WBR0056
| Author | PageAuthor::William J Gibson |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Microbiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Dermatology, SubCategory::General Principles, SubCategory::Infectious Disease |
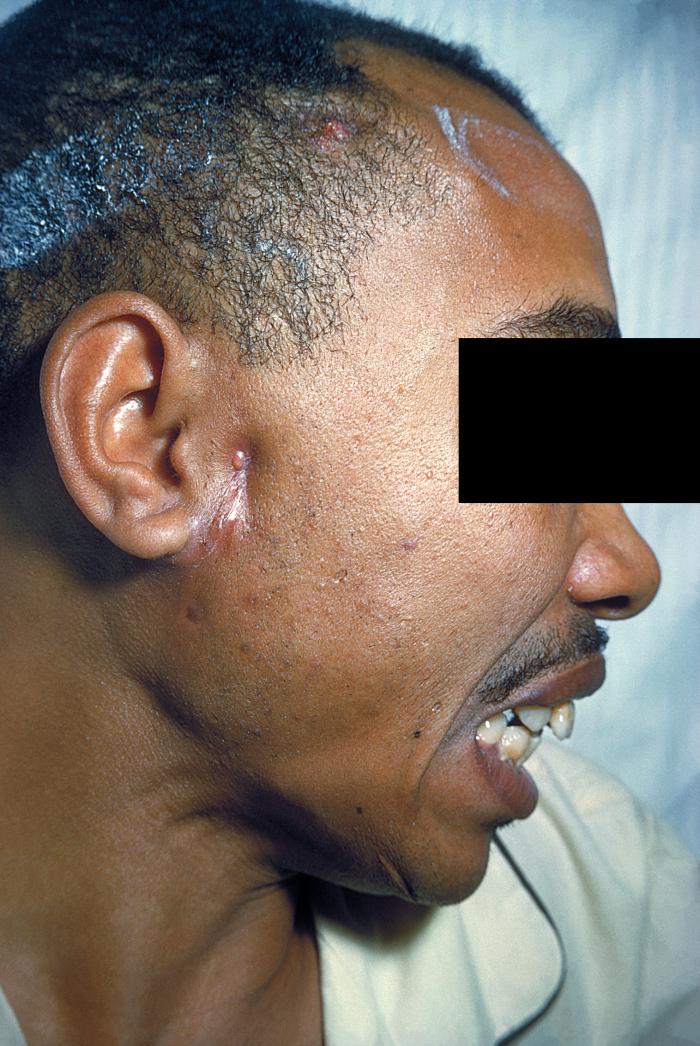
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 35-year-old homeless man presents to his primary care physician for a right facial lesion that has developed slowly over the past six months. The lesion forms a sinus tract and is pictured below. On closer inspection, the physician notices yellow "sulfur" granules within the lesion. Physical exam is otherwise notable for poor dentition, a lack of lymphadenopathy. What is the most likely causal organism? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Staphylococcus aureus |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::Incorrect: Staphylococcus aureus can cause cutaneous infection (eg Impetigo, Cellulitis) but it is not associated with the deeper infection that crosses tissue boundaries seen in this patient. S. aureus is also not associated with with sulfur granules (not to be confused with the yellow pigment S. aureus can produce).]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Nocardia asteroides |
| Answer B Explanation | [[AnswerBExp::Incorrect: Nocardia is similar to Actinomyces israelii in that both are gram-positive rods which form branching filaments. However, Nocardia is not associated with sulfur granules and typically causes pulmonary infection in immunocompromised patients.]] |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Bacillus anthracis |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::'''Incorrect:''' While B. anthracis can cause cutaneous infections, the infected areas tends to develop acutely and are darkly colored. Anthrax infection is not associated with draining sinus tracts or sulfur granules. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Actinomyces israelii |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::'''Correct:''' Actinomycosis causes penetrating abscesses that have a characteristic "wooden" appearance and "sulfur" granules. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Mycobacterim leprae |
| Answer E Explanation | [[AnswerEExp::Incorrect: Mycobacterium leprae causes leprosy (Hansen’s disease). Several features make actinomycosis more probable in this patient than leprosy: Whereas this patient has a single nidus of infection, leprosy causes disseminated lesions. Leprosy is also not associated with the formation of sinus tracts (new, pathologic paths from the skin surface into the body) or "sulfur" granules.]] |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient in this vignette is suffering from Actinomyces israelii. Actinomyces israelii is a facultative anaerobe, part of the normal oral flora and able to cause disease only when it is free to replicate in an anoxic environment. Patients have often recently had dental work, poor oral hygiene, periodontal disease, or radiation therapy causing local tissue damage to the oral mucosa, all of which predispose the person to developing actinomycosis. Infection often presents as a penetrating lesion that forms a sinus tract (a new, pathologic path from the skin surface into the body). Microscopically, Actinomyces israelii is a species of gram-positive rod-shaped bacteria that forms yellow "sulfur" granules.
Educational Objective: Actinomycosis causes penetrating abscesses that have a characteristic "wooden" appearance and "sulfur" granules. References: First Aid 2014 page 134 First Aid 2012 page 159 |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Microbiology, WBRKeyword::Bacteria, WBRKeyword::Actinomyces, WBRKeyword::Abscess, WBRKeyword::Dermatology |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |