ATP1A2
ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 2 (+) polypeptide, also known as ATP1A2, is a human gene.[1]
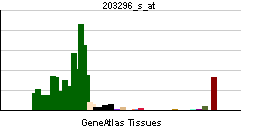
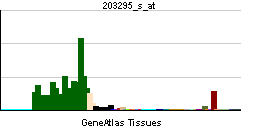
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+-ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 2 subunit.[1]
References
Further reading
- Lingrel JB, Orlowski J, Shull MM, Price EM (1990). "Molecular genetics of Na,K-ATPase". Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 38: 37–89. PMID 2158121.
- Dunbar LA, Caplan MJ (2001). "Ion pumps in polarized cells: sorting and regulation of the Na+, K+- and H+, K+-ATPases". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (32): 29617–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100023200. PMID 11404365.
- Shull MM, Pugh DG, Lingrel JB (1989). "Characterization of the human Na,K-ATPase alpha 2 gene and identification of intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (29): 17532–43. PMID 2477373.
- Sverdlov ED, Bessarab DA, Malyshev IV; et al. (1989). "Family of human Na+,K+-ATPase genes. Structure of the putative regulatory region of the alpha+-gene". FEBS Lett. 244 (2): 481–3. PMID 2537767.
- Yang-Feng TL, Schneider JW, Lindgren V; et al. (1988). "Chromosomal localization of human Na+, K+-ATPase alpha- and beta-subunit genes". Genomics. 2 (2): 128–38. PMID 2842249.
- Shull MM, Lingrel JB (1987). "Multiple genes encode the human Na+,K+-ATPase catalytic subunit". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (12): 4039–43. PMID 3035563.
- Sverdlov ED, Monastyrskaya GS, Broude NE; et al. (1987). "The family of human Na+,K+-ATPase genes. No less than five genes and/or pseudogenes related to the alpha-subunit". FEBS Lett. 217 (2): 275–8. PMID 3036582.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. PMID 8125298.
- Zahler R, Gilmore-Hebert M, Baldwin JC; et al. (1993). "Expression of alpha isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase in human heart". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1149 (2): 189–94. PMID 8391840.
- Stengelin MK, Hoffman JF (1997). "Na,K-ATPase subunit isoforms in human reticulocytes: evidence from reverse transcription-PCR for the presence of alpha1, alpha3, beta2, beta3, and gamma". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (11): 5943–8. PMID 9159180.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K; et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. PMID 9373149.
- Ducros A, Joutel A, Vahedi K; et al. (1998). "Mapping of a second locus for familial hemiplegic migraine to 1q21-q23 and evidence of further heterogeneity". Ann. Neurol. 42 (6): 885–90. doi:10.1002/ana.410420610. PMID 9403481.
- Terwindt GM, Ophoff RA, Lindhout D; et al. (1998). "Partial cosegregation of familial hemiplegic migraine and a benign familial infantile epileptic syndrome". Epilepsia. 38 (8): 915–21. PMID 9579893.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M; et al. (1999). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XI. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 5 (5): 277–86. PMID 9872452.
- Katzmarzyk PT, Rankinen T, Pérusse L; et al. (1999). "Linkage and association of the sodium potassium-adenosine triphosphatase alpha2 and beta1 genes with respiratory quotient and resting metabolic rate in the Québec Family Study". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 (6): 2093–7. PMID 10372716.
- Rankinen T, Pérusse L, Borecki I; et al. (2000). "The Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha2 gene and trainability of cardiorespiratory endurance: the HERITAGE family study". J. Appl. Physiol. 88 (1): 346–51. PMID 10642400.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH; et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932.
- Ukkola O, Joanisse DR, Tremblay A, Bouchard C (2003). "Na+-K+-ATPase alpha 2-gene and skeletal muscle characteristics in response to long-term overfeeding". J. Appl. Physiol. 94 (5): 1870–4. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00942.2002. PMID 12496141.
| This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |