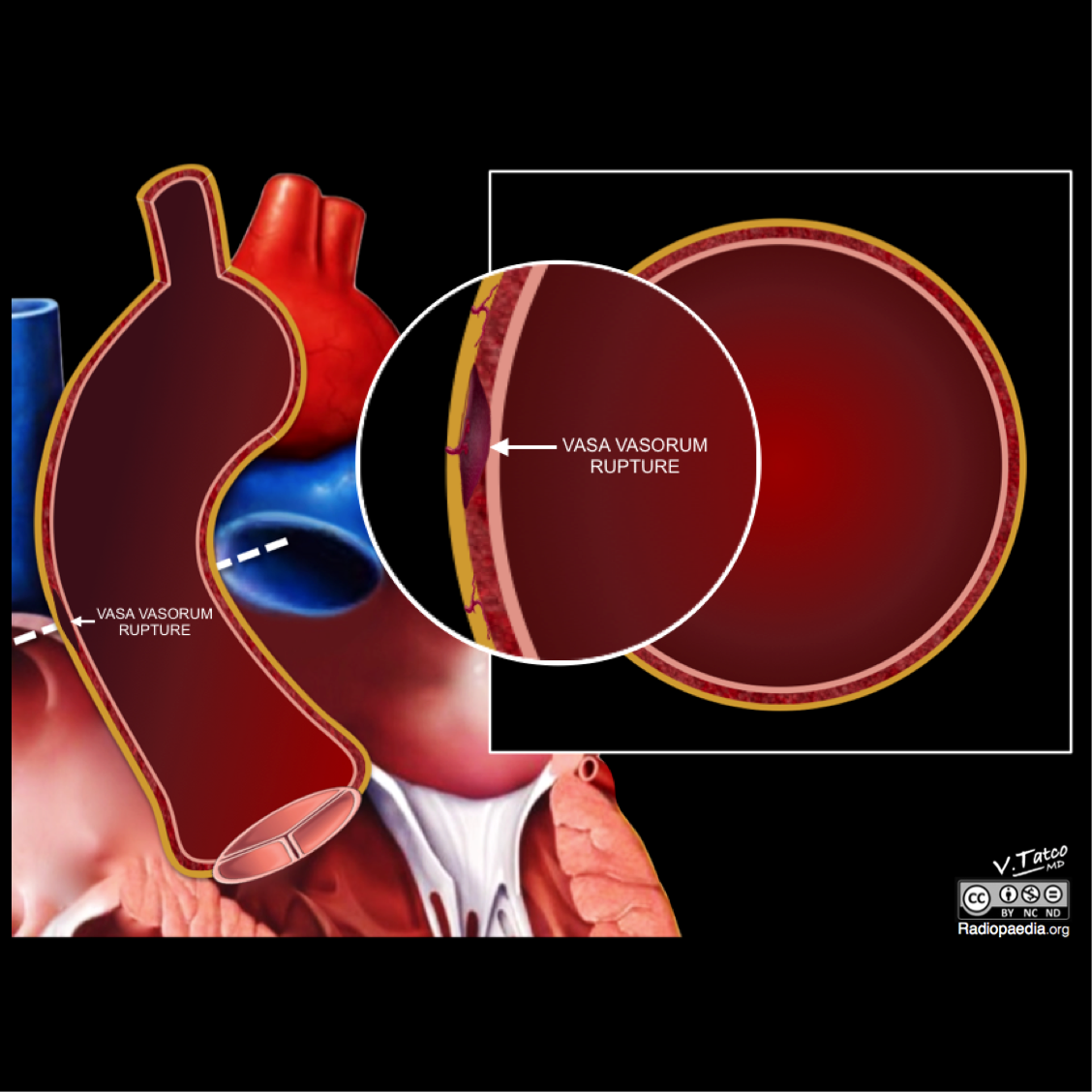
Aortic intramural hematoma is classically abbreviated as IMH. It may occur as a primary event in hypertensive patients in whom there is spontaneous bleeding from vasa vasorum into the media or may be caused by a penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer. Intramural hematoma may also develop as a result of blunt chest trauma with aortic wall injury. Thought to begin with the rupture of the vasa vasorum, the blood vessels that penetrate the outer half of the aortic media from the adventitia and arborize within the media to supply the aortic wall. The hematoma propagates along with the medial layer of the aorta. Consequently, intramural hematoma weakens the aorta and may progress either to outward rupture of the aortic wall or to inward disruption of the intima, the latter leading to communicating aortic dissection. Unlike aortic dissection, no intimal flap is present. If it involves the ascending aorta, treatment is surgical to prevent rupture or progression to a classic aortic dissection. Conservative management is indicated for aortic intramural hematomas of the descending aorta.
Historical Perspective
- The diagnosis of aortic intramural hematoma dates back to early 1980s when the choice of diagnosis was transesophageal echocardiography.[2]
Classification
IMH is classified into two types on the basis of Standford classification.[3]
- Type A IMH: Involves the ascending aorta, and may or may not involve descending aorta
- Type B IMH: Involves the descending aorta only distal to left subclavian artery
Pathophysiology
- The pathogenesis of IMH is characterized by either rupture of vasa vasorum or tear in the intimal layer.
- Rupture of vasa vasorum is seen in the majority of cases, which separates medial wall of the aorta leading to a tear but there is no continuous flow. The hematoma is contained within the wall.[4]
- Small microscopic tear in the penetrating aortic ulcer is another mechanism leading to formation of IMH. These ulcers are mostly associated with atherosclerotic changes of the aortic wall as well.[4]
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, hematoma is seen in the media layer of the aorta.
Clinical Features
- Pain is the most common presentation of patients with IMH. The location of pain depends on the location of IMH.
- Chest pain is the most common presenting symptoms in 82.5 % of the patients, followed by back pain (41%), and abdominal pain (13.1%).[4]
- Pain is reportedly severe on onset in almost all the cases, abrupt in onset.
- Radiation of pain is seen 45.9% of patients commonly radiating to the back and shoulders.
- Up to 32% of these patients can present with hypertension, whereas a minority (11.9%) present with hypotension.
- Patient with Type A IMH can present with murmur of aortic regurgitation (35.2%) and pulse deficit is seen in a minority(15.1%) of the patients.
Differentiating Aortic Intramural Hematoma from other Diseases
- IMH must be differentiated from other diseases that cause sudden onset chest pain, back pain, abdominal pain with or without radiation such as aortic dissection, acute coronary syndrome, pulmonary embolism, renal infarct, meseneteric ischemia, and trauma to the back.
Epidemiology and Demographics
- The prevalence of IMH is approximately 2 to 4 cases per 100,000 individuals worldwide.[5]
- IMH is more commonly observed among patients age in the range of 60-80 years old.
- Mean age for presentation is 69 years.[6]
- IMH is more common in men with 50-81% of cases occurring commonly in men.[6]
- There is no racial predilection for IMH.[6]
Risk Factors
- Common risk factors in the development of IMH are hypertension, smoking, connective tissue disorder (Marfan's syndrome, Loeys-Dietz syndrome), bicuspid aortic valve, prior aortic surgery, aortic aneurysm and atherosclerosis.[7]
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- IMH resolve spontaneously in about 10% of patients.[8]
- Early clinical features include sudden onset chest pain, back pain and hypertensive emergency.
- If left untreated, 16-47% of patients with IMH may progress to develop aortic dissection which can be life threatening.[9]
- Common complications of IMH include progression to aortic dissection, formation of periaortic hematoma, pericardial effusion, pericardial tamponade, pseudoaneurysm, and aortic regurgitation.[10]
- Prognosis is generally poor, and depends on multitude of factors like location of IMH, presentation, mode of management (medical vs surgical).
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria
- The diagnosis of IMH is made with clinical examination in combination of radiological or echocardiographic findings. Although, there is no specific diagnostic criteria set for IMH. A study has suggested mean thickness of Type A IMH was in the range of 5-40 mm, and type B IMH was reported in the range of 5-23 mm.[11]
History and Symptoms
- Symptoms of IMH may include sudden onset chest pain, back pain, radiation of pain from chest to back, abdominal pain, and sweating.[11]
Physical Examination
- Patients with IMH usually appear distressed and it depends on the stage of their presentation.[11]
- Physical examination may be remarkable for sweating, tachycardia, hypertension, aortic regurgitation murmur, and radial-radial pulse deficit or radial-femoral pulse deficit depending on the location of the IMH.
Laboratory Findings
- There are no specific laboratory findings associated with IMH.
- Occasionally, a drop in hemoglobin or hematocrit can be seen in patients where IMH is progressing to aortic dissection.
 |
 |
Imaging Findings
- Transthoracic echocardiography, transesophageal echocardiography, CT angiography, MR angiography are the modality of imaging which can be used.[11]
- MR angiography is the imaging modality of choice for IMH. However, as it requires 25-35 minutes; thus in an emergency situation CT angiography or echocardiogram is the test of choice in the emergency situation.
- When CT or echocardiorgraphy is equivocal, MR should be the next step.
- On echocardiography, an echolucent crescent can be seen in the aorta. This is seen in 70-80% of the patients. M-mode echocardiography is more useful in the diagnosis of IMH.
- CT shows attenuation by the aortic wall and intimal flap can be seen. Crescentic aortic wall thickening can be seen as well.
