Avacopan
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Tejasvi Aryaputra
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Avacopan is a complement 5a receptor antagonist that is FDA approved for the treatment of severe active anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis) in combination with standard therapy, including glucocorticoids. Common adverse reactions include hypertension, blood creatinine increase, fatigue, upper abdominal pain, nausea, headache, vomiting, rash, dizziness, and paresthesia.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Three 10 mg capsules (30 mg) taken with food orally, twice daily.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Avacopan in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Avacopan in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Avacopan FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Avacopan in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Avacopan in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- In patients with serious hypersensitivity when taking Avacopan.
- In patients with serious hypersensitivity when taking any of the excipients.
Warnings
Hepatotoxicity
- Higher incidences of hepatobiliary and transaminase elevations were found in controlled studies of patients taking Avacopan.
- Patients before starting Avacopan treatment, every 4 weeks after start of Avacopan, and for the first 6 months of taking Avacopan as clinically indicated thereafter should take liver test panels.
- Consult medical consultation and promptly pause use of Avacopan in patients who have an elevation in ALT or AST to >3 times the upper limit of normal.
- Discontinue the use of Avacopan until Avacopan-induced liver injury is ruled out in patients who have transaminases >3 times the upper limit of normal with elevation of bilirubin to >2 times the upper limit of normal or AST or ALT is >5 times the upper limit of normal.
- Patients should be advised to not take Avacopan with active, untreated and/or uncontrolled chronic liver disease.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Two cases of Angioedema occurred in clinical studies of patients taking Avacopan with one of the cases requiring the hospitalization of a patient.
- Discontinue the use of Avacopan in patients with Angioedema.
- Monitor patients airways and provide appropriate treatment in patients taking Avacopan who experience Angioedema.
- Advise patients about the possible symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction and immediatly seek medical attention if symptoms of hypersensitivity arise.
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Reactivation
- Clincal studies show signs of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation when taking Avacopan.
- HBV reactivation is defined as an abrupt increase in HBV replication, manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA levels or detection of HBsAg, in a person who was previously HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive.
- Before starting Avacopan treatment, measure HBsAg and anti-HBc in patients.
- Consider HBV antiviral therapy for patients who show signs of prior hepatitis B infection before, during, or after Avacopan treatment.
- Patients that show any evidence of current and prior history of HBV infection or HBV reactivation should be monitored during and 6 months after Avacopan treatment.
- Discontinue use of Avacopan and all concomitant drugs asscociated with HBV reactivation in patients who develop signs of reactivation of HBV.
Serious Infections
- Fatal infections such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections were found in patients taking Avacopan.
- Patients with active, serious infections should be advised not to take Avacopan.
- Patients who have been exposed to tuberculosis, have underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection, have chronic or recurrent infection, have a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection, or have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses should be advised of the risks and benefits of taking Avacopan.
- Signs of infection during or after treatment with Avacopan should be monitored.
- Avacopan treatment should be interrupted if signs of serious or opportunistic infection develop.
- Diagnostic tests should be advised in patients who develop new infections when taking Avacopan.
- Avacopan treatment can be resumed when infection is under control.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical Trial Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions and durations of follow up, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. A randomized 1:1 Avacopan or Prednisone was clinically tested on patients that had ANCA-associated vasculitis to see for adverse reactions in a phase 3 trial. Two phase 2 trials were also conducted on patients that also had ANCA-associated vasculitis. The phase 3 trial was conducted on 330 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. The patient population was largely Caucasian (84.2%), and included 56.4% men that had a mean age of 60.9 years.
Phase 3 Clinical Data
- Adverse reactions included GPA (3.0% Avacopan vs. 0.6% Prednisone), urinary tract infection (1.8% Avacopan vs. 1.2% Prednisone), acute kidney injury (1.8% Avacopan vs. 0.6% Prednisone), and pneumonia (4.8% Avacopan vs. 3.7% Prednisone).
- 1.2% of patients in the Avacopan treatment and 2.4% of patients in the Prednisone treatment died during a 52 week span.
- Discontinuation of treatments occurred in both groups (4.2% taking Avacopan and 1.2% taking prednisone) due to hepatic-related adverse reactions.
- Hepatic function abnormal (1.8%) was reported by > 1 patient with more being reported by patients in the Avacopan treatment.
Table 1 shows the Adverse Reactions (≥5%) reported more in patients taking Avacopan than Prednisone.

Hepatotoxicity and Elevated Liver Function Tests
- Hepatic-related adverse reactions occurred in both the Avacopan treatment (13.3%) and Prednisone treatment (11.6%) for patients in the Phase 3 trial.
- Liver enzyme abnormalities and hepatobiliary adverse reactieventsons were some of the hepatic-related adverse reactions reported by patients.
- 5.4% of patients in the Avacopan treatment group and 3.7% of patients in the Prednisone treatment group reported serious hepatic-related adverse reaction in the Phase 3 trial.
Angioedema
- 1.2% of patients in the Avacopan treatment reported Angioedema with one patient requiring hospitalization in the Phase 3 trials.
Elevated Creatine Phosphokinase
- 3.6% of patients in the Avacopan treatment group and 0.6% of patients in the Prednisone treatment group reported increased creatine phosphokinase in the Phase 3 trial.
- Discontinuation of treatment occurred in one patient part of the Avacopan treatment group.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information about "Postmarketing Experiance" in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 Inducers
- Co-administration of Avacopan and Rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducer, causes a decrease in Avacopan exposure.
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Co-administration of Avacopan and Itraconazole, a strong CYP3A4 enzyme inhibitor, causes an increase in Avacopan exposure.
CYP3A4 Substrates
- Adverse reactions may occur with co-administration of Avacopan and sensitive CYP3A4 substrates with a narrow therapeutic window.
- A CYP3A4 inhibitor is Avacopan.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
Reproduction studies done on pregnant hamsters showed no fetal harm to the embryo during organogenesis when using 5 times the MRHD of Avacopan. No structural abnormalities in hamsters were found, but increase in skeletal variations were reported when using 5 times the MRHD of Avacopan. Studies on rabbits showed no fetal harm to the embryo during organogenesis, but showed increased abortions when using 0.6 times the MRHD of Avacopan. Maternal toxicities were reported in rabbits when using 0.6 times the MRHD of Avacopan. These studies display the potential harms and risks in the embryo of pregnant woman when taking Avacopan.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Avacopan in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Avacopan during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
No data has been conducted on nursing in human when taking Avacopan. Based on studies done on hamsters, Avacopan was found in the plasma of nursing offspring. Advise patients about the potential secretion of Avacopan in milk of nursing hamsters.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Avacopan with respect to pediatric populations.
Geriatic Use
In the phase 3 randomized clinical trial for ANCA-associated vasculitis, 62 of the 86 geriatric patients were between the ages of 65 to 74 while 24 of the 86 geriatric patients were 75 years or older. All these patients received the Avacopan treatment. No differences among young patients compared to geriatric patients were found when looking at safety and efficacy of Avacopan.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Avacopan with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Avacopan with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
Patients with mild and severe renal impairment require no change to dosage usage.
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild and severe hepatic impairment require no change to dosage usage.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Avacopan in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Avacopan with respect to immunocompromised populations.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Before using Avacopan, patients should be advised to conduct liver function tests and conduct HBV screening.
- Instruct patients to not chew, crush, or break tablets.
- Take orally with food.
- If scheduled dosage is missed, skip dosage and wait until next regularly scheduled dosage.
- Advise patients to not double dose if dosage is missed.
Monitoring
- Advise patients to reduce to 30 mg of Avacopan dosage once daily with concomitant use of Avacopan and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Avacopan and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Avacopan overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- Avacopan is a complement 5a receptor antagonist.
- Interaction between the anaphylatoxin C5a and C5aR is inhibited by Avacopan. Activation and migration of C5a-mediated neutrophil is blocked through the use of Avacopan.
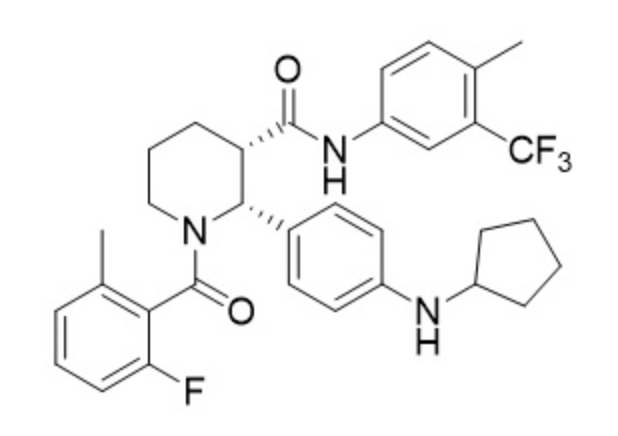
Structure
- Avacopan is a complement 5a receptor antagonist for oral administration. It has an empirical formula of C33H35F4N3O2 and a molecular weight of 582 g/mol.
- The chemical name is (2R,3S)-2-[4-(cyclopentylamino)phenyl]-1-(2-fluoro-6-methylbenzoyl)-N-[4-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]piperidine-3-carboxamide.

