Aortic arch anomalies pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{WikiDoc Cardiology Network Infobox}} +, -<references /> +{{reflist|2}}, -{{reflist}} +{{reflist|2}})) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Aortic arch anomalies}} | {{Aortic arch anomalies}} | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
'''Assistant Editor-In-Chief:''' [[Kristin Feeney|Kristin Feeney, B.S.]] [[mailto:kfeeney@perfuse.org]] | '''Assistant Editor-In-Chief:''' [[Kristin Feeney|Kristin Feeney, B.S.]] [[mailto:kfeeney@perfuse.org]] | ||
== Pathophysiology | ==Overview== | ||
== Pathophysiology== | |||
Vascular rings encircle the trachea and esophagus, which results in variable degrees of compression of both structures. Compression of the trachea causes upper airway obstruction that impairs airflow. The extent of airway compression is variable. Double aortic arch is more often associated airway compression and is also associated with more severe airway compression than other forms of vascular ring. | Vascular rings encircle the trachea and esophagus, which results in variable degrees of compression of both structures. Compression of the trachea causes upper airway obstruction that impairs airflow. The extent of airway compression is variable. Double aortic arch is more often associated airway compression and is also associated with more severe airway compression than other forms of vascular ring. | ||
===Gross Pathology== | |||
<gallery> | |||
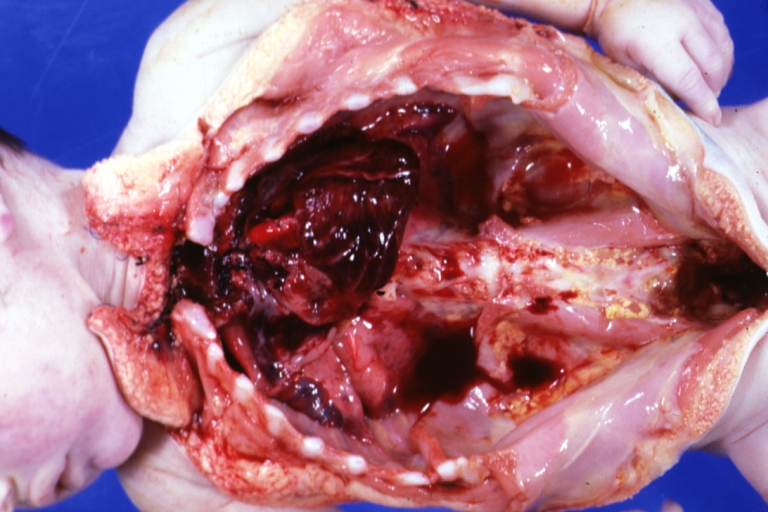
Image:Interrupted aortic arch.png| Hemorrhagic Necrosis; Massive, Postoperative: Gross; natural color, heart, in situ, a 2 day old infant, operative death, interrupted aortic arch and [[VSD]] ([http://www.peir.net Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology]) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 24 September 2012
|
Aortic arch anomalies Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Aortic arch anomalies pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Aortic arch anomalies pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Aortic arch anomalies pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2] Keri Shafer, M.D. [3] Priyamvada Singh, MBBS [[4]]
Assistant Editor-In-Chief: Kristin Feeney, B.S. [[5]]
Overview
Pathophysiology
Vascular rings encircle the trachea and esophagus, which results in variable degrees of compression of both structures. Compression of the trachea causes upper airway obstruction that impairs airflow. The extent of airway compression is variable. Double aortic arch is more often associated airway compression and is also associated with more severe airway compression than other forms of vascular ring.
=Gross Pathology
-
Hemorrhagic Necrosis; Massive, Postoperative: Gross; natural color, heart, in situ, a 2 day old infant, operative death, interrupted aortic arch and VSD (Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology)