Sumatriptan (transdermal)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Turky Alkathery, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Sumatriptan (transdermal) is a serotonin (5HT) 1b/1d receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults. Common adverse reactions include application site pain, paresthesia, pruritus, warmth, and discomfort.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- ZECUITY is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
- Limitations of Use:
- Use only if a clear diagnosis of migraine has been established.
- If a patient has no response to the first migraine attack treated with ZECUITY reconsider the diagnosis of migraine before ZECUITY is administered to treat any subsequent attacks.
- ZECUITY is not intended for the prevention of migraine attacks.
Dosage
ZECUITY is for transdermal use only and is designed for patient self-administration to the upper arm or thigh (see Figure 1). ZECUITY should not be applied to other areas of the body. ZECUITY should not be cut.
The maximum recommended single dose is one ZECUITY iontophoretic transdermal system (TDS). No more than two ZECUITY TDS should be used in any 24 hour period, and the second ZECUITY TDS should be applied no sooner than 2 hours after activation of the first ZECUITY TDS. There is no evidence of benefit for the use of a second ZECUITY TDS to treat headache recurrence or incomplete headache relief during a migraine attack.
ZECUITY should be applied to dry intact, non-irritated skin on the upper arm or thigh on a site that is relatively hair free and is without scars, tattoos, abrasions, or other skin conditions (i.e., generalized skin irritation or disease including eczema, psoriasis, melanoma, contact dermatitis). ZECUITY should not be applied to a previous application site until the site remains erythema free for at least 3 days.

ZECUITY delivers 6.5 mg of sumatriptan over 4 hours. Once applied, the activation button must be pushed, and the red light emitting diode (LED) will turn on. ZECUITY TDS must be applied and activated within 15 minutes of initiation of assembly. When dosing is completed, the system stops operating and the activation light turns off, signaling that the system can be removed. Once dosing is completed, the system cannot be reactivated. If the light turns off before 4 hours, dosing has stopped and ZECUITY can be removed. If headache relief is incomplete, a second ZECUITY TDS can be applied to a different site. [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
The ZECUITY TDS should remain in place for 4 hours or until the red LED light goes off. The iontophoretic device can be secured with medical tape if needed.
The safety of using more than 4 ZECUITY in one month has not been established.
ZECUITY is for single use only. After use, the TDS should be folded so the adhesive side sticks to itself and safely discarded away from children and pets. ZECUITY contains lithium-manganese dioxide batteries; it should be disposed in accordance with state and local regulations.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with:
Ischemic coronary artery disease (CAD) (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction, or documented silent ischemia) or coronary artery vasospasm, including Prinzmetal’s angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. History of stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or history of hemiplegic or basilar migraine because these patients are at a higher risk of stroke [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Peripheral vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Ischemic bowel disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Recent (i.e., within 24 hours) use of ergotamine-containing medication, ergot-type medication (such as dihydroergotamine or methysergide), or another 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) agonist [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.3)]. Concurrent administration of an MAO-A inhibitor or recent (within 2 weeks) use of a MAO-A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Known hypersensitivity to sumatriptan or components of ZECUITY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.11)]. Severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Allergic contact dermatitis to ZECUITY [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Warnings
5.1 Risk of Injury During Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Procedure Zecuity contains metal parts and must be removed before an MRI procedure.
5.2 Allergic Contact Dermatitis Use of ZECUITY may lead to allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). In two long-term open-label studies where patients were allowed to treat multiple migraine attacks for up to 1 year, the overall adverse event rate of ACD was 4%. ZECUITY should be discontinued if ACD is suspected. Erythema is commonly seen with use of ZECUITY and is not by itself an indication of sensitization. Following sensitization with ZECUITY, erythematous plaque and/or erythemato-vesicular or erythemato-bullous eruptions may develop. Clinical course is characterized by crescendo phenomenon of worsening pruritus and appearance over time with slower resolution to normal of affected skin areas.
Patients sensitized from use of ZECUITY, as evidenced by development of ACD, may develop systemic sensitization or other systemic reactions if sumatriptan-containing products are taken via other routes, e.g., orally or subcutaneously. It is possible that some patients who developed ACD with sumatriptan by exposure to ZECUITY, and who have developed systemic sensitization, may not be able to take sumatriptan in any form.
Patients who develop ACD with ZECUITY and require treatment with sumatriptan via other routes should receive their first subsequent dose under close medical supervision.
5.3 Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal’s Angina The use of ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with ischemic or vasospastic CAD. There have been rare reports of serious cardiac adverse reactions, including acute myocardial infarction, occurring within a few hours following administration of sumatriptan. Some of these reactions occurred in patients without known CAD. 5-HT1 agonists, including ZECUITY, may cause coronary artery vasospasm (Prinzmetal’s angina), even in patients without a history of CAD.
Perform a cardiovascular evaluation in triptan-naive patients who have multiple cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., increased age, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to using ZECUITY. Do not use ZECUITY if there is evidence of CAD or coronary artery vasospasm [see Contraindications (4)]. For patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors who have a negative cardiovascular evaluation, consider using the first ZECUITY TDS in a medically supervised setting and performing an electrocardiogram (ECG) upon activation of ZECUITY. For such patients, consider periodic cardiovascular evaluation in intermittent long-term users of ZECUITY.
5.4 Arrhythmias Life-threatening disturbances of cardiac rhythm, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation leading to death, have been reported within a few hours following the administration of 5-HT1 agonists. Discontinue ZECUITY if these disturbances occur. ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders [see Contraindications (4)].
5.5 Chest, Throat, Neck and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure Sensations of tightness, pain, pressure, and heaviness in the chest, throat, neck, and jaw commonly occur after treatment with sumatriptan and are usually non-cardiac in origin. However, perform a cardiac evaluation if these patients are at high cardiac risk. The use of ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients shown with CAD and those with Prinzmetal’s variant angina [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Cerebrovascular Events Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke have occurred in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the 5-HT1 agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine when they were not.
As with other acute migraine therapies, before treating headaches in patients not previously diagnosed as migraineurs, and in migraineurs who present with atypical symptoms, exclude other potentially serious neurological conditions. ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with a history of stroke or TIA [see Contraindications (4)].
5.7 Other Vasospasm Reactions 5-HT1 agonists, including ZECUITY, may cause non-coronary vasospastic reactions, such as peripheral vascular ischemia, gastrointestinal vascular ischemia and infarction (presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea), splenic infarction, and Raynaud’s syndrome. In patients who experience symptoms or signs suggestive of a vasospastic reaction following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist, rule out a vasospastic reaction before using ZECUITY [see Contraindications (4)].
Reports of transient and permanent blindness and significant partial vision loss have been reported with the use of 5-HT1 agonists. Since visual disorders may be part of a migraine attack, a causal relationship between these events and the use of 5-HT1 agonists have not been clearly established.
5.8 Medication Overuse Headache Overuse of acute migraine drugs (e.g., ergotamine, triptans, opioids, combination of drugs for 10 or more days per month) may lead to exacerbation of headache (medication overuse headache). Medication overuse headache may present as migraine-like daily headaches or as a marked increase in frequency of migraine attacks. Detoxification of patients, including withdrawal of the overused drugs, and treatment of withdrawal symptoms (which often includes a transient worsening of headache) may be necessary.
5.9 Serotonin Syndrome Serotonin syndrome may occur with triptans, including ZECUITY, particularly during coadministration with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and MAO inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.4)]. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms usually occurs within minutes to hours of receiving a new or a greater dose of a serotonergic medication. Discontinue ZECUITY if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
5.10 Increase in Blood Pressure Significant elevation in blood pressure, including hypertensive crisis with acute impairment of organ systems, has been reported on rare occasions in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, including patients without a history of hypertension. Monitor blood pressure in patients treated with ZECUITY. ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension [see Contraindications (4)].
5.11 Anaphylactic/Anaphylactoid Reactions Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions have occurred in patients receiving sumatriptan. Such reactions can be life threatening or fatal. In general, anaphylactic reactions to drugs are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. ZECUITY is contraindicated in patients with prior serious anaphylactic reaction.
5.12 Seizures Seizures have been reported following administration of sumatriptan. Some have occurred in patients with either a history of seizures or concurrent conditions predisposing to seizures. There are also reports in patients where no such predisposing factors are apparent. ZECUITY should be used with caution in patients with a history of epilepsy or conditions associated with a lowered seizure threshold.
5.13 Electrically-active Implantable or Body-worn Medical Devices ZECUITY should not be applied in areas near or over electrically-active implantable or body-worn medical devices (e.g., implantable cardiac pacemaker, body-worn insulin pump, implantable deep brain stimulator).
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two long-term, open-label studies in which patients were allowed to treat multiple migraine attacks for up to 1 year, 15% (99 out of 662) withdrew from the study because of adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions leading to withdrawal from the study were contact dermatitis (4%) and application site pain (4%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) in a controlled single dose study were application site pain, paresthesia, pruritus, warmth, and discomfort.
Controlled single dose acute migraine study
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred at a frequency of 2% or greater in a controlled clinical study of ZECUITY in patients with acute migraine (Study 1) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. In that study, patients randomized to the control group used the same activated iontophoretic transdermal delivery system (TDS) as patients randomized to ZECUITY, with the only difference being the absence of sumatriptan in the drug reservoir. Therefore, patients in the control group were exposed to same TDS-related risks as patients in the ZECUITY group, minus the risks related to sumatriptan. Only reactions that occurred at a frequency of 2% or more in patients treated with ZECUITY or control are included in Table 1.

The incidence of "atypical sensations" adverse events (paresthesia, sensation warm/cold) and "pain and other pressure sensations" (chest pain/tightness/pressure/heaviness or neck/throat/jaw pain, tightness, pressure or heaviness) was 2% each in ZECUITY-treated patients, vs. 0% in the control group. Application site bruising was reported in 2 ZECUITY-treated patients (0.9%) vs. no patient in the control group.
Subgroup analyses of age (≤41 years, >41 years), race (Caucasian, non-Caucasian) and body mass index (BMI) (≤25.7 mg/kg2, >25.7 mg/kg2) showed no difference between subgroups for adverse events.
Skin Irritation Examination
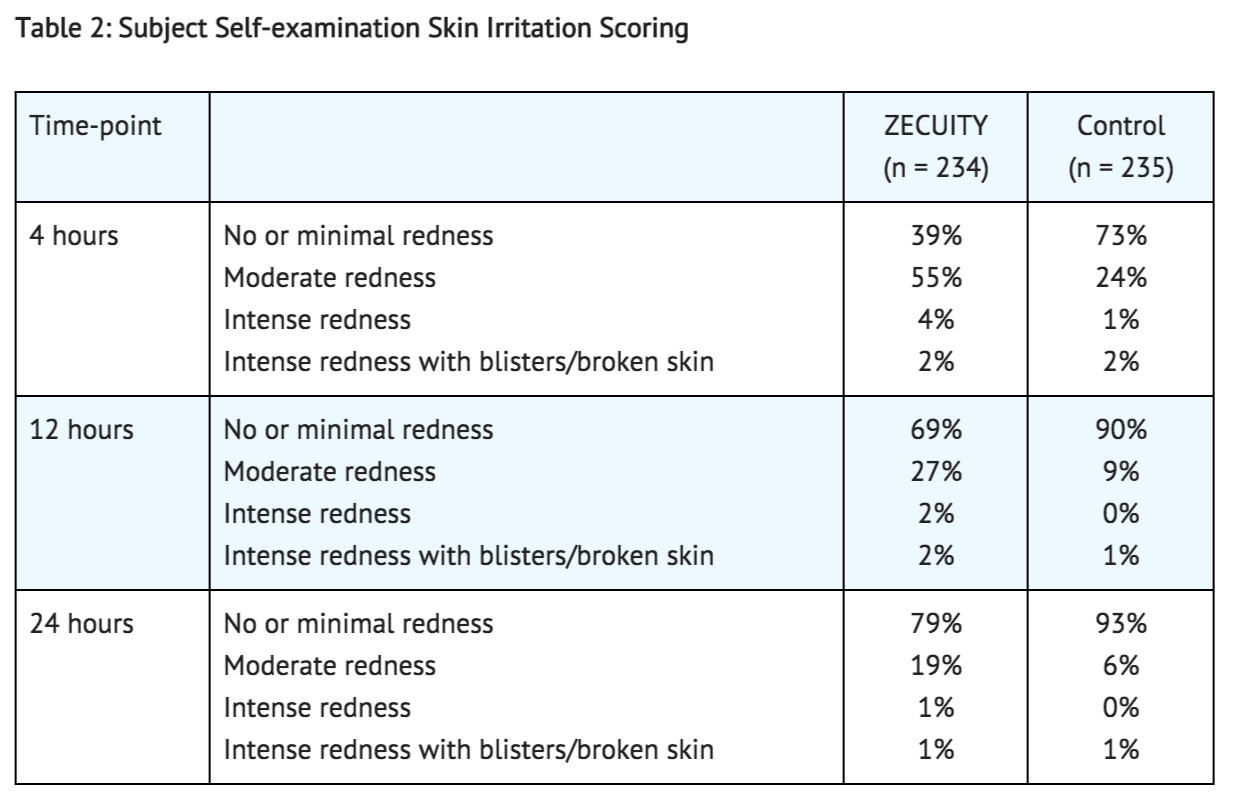
In Study 1, patients performed their own examination of the TDS application site at 4, 12, and 24 hours post TDS activation, and daily thereafter until resolution. Skin irritation examination scores are summarized in Table 2. The median time to "no redness" was 2.6 days for Zecuity compared with 0.3 day in the control group.
