Alzheimer's disease MRI
|
Alzheimer's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Alzheimer's disease MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Alzheimer's disease MRI |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Alzheimer's disease MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Aravind Reddy Kothagadi M.B.B.S[2]
Overview
Structural MRI of the brain may be helpful in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Characteristic findings on MRI suggestive of Alzheimer's disease include reduced hippocampal volume and medial temporal lobe atrophy.
MRI
- Structural MRI of the brain may be helpful in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Characteristic findings on MRI suggestive of Alzheimer's disease include: [1] [2] [3]
- Reduced hippocampal volume
- Medial temporal lobe atrophy
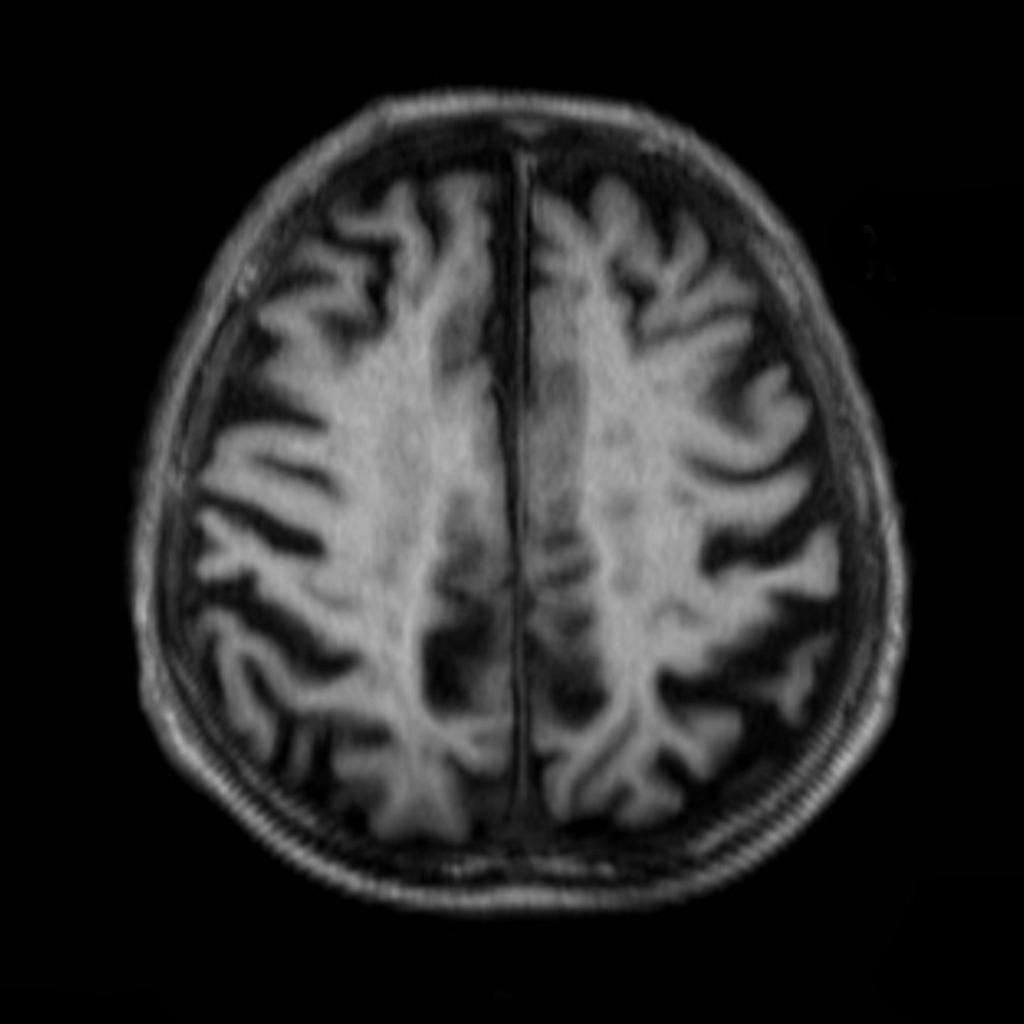
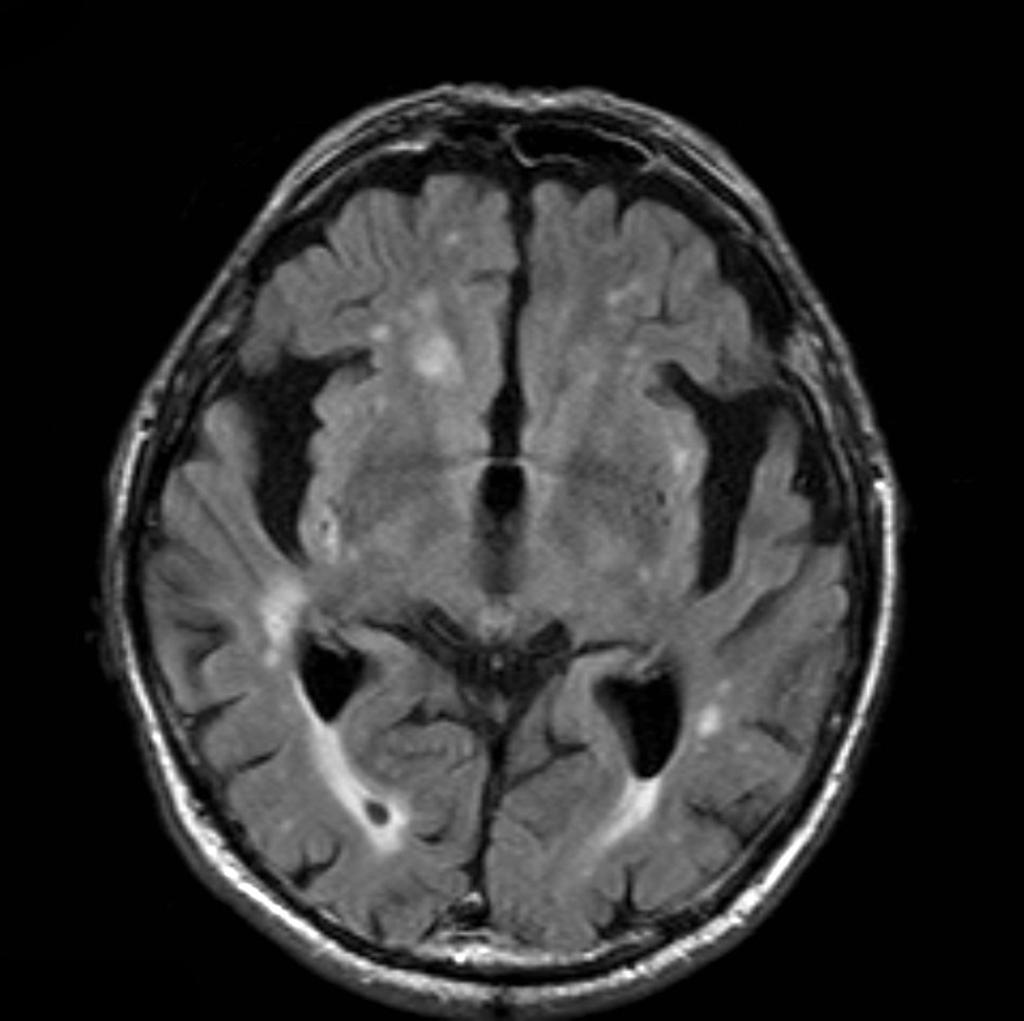
- Findings on MRI in an elderly patient with memory loss demonstrates cerebral volume loss, particularly pronounced in the temporal and parietal lobes, consistent with the clinical impression of Alzheimer disease.
- Multiple white matter T2 hyperintense regions are suggestive of chronic small vessel ischemic change.
References
- ↑ Whitwell JL, Dickson DW, Murray ME, Weigand SD, Tosakulwong N, Senjem ML; et al. (2012). "Neuroimaging correlates of pathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer's disease: a case-control study". Lancet Neurol. 11 (10): 868–77. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70200-4. PMC 3490201. PMID 22951070.
- ↑ Brook RH (1992). "Improving practice: the clinician's role". Br J Surg. 79 (7): 606–7. PMID 1643466.
- ↑ Barkhof F, Polvikoski TM, van Straaten EC, Kalaria RN, Sulkava R, Aronen HJ; et al. (2007). "The significance of medial temporal lobe atrophy: a postmortem MRI study in the very old". Neurology. 69 (15): 1521–7. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000277459.83543.99. PMID 17923614.