Sitagliptin
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Sitagliptin is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Common adverse reactions include hypoglycemia, headache, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory infection.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Monotherapy and Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Dosing Information
- The recommended dose of JANUVIA is 100 mg once daily. JANUVIA can be taken with or without food.
- Patients with Renal Insufficiency
- For patients with mild renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance [CrCl] greater than or equal to 50 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of less than or equal to 1.7 mg/dL in men and less than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL in women), no dosage adjustment for JANUVIA is required.
- For patients with moderate renal insufficiency (CrCl greater than or equal to 30 to less than 50 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of greater than 1.7 to less than or equal to 3.0 mg/dL in men and greater than 1.5 to less than or equal to 2.5 mg/dL in women), the dose of JANUVIA is 50 mg once daily.
- For patients with severe renal insufficiency (CrCl less than 30 mL/min, approximately corresponding to serum creatinine levels of greater than 3.0 mg/dL in men and greater than 2.5 mg/dL in women) or with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, the dose of JANUVIA is 25 mg once daily. JANUVIA may be administered without regard to the timing of dialysis.
- Because there is a need for dosage adjustment based upon renal function, assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiation of JANUVIA and periodically thereafter. Creatinine clearance can be estimated from serum creatinine using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. There have been postmarketing reports of worsening renal function in patients with renal insufficiency, some of whom were cascribed inappropriate doses of sitagliptin.
- Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or with Insulin
- When JANUVIA is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or with insulin, a lower dose of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sitagliptin in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sitagliptin in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
- Safety and effectiveness of JANUVIA in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sitagliptin in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sitagliptin in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- History of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to sitagliptin, such as anaphylaxis or angioedema.
Warnings
- Pancreatitis
- There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, in patients taking JANUVIA. After initiation of JANUVIA, patients should be observed carefully for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, JANUVIA should promptly be discontinued and appropriate management should be initiated. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using JANUVIA.
- Renal Impairment
- Assessment of renal function is recommended prior to initiating JANUVIA and periodically thereafter. A dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency and in patients with ESRD requiring hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Caution should be used to ensure that the correct dose of JANUVIA is prescribed for patients with moderate (creatinine clearance ≥30 to <50 mL/min) or severe (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) renal impairment.
- There have been postmarketing reports of worsening renal function, including acute renal failure, sometimes requiring dialysis. A subset of these reports involved patients with renal insufficiency, some of whom were prescribed inappropriate doses of sitagliptin. A return to baseline levels of renal insufficiency has been observed with supportive treatment and discontinuation of potentially causative agents. Consideration can be given to cautiously reinitiating JANUVIA if another etiology is deemed likely to have precipitated the acute worsening of renal function.
- JANUVIA has not been found to be nephrotoxic in preclinical studies at clinically relevant doses, or in clinical trials.
- Use with Medications Known to Cause Hypoglycemia
- When JANUVIA was used in combination with a sulfonylurea or with insulin, medications known to cause hypoglycemia, the incidence of hypoglycemia was increased over that of placebo used in combination with a sulfonylurea or with insulin. Therefore, a lower dose of sulfonylurea or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with JANUVIA. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Onset of these reactions occurred within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with JANUVIA, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue JANUVIA, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes.
- Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema with another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with