AV nodal reentrant tachycardia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Infobox_Disease | | {{Infobox_Disease | | ||
Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | ||
Image = AV nodal reentrant tachycardia.png | | Image = AV nodal reentrant tachycardia.png | | ||
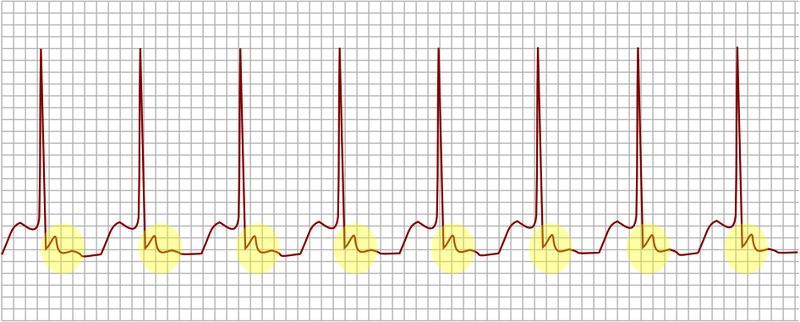
Caption = AV nodal reentrant tachycardia. In yellow, is evidenced the P wave that falls after the QRS complex.| | Caption = AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, uncommon variant with antegrade conduction down the slow pathway. In yellow, is evidenced the P wave that falls after the QRS complex.| | ||
DiseasesDB = | | DiseasesDB = | | ||
ICD10 = {{ICD10|I|47|1|i|30}} | | ICD10 = {{ICD10|I|47|1|i|30}} | | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{AVNRT}} | {{AVNRT}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} : {{AE}} {{RG}} | ||
{{SK}} AVNRT; AV node reentrant tachycardia; AV nodal reentry tachycardia; AV node reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia; atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentry tachycardia; | {{SK}} AVNRT; AV node reentrant tachycardia; AV nodal reentry tachycardia; AV node reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia; atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentry tachycardia; junctional reciprocating tachycardia; reciprocal or reciprocating AV nodal reentrant tachycardia | ||
==[[AVNRT overview|Overview]]== | ==[[AVNRT overview|Overview]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ==[[AVNRT historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT classification|Classification]]== | |||
==[[AVNRT pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ==[[AVNRT pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT | ==[[AVNRT causes|Causes]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT differential diagnosis|Differentiating AVNRT from other Disorders]]== | ==[[AVNRT differential diagnosis|Differentiating AVNRT from other Disorders]]== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
==[[AVNRT epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ==[[AVNRT epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications | ==[[AVNRT risk factors|Risk Factors]]== | ||
==[[AVNRT natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 42: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
[[AVNRT treatment overview|Overview]] | [[AVNRT patient position|Patient | [[AVNRT treatment overview|Overview]] | [[AVNRT patient position|Patient Position]] | [[AVNRT vagal maneuvers|Vagal Maneuvers]] | [[AVNRT medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[AVNRT cardioversion|Cardioversion]] | [[AVNRT electrophysiologic testing and radiofrequency ablation|Electrophysiologic Testing and Radiofrequency Ablation]] | [[AVNRT prevention|Prevention]] | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
[[CME Category::Cardiology]] | |||
[[Category:Electrophysiology]] | [[Category:Electrophysiology]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Arrhythmia]] | |||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Intensive care medicine]] | [[Category:Intensive care medicine]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 8 April 2020
| AV nodal reentrant tachycardia | |
 | |
|---|---|
| AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, uncommon variant with antegrade conduction down the slow pathway. In yellow, is evidenced the P wave that falls after the QRS complex. | |
| ICD-10 | I47.1 |
| ICD-9 | 426.89, 427.0 |
| MeSH | D013611 |
|
AVNRT Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of AV nodal reentrant tachycardia |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for AV nodal reentrant tachycardia |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] : Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ramyar Ghandriz MD[2]
Synonyms and keywords: AVNRT; AV node reentrant tachycardia; AV nodal reentry tachycardia; AV node reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia; atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia; atrioventricular node reentry tachycardia; junctional reciprocating tachycardia; reciprocal or reciprocating AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differentiating AVNRT from other Disorders
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Symptoms | Physical Examination | Laboratory Findings | Electrocardiogram
Treatment
Overview | Patient Position | Vagal Maneuvers | Medical Therapy | Cardioversion | Electrophysiologic Testing and Radiofrequency Ablation | Prevention