Adrenocortical carcinoma MRI: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (23 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Adrenocortical carcinoma}} | {{Adrenocortical carcinoma}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{AAM}} {{MAD}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[MRI]] scans are helpful in differentiating between [[adrenal adenoma]], [[carcinoma]], and [[Metastasis|metastatic]] lesions. Due to the multi-planar capability of [[MRI]], direct [[invasion]] of adjacent [[organs]] may be better shown. [[Inferior vena cava]] [[invasion]] has been reported in 9% to 19% of cases at presentation. | |||
* Adrenal | ==MRI Findings in adrenocortical carcinoma== | ||
* | * Adrenocortical carcinomas are usually large and appear as [[heterogeneous]] masses on both T1- and T2-weighted images owing to the presence of internal [[hemorrhage]] and [[necrosis]].<ref name="pmid21606258">{{cite journal| author=Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB et al.| title=Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI. | journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol | year= 2011 | volume= 196 | issue= 6 | pages= W706-14 | pmid=21606258 | doi=10.2214/AJR.10.5540 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21606258 }}</ref> | ||
* Adrenocortical carcinoma may contain foci of intra-[[cytoplasmic]] [[lipid]], which results in a loss of signal intensity on out-of-phase images.<ref name="pmid12478091">{{cite journal| author=Ng L, Libertino JM| title=Adrenocortical carcinoma: diagnosis, evaluation and treatment. | journal=J Urol | year= 2003 | volume= 169 | issue= 1 | pages= 5-11 | pmid=12478091 | doi=10.1097/01.ju.0000030148.59051.35 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12478091 }}</ref> | |||
* Large [[Adrenal gland|adrenal]] [[carcinomas]] tend to invade the [[Adrenal gland|adrenal]] [[vein]] and [[inferior vena cava]].<ref name="pmid21606258" /> | |||
* On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], ACCs appear iso-intense to hypo-intense relative to [[liver]] parenchyma on T1-weighted images and hyper-intense relative to [[liver]] [[parenchyma]] on T2-weighted images.<ref name="pmid216062582">{{cite journal| author=Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB et al.| title=Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI. | journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol | year= 2011 | volume= 196 | issue= 6 | pages= W706-14 | pmid=21606258 | doi=10.2214/AJR.10.5540 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21606258 }}</ref> | |||
* On [[Chemical shift|chemical-shift]] [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], the presence of [[intracellular]] [[lipid]] can cause regions of signal loss on out-of-phase images relative to in-phase images.<ref name="pmid216062583">{{cite journal| author=Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB et al.| title=Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI. | journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol | year= 2011 | volume= 196 | issue= 6 | pages= W706-14 | pmid=21606258 | doi=10.2214/AJR.10.5540 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21606258 }}</ref> | |||
* [[Inferior vena cava]] invasion has been reported in 9% to 19% of cases at presentation. | |||
* Due to the multi-planar capability of [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], [[Invasion|direct invasion]] of adjacent [[organs]] may be better shown. | |||
==MRI Examples of adrenocortical carcinoma== | |||
[[File:MRI SHOWING ACC.gif|300px|left|thumb| MRI abdomen shows ACC, source: Case courtesy of Dr Roberto Schubert, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 13777 mri]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 001.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 002.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 003.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 004.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 005.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 006.jpg | |||
Image: | |||
Adrenal cortical carcinoma 007.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Source: Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11176 | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
{{ | |||
{{ | |||
Latest revision as of 19:06, 30 October 2017
|
Adrenocortical carcinoma Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Adrenocortical carcinoma from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Study |
|
Adrenocortical carcinoma MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Adrenocortical carcinoma MRI |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Adrenocortical carcinoma MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmad Al Maradni, M.D. [2] Mohammed Abdelwahed M.D[3]
Overview
MRI scans are helpful in differentiating between adrenal adenoma, carcinoma, and metastatic lesions. Due to the multi-planar capability of MRI, direct invasion of adjacent organs may be better shown. Inferior vena cava invasion has been reported in 9% to 19% of cases at presentation.
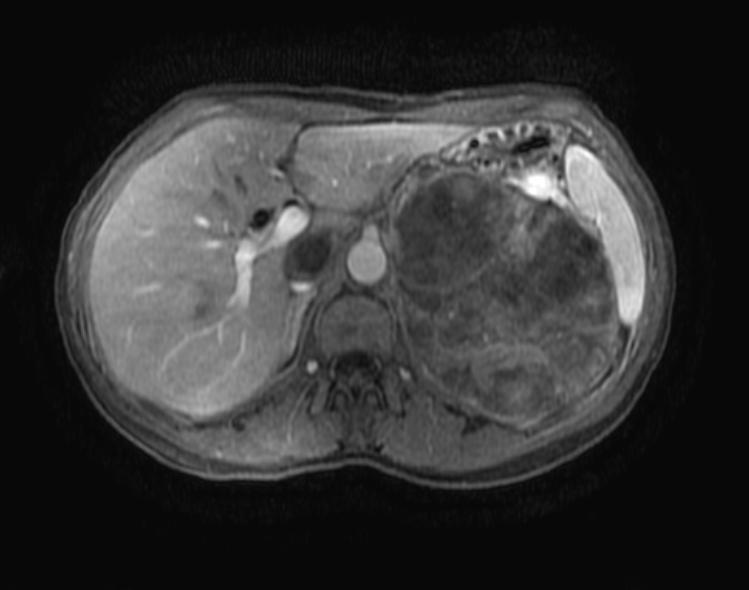
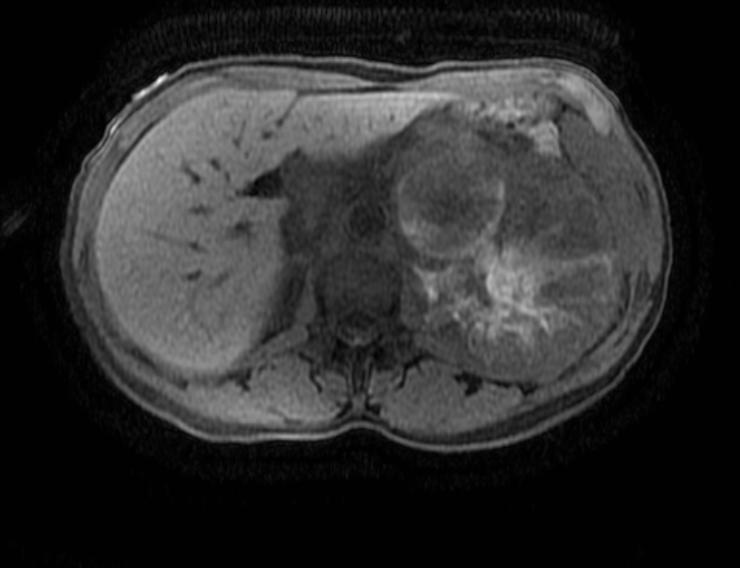
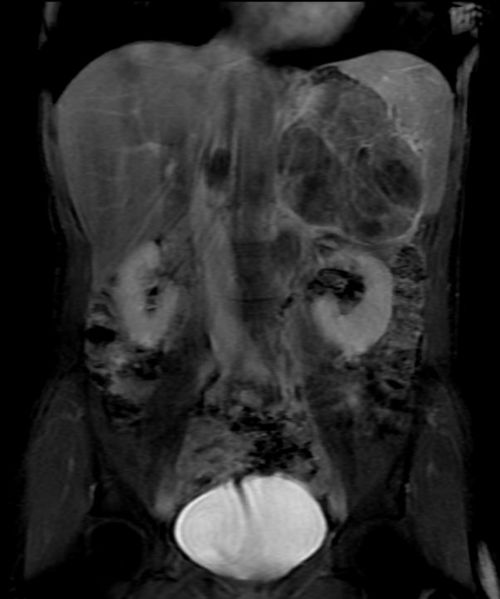
MRI Findings in adrenocortical carcinoma
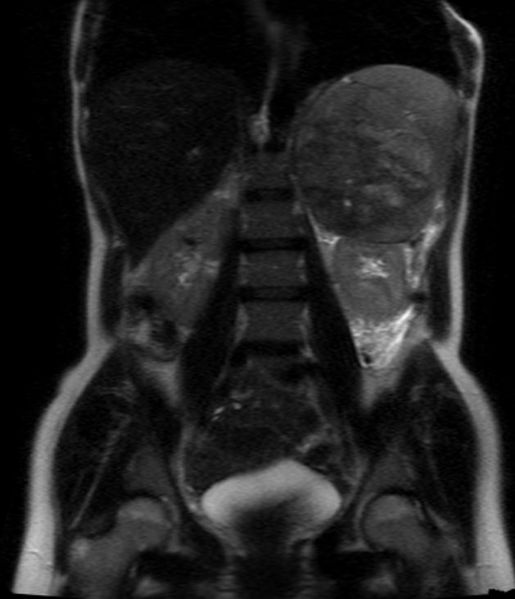
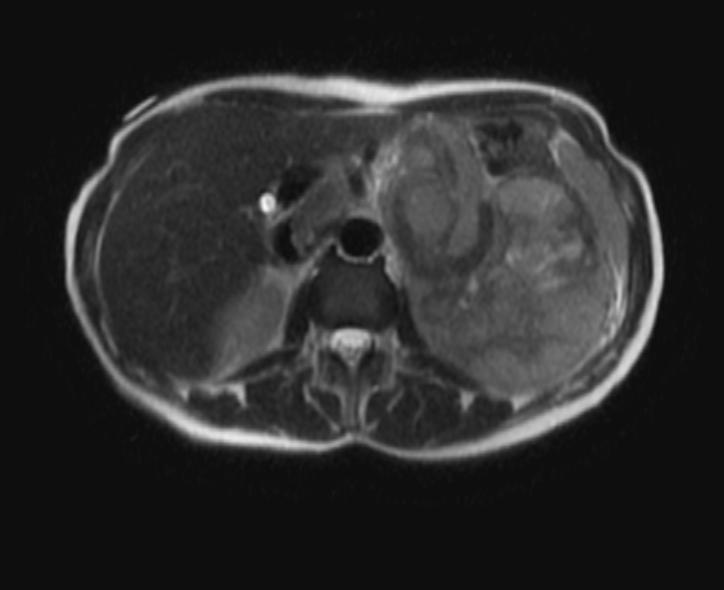
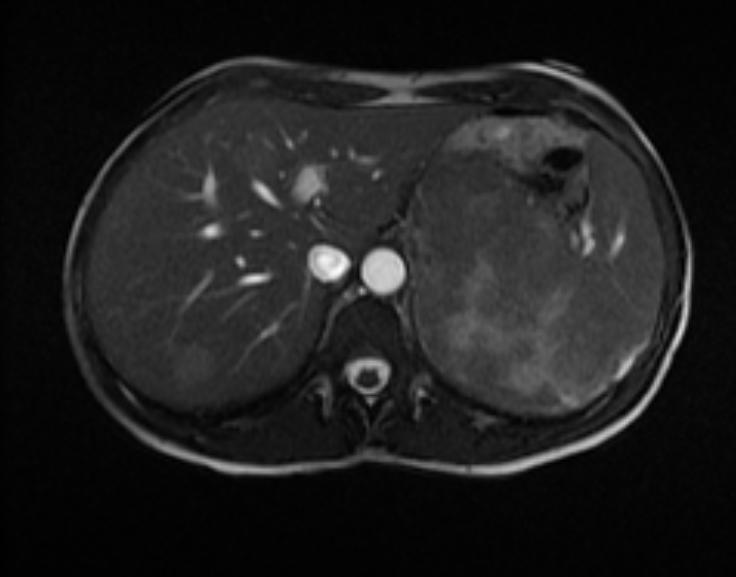
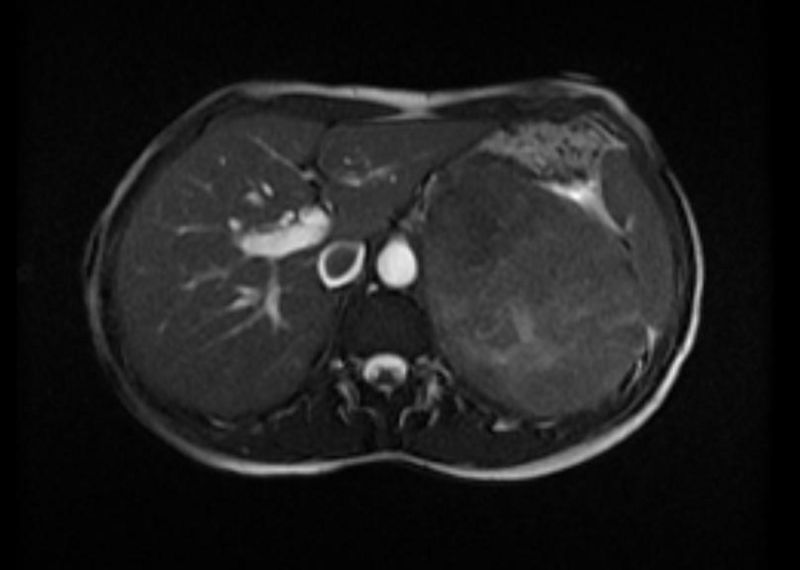
- Adrenocortical carcinomas are usually large and appear as heterogeneous masses on both T1- and T2-weighted images owing to the presence of internal hemorrhage and necrosis.[1]
- Adrenocortical carcinoma may contain foci of intra-cytoplasmic lipid, which results in a loss of signal intensity on out-of-phase images.[2]
- Large adrenal carcinomas tend to invade the adrenal vein and inferior vena cava.[1]
- On MRI, ACCs appear iso-intense to hypo-intense relative to liver parenchyma on T1-weighted images and hyper-intense relative to liver parenchyma on T2-weighted images.[3]
- On chemical-shift MRI, the presence of intracellular lipid can cause regions of signal loss on out-of-phase images relative to in-phase images.[4]
- Inferior vena cava invasion has been reported in 9% to 19% of cases at presentation.
