Aortic dissection classification
|
Aortic dissection Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Special Scenarios |
|
Case Studies |
|
|
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
Several different classification systems have been used to describe aortic dissections. The systems commonly in use are either based on either the anatomy of the dissection (proximal, distal) or the duration of onset of symptoms (acute, chronic) prior to presentation.
Classification
Aortic dissection can be classified into four types. DeBakey and Daily (Stanford) systems are the commonly used systems to classify aortic dissection.[1][2][3][4]
DeBakey Classification System
The DeBakey system is an anatomical description of the aortic dissection. It categorizes the dissection based on where the original intimal tear is located and the extent of the dissection (localized to either the ascending aorta or descending aorta, or involves both the ascending and descending aorta.[5]
- Type I - Originates in ascending aorta, propagates at least to the aortic arch and often beyond it distally.
- Type II – Originates in and is confined to the ascending aorta.
- Type III – Originates in descending aorta, rarely extends proximally.
- Type III A: Restricted till the descending thoracic aorta
- Type III B: Dissection extending below the diaphragm
Chronic dissection is almost twice as common in patients with type III (45%) when compared with type I (24%) and type II dissection (27%).

|

|

| |
| Percentage | 60 % | 10-15 % | 25-30 % |
| Type | DeBakey I | DeBakey II | DeBakey III |
| Stanford A | Stanford B | ||
| Proximal | Distal | ||
| Classification of aortic dissection | |||
Stanford Classification System
Divided into 2 groups; A and B depending on whether the ascending aorta is involved.[6]
- A = Type I and II DeBakey
- B = Type III Debakey
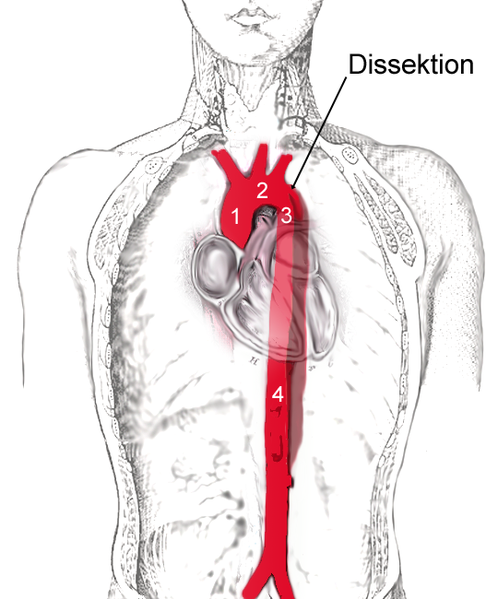
Classification based on the Proximity
- Proximal: Ascending aortic involvement
- Distal: Descending aortic involvement distal to left subclavian artery
Classification by the Time of Onset
- Acute: Onset within 2 weeks of onset of pain
- Subacute: Onset within 2-6 weeks of onset of pain
- Chronic: Onset within 6 weeks of pain.
References
- ↑ Nienaber, CA.; Eagle, KA. (2003). "Aortic dissection: new frontiers in diagnosis and management: Part I: from etiology to diagnostic strategies". Circulation. 108 (5): 628–35. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000087009.16755.E4. PMID 12900496. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Tsai, TT.; Nienaber, CA.; Eagle, KA. (2005). "Acute aortic syndromes". Circulation. 112 (24): 3802–13. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.534198. PMID 16344407. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ DEBAKEY, ME.; HENLY, WS.; COOLEY, DA.; MORRIS, GC.; CRAWFORD, ES.; BEALL, AC. (1965). "SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 49: 130–49. PMID 14261867. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Daily, PO.; Trueblood, HW.; Stinson, EB.; Wuerflein, RD.; Shumway, NE. (1970). "Management of acute aortic dissections". Ann Thorac Surg. 10 (3): 237–47. PMID 5458238. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ DeBakey ME, Henly WS, Cooley DA, Morris GC Jr, Crawford ES, Beall AC Jr. Surgical management of dissecting aneurysms of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1965;49:130-49. PMID 14261867.
- ↑ Daily PO, Trueblood HW, Stinson EB, Wuerflein RD, Shumway NE. Management of acute aortic dissections. Ann Thorac Surg 1970;10:237-47. PMID 5458238.