Pharmacodynamics
- In human dosage, C5a-induced upregulation of CD11b on neutrophils is blocked by Avacopan.
- Avacopan does not prolong the QT interval when looking at cardiac electrophysiology at the recommended dosages.
Pharmacokinetics
Steady State Exposure
- 3466 ± 1921 ng•h/mL is the mean steady state plasma exposure in the 12-hour area under the plasma drug concentration over time curve within patients who have ANCA-associated vasculitis that are receiving 30 mg twice daily of Avacopan.
- 349 ± 169 ng/mL is the mean steady state plasma exposure in the maximum plasma concentration within patients who have ANCA-associated vasculitis that are receiving 30 mg twice daily of Avacopan.
Absorption
- In high-fat, high-calorie meal, AUC increased by 72% and Cmax increased by 8% when co-administered with 30 mg of Avacopan in capsule formulation.
- In high-fat, high-calorie meal, Tmax is also delayed from 2 hours to 6 hours when co-administered with 30 mg of Avacopan in capsule formulation.
Distribution
- Avacopan and M1 has a plasma protein binding percentage greater than 99.9%.
- 345 L is the volume of distribution found in Avacopan.
Elimination
- 16.3 L is the total apparent body clearance found in Avacopan.
- 97.6 hours is the mean elimination half-live of Avacopan when given a single dose, with food, of 30 mg of Avacopan.
- 55.6 hours is the mean elimination half-live of M1 when given a single dose, with food, of 30 mg of Avacopan.
Metabolism
- An enzyme responsible for the clearance of Avacopan is CYP3A4.
- An enzyme responsible for the clearance and formation of M1 is CYP3A4.
- Avacopan and M1 have the same activity in C5aR.
- In plasma, approximately 12% of the total drug-related materials is M1 present.
Excretion
- In feces, after oral administration of radiolabelled Avacopan, 77% of Avacopan was found in which 7% was found unchanged.
- In urine, after oral administration of radiolabelled Avacopan, 10% of Avacopan was found in which <0.1% was found unchanged.
Specific Populations
- In plasma exposure of M1 and Avacopan, gender, body weight, age, race, and renal function had no significant differences in the clinical data.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- When looking at Avacopan and M1, mild or moderate hepatic impairment showed no significant effect when looking at the clinical data for plasma exposure.
- When treated with Avacopan, AUC increased 12% and Cmax decreased 13% in patients with mild hepatic impairment. AUC increased 12% and Cmax decreased 17% in patients with moderate hepatic impairment.
- In M1, AUC increased 11% and Cmax decreased 5% in patients with mild hepatic impairment. AUC increased 18% and Cmax decreased 16% in patients with moderate hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
Effects of Other Drugs on Avacopan
- CYP3A4 metabolizes Avacopan. In vitro studies, Avacopan for certain uptake transporters such as BCRP and P-gp efflux or OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 is not a substrate. M1 for certain uptake transporters such as OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 or BCRP efflux is not a substrate. For P-gp, M1 is a substrate.
Table 2 shows Pharmacokinetics Changes in Both M1 and Avacopan when Co-administered Drugs are Present.

Effect of Avacopan on Other Drug Substances
- In vitro studies, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 are not inhibited by Avacopan. CYP2B6 and CYP1A2 are not induced by Avacopan. CYP3A4 shows potential signs of both being induced and inhibited by Avacopan. CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C19, CYP1A2, and CYP2D6 are not inhibited by M1. CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4 have low potential to be induced by M1. CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 potentially may be inhibited by M1. OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1, OAT3, MATE1, P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, and MATE2K are not inhibited by M1 or Avacopan at relevant concentrations clinically.
Table 3 shows Pharmacokinetics Changes in the Presence of Avacopan and Other Drugs.

Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis
- Studies done on both rats and hamsters receiving 100 mg/kg/day orally shows no tumorigenic potential.
Mutagenesis
- Avacopan has shown no signs of it being clastogenic or mutagenic when looking at the data from vitro mouse lymphoma assay, vitro bacterial reverse mutation test, or vivo rat micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
- Studies done on male and female hamsters showed no changes in reproductive performance or fertility after receiving doses of Avacopan up to 1000 mg/kg/day orally.
Clinical Studies
Double-blind, active-controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trial
- A phase 3 clinical trial tested the safety and effectiveness of Avacopan on patients that have ANCA-associated vasculitis. 330 patients were part of the study and were either put in Avacopan or Prednisone group. The patient population was largely Caucasian (84.2%), and included 56.4% women, and either had a presence of anti-MPO (57.0%) antibodies or anti-PR3 (43.0%) antibodies. Patients in the Avacopan treatment received a twice daily dosage of 30 mg of Avacopan for 52 weeks, and prednisone-matching placebo for 20 weeks. Patients in the Prednisone group received prednisone and twice daily dosage of an avacopan-matched placebo for 52 weeks. All patients received 1 of the 3 different possible standard immunosuppressive regimens: IV cyclophosphamide, oral cyclophosphamide, or rituximab. Patients from week 15 part of the IV cyclophosphamide group received IV cyclophosphamide 15 mg/kg IV up to 1.2 g maximum every 2 to 3 weeks for 13 weeks followed by oral azathioprine 1 mg/kg/day with titration up to 2 mg/kg/day. 31% of patients in this study received standard immunosuppressive regimen. Patients from week 15 part of the oral cyclophosphamide group received oral cyclophosphamide 2 mg/kg/day for 14 weeks followed by azathioprine 1 mg/kg/day with titration up to 2 mg/kg/day. 4% of patients in this study received this standard immunosuppressive regimen. Patients part of the rituximab group received IV rituximab 375 mg/m2 once weekly for 4 weeks without azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil. To prevent hypersensitivity reactions from rituximab a pre-medication for Glucocorticoids may be taken. 65% of patients received this standard immunosuppressive regimen. 3 factors determined randomization: proteinase 3 positive or myeloperoxidase positive ANCA-associated vasculitis, newly-diagnosed or relapsing ANCA-associated vasculitis, and the type of immunosuppressive regimen. The goal of the study is to understand how the two treatment groups affect disease remission at week 26 and sustained remission at week 52.
Remission at Week 26 and Sustained Remission at Week 52
- Patients in the Avacopan group had 72.3% of patients achieve remission at Week 26 and 65.7% achieve sustained remission at Week 52. Patients in the Prednisone group had 70.1% of patients achieve remission at Week 26 and 54.9% achieve sustained remission at Week 52. Disease remission was defined as achieving a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS) of 0 and no use of glucocorticoids for treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis from Week 22 to Week 26 in this clinical study. Sustained remission was defined as remission at Week 26 and remission at Week 52, without relapse between Week 26 and Week 52 in this clinical study.
Table 4 shows the results of patients that had sustained remission at week 52 in the Double-blind, active-controlled, Phase 3 Clinical Trial.

Figure 1 shows stratification factors and GPA/MPA disease in patients at sustained remission at week 52

How Supplied
- 10 mg dose pack (180 tablets), bottle seals are child resistant.
- 10 mg dose pack (180 tablets), bottle seals are child resistant.
- Tablets are light orange and opaque yellow.
Storage
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Avacopan |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel





{{#ask: Label Page::Avacopan |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Dosage and Administration
- Instruct patients to not chew, crush, or break tablets.
- Swallow Avacopan capsules whole.
- If scheduled dosage is missed, skip dosage and wait until next regularly scheduled dosage.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Advise patients that experience signs of angioedema to seek immediate medical attention.
- Advise patients with any signs of hypersensitivity reactions to discontinue use of Avacopan until consultation with physician.
Hepatotoxicity
- Seek immediate medical consultation if patients receive symptoms of liver problems such as pain on the upper right side of the stomach area, bruising, bleeding, dark urine, brown urine, or yellowing of the skin, or yellowing of the white part of the eyes during Avacopan treatment.
Infections
- Reactivation of hepatitis B infection is one of many possible serious infections reported by patients when using Avacopan.
- Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they show signs of serious infections.
Lactation
- Advise patients about both the risks and benefits of nursing when taking Avacopan.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Avacopan interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Tavneos
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Avacopan Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.