- Due to the multi-planar capability of MRI, direct invasion of adjacent organs may be better shown.
MRI Examples of adrenocortical carcinoma
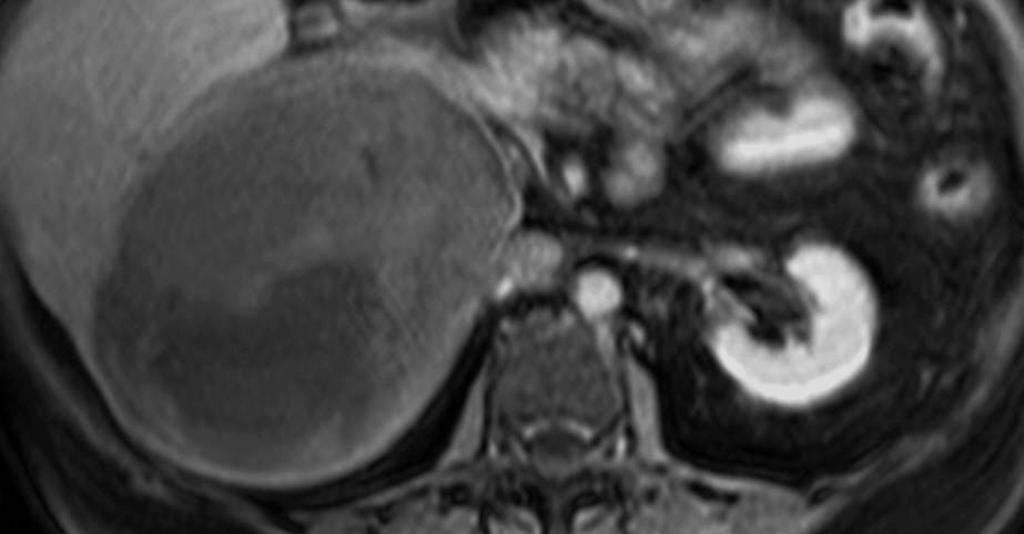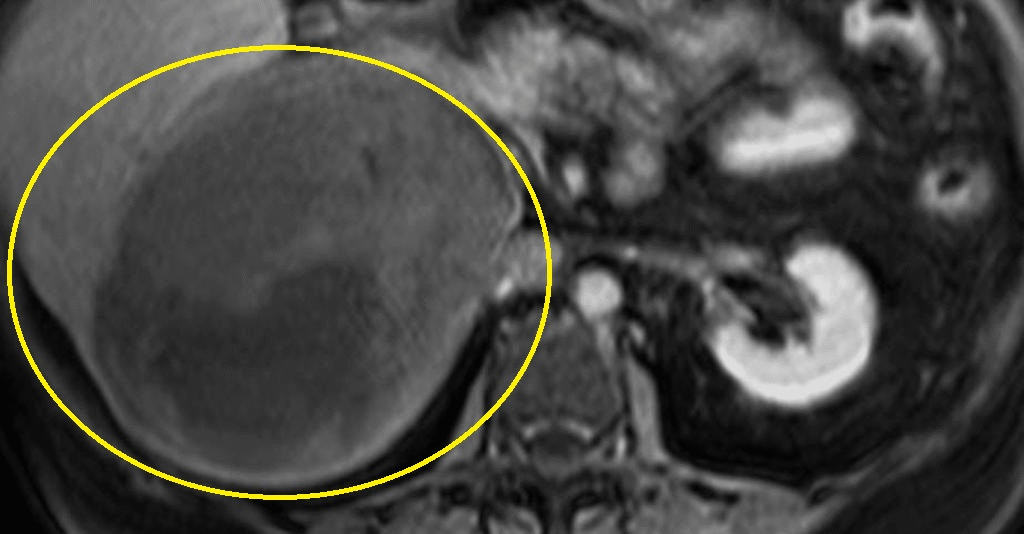
Source: Case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11176
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB; et al. (2011). "Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196 (6): W706–14. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5540. PMID 21606258.
- ↑ Ng L, Libertino JM (2003). "Adrenocortical carcinoma: diagnosis, evaluation and treatment". J Urol. 169 (1): 5–11. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000030148.59051.35. PMID 12478091.
- ↑ Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB; et al. (2011). "Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196 (6): W706–14. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5540. PMID 21606258.
- ↑ Bharwani N, Rockall AG, Sahdev A, Gueorguiev M, Drake W, Grossman AB; et al. (2011). "Adrenocortical carcinoma: the range of appearances on CT and MRI". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196 (6): W706–14. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5540. PMID 21606258.