Application site reactions across clinical studies (Controlled single dose acute migraine study and long term safety studies)
In the controlled and uncontrolled clinical studies combined (n = 796 unique ZECUITY-treated subjects), the frequency of application site reactions of clinical interest is presented in Table 3.

Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
7.1 Ergot-Containing Drugs Ergot-containing drugs have been reported to cause prolonged vasospastic reactions. Because these effects may be additive, use of ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medications (like dihydroergotamine or methysergide) and ZECUITY within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated [see Warnings and Precautions (4)].
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase-A Inhibitors MAO-A inhibitors increase systemic exposure by 2-fold. Therefore, the use of ZECUITY in patients receiving MAO-A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Other 5-HT1 Agonists Because their vasospastic effects may be additive, coadministration of ZECUITY and other 5-HT1 agonists (e.g., triptans) within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated.
7.4 Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors/Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors and Serotonin Syndrome Cases of serotonin syndrome have been reported during coadministration of triptans and SSRIs or SNRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAO inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): C There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ZECUITY should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
When sumatriptan was administered intravenously to pregnant rabbits daily throughout the period of organogenesis, embryolethality was observed at doses at or close to those producing maternal toxicity. Oral administration of sumatriptan to rabbits during organogenesis was associated with increased incidences of fetal vascular and skeletal abnormalities; the highest no-effect dose for these effects was 15 mg/kg/day. The intravenous administration of sumatriptan to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis did not produce evidence of embryolethality. The subcutaneous administration of sumatriptan to pregnant rats prior to and throughout pregnancy did not produce evidence of embryolethality or teratogenicity.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether sumatriptan is excreted in human milk following transdermal administration. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ZECUITY, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Two controlled clinical trials evaluated sumatriptan nasal spray (5 to 20 mg) in 1,248 adolescent migraineurs aged 12 to 17 years who treated a single attack. The trials did not establish the efficacy of sumatriptan nasal spray compared with placebo in the treatment of migraine in adolescents. Adverse reactions observed in these clinical trials were similar in nature to those reported in clinical trials in adults.
Five controlled clinical trials (2 single-attack studies, 3 multiple-attack studies) evaluating oral sumatriptan (25 to 100 mg) in pediatric patients aged 12 to 17 years enrolled a total of 701 adolescent migraineurs. These studies did not establish the efficacy of oral sumatriptan compared to placebo in the treatment of migraine in adolescents. Adverse events observed in these clinical trials were similar in nature to those reported in clinical trials in adults. The frequency of all adverse events in these patients appeared to be both dose- and age dependent, with younger patients reporting events more commonly than older adolescents.
Post-marketing experience documents that serious adverse events have occurred in the pediatric population after use of subcutaneous, oral, and/or intranasal sumatriptan. These reports include events similar in nature to those reported rarely in adults, including stroke, visual loss, and death. A myocardial infarction has been reported in a 14-year-old male following the use of oral sumatriptan; clinical signs occurred within 1 day of drug administration. Since clinical data to determine the frequency of serious adverse reactions in pediatric patients who might receive subcutaneous, oral, or intranasal sumatriptan are not presently available, the use of ZECUITY in patients under 18 years of age is not recommended.
Geriatic Use
Clinical trials of ZECUITY did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
A cardiovascular evaluation is recommended for geriatric patients who have other cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to using ZECUITY
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Sumatriptan (transdermal) in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Sumatriptan (transdermal) and IV administrations.
Overdosage
No gross overdoses in clinical practice have been reported. Coronary vasospasm was observed after intravenous administration of sumatriptan injection [see Contraindications (4)]. Overdoses would be expected from animal data (dogs at 0.1 g/kg, rats at 2 g/kg) to possibly cause convulsions, tremor, inactivity, erythema of the extremities, reduced respiratory rate, cyanosis, ataxia, mydriasis, injection site reactions (desquamation, hair loss, and scab formation), and paralysis.
The apparent elimination half-life of sumatriptan after ZECUITY administration is about 3 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], and therefore monitoring of patients after overdose with ZECUITY should continue for at least 15 hours or while symptoms or signs persist.
It is unknown what effect hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis has on the serum concentrations of sumatriptan.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
ZECUITY (sumatriptan iontophoretic transdermal system) is a disposable, single use system designed to deliver sumatriptan through the skin using iontophoresis. Iontophoresis is a non-invasive method of delivering a drug through the skin using a low electrical current. The ZECUITY electronics, powered by two coin cell lithium batteries, control the amount of current applied and the rate and amount of sumatriptan delivered.
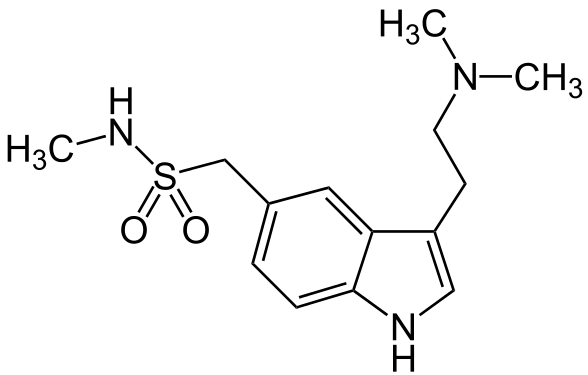
Sumatriptan succinate, the active component of ZECUITY, is a selective 5-hydroxy-tryptamine receptor subtype 1 (5-HT1) agonist (triptan). Sumatriptan succinate is chemically designated as 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-N-methyl-indole-5-methanesulfonamide succinate (1:1), and has the following structure:

The empirical formula is C14H21N3O2S•C4H6O4 representing a molecular weight of 413.5.
Sumatriptan succinate is a white to off-white powder that is freely soluble in water. Each ZECUITY iontophoretic transdermal system contains 86 mg sumatriptan (base) as the succinate salt in an aqueous formulation. ZECUITY, upon activation, delivers 6.5 mg of sumatriptan through the skin over 4 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
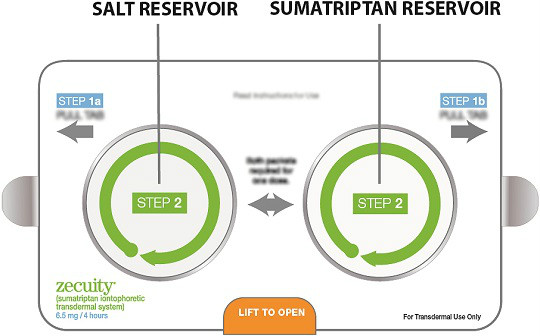
ZECUITY iontophoretic transdermal system is composed of an iontophoretic device and a drug reservoir card. The reservoir card contains 2 non-woven pads and 2 different gel formulations; one a sumatriptan succinate formulation and the other a sodium salt formulation. The sumatriptan succinate formulation and pad contains the following inactive ingredients: purified water, basic butylated methacrylate copolymer (polyamine), lauric acid, adipic acid, methylparaben and a non-woven viscose pad. The salt formulation and pad contains: purified water, hydroxypropylcellulose, sodium chloride, methylparaben and a non-woven viscose pad. ZECUITY is a non-sterile product.
The iontophoretic device consists of medical grade adhesive fabric and foam and a plastic dome that contains an activation button, batteries, and electronics (see Figure 2). Figure 2: Iontophoretic Device

The sumatriptan and salt pads are housed in individual reservoirs. Each reservoir is sealed by a foil strip that is removed prior to transfer of the pads to the iontophoretic device (see Figure 3). The iontophoretic device and foil reservoirs are co-packaged in a single unit pouch [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Figure 3: Reservoir Card
For ZECUITY to function, the pads must completely cover the electrodes.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Sumatriptan (transdermal) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Sumatriptan (transdermal) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Sumatriptan (transdermal) interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Sumatriptan (transdermal) Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.