- MR is superior to CT to CT and echocardiography for diagnosis of IMH.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- The mainstay of therapy for IMH is control of hypertension as the hypertensive emergency. In patients with IMH, the target blood pressure should be lower than 130/80 mm of Hg. Labetalol IV or infusion can be a treatment of choice as it controls blood pressure as well as heart rate. Drugs causing reflex tachycardia should be avoided.[14][15]
- Heart rate should be controlled prior to initiating blood pressure medications.
- Anti-hypertensive medication acts by decreasing the stress in the media thereby preventing the extension of IMH.
- Response to anti-hypertensive can be monitored with a change in blood pressure and heart rate every 30 minutes.
- When patients are clinically stable, they can be closely monitored without proceeding to surgery.
Surgery
- Surgery is preferred options in patients who are at high risk to proceed to aortic dissection.[14]
- Surgical option depends on the location of IMH. Replacement of aortic root is advised for type A IMH whereas minimal invasive surgery can be performed.[15]
Prevention
- There are no primary preventive measures available for IMH.
- Once diagnosed and successfully treated, patients with IMH who are medically managed are followed-up every 3-6 months by imaging.
Guideline
2014 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases (DO NOT EDIT)[16]
| Recommendations | Class | Level |
|---|---|---|
|
I | C |
| I | C | |
|
I | C |
| I | C | |
|
IIa | C |
|
IIb | C |
Abbreviations: CT = computed tomography; IMH = intramural haematoma; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; TEVAR = thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
See also
External Links
References
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Vincent Tatco, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 48454
- ↑ Vilacosta I, San Román JA, Ferreirós J, Aragoncillo P, Méndez R, Castillo JA; et al. (1997). "Natural history and serial morphology of aortic intramural hematoma: a novel variant of aortic dissection". Am Heart J. 134 (3): 495–507. PMID 9327708.
- ↑ Lempel JK, Frazier AA, Jeudy J, Kligerman SJ, Schultz R, Ninalowo HA; et al. (2014). "Aortic arch dissection: a controversy of classification". Radiology. 271 (3): 848–55. doi:10.1148/radiol.14131457. PMID 24617732.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Alomari IB, Hamirani YS, Madera G, Tabe C, Akhtar N, Raizada V (2014). "Aortic intramural hematoma and its complications". Circulation. 129 (6): 711–6. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001809. PMID 24515957.
- ↑ Larson EW, Edwards WD (1984). "Risk factors for aortic dissection: a necropsy study of 161 cases". Am J Cardiol. 53 (6): 849–55. PMID 6702637.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Mussa FF, Horton JD, Moridzadeh R, Nicholson J, Trimarchi S, Eagle KA (2016). "Acute Aortic Dissection and Intramural Hematoma: A Systematic Review". JAMA. 316 (7): 754–63. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10026. PMID 27533160.
- ↑ Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, Russman PL; et al. (2000). "The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease". JAMA. 283 (7): 897–903. PMID 10685714.
- ↑ Braverman AC (2010). "Acute aortic dissection: clinician update". Circulation. 122 (2): 184–8. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958975. PMID 20625143.
- ↑ Nienaber CA, Sievers HH (2002). "Intramural hematoma in acute aortic syndrome: more than one variant of dissection?". Circulation. 106 (3): 284–5. PMID 12119238.
- ↑ Ganaha F, Miller DC, Sugimoto K, Do YS, Minamiguchi H, Saito H; et al. (2002). "Prognosis of aortic intramural hematoma with and without penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer: a clinical and radiological analysis". Circulation. 106 (3): 342–8. PMID 12119251.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Song JK (2004). "Diagnosis of aortic intramural haematoma". Heart. 90 (4): 368–71. PMC 1768152. PMID 15020502.
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Sachintha Hapugoda, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50557
- ↑ Case courtesy of Dr Sachintha Hapugoda, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 50557
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Dake MD (2004). "Aortic intramural haematoma: current therapeutic strategy". Heart. 90 (4): 375–8. PMC 1768168. PMID 15020506.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Saborio DV, Sadeghi A, Burack JH, Lowery RC, Genovesi MH, Brevetti GR (2003). "Management of intramural hematoma of the ascending aorta and aortic arch: the risks of limited surgery". Tex Heart Inst J. 30 (4): 325–7. PMC 307723. PMID 14677748.
- ↑ Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E, Bartolomeo RD, Eggebrecht H, Evangelista A, Falk V, Frank H, Gaemperli O, Grabenwöger M, Haverich A, Iung B, Manolis AJ, Meijboom F, Nienaber CA, Roffi M, Rousseau H, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Allmen RS, Vrints CJ (November 2014). "2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)". Eur. Heart J. 35 (41): 2873–926. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281. PMID 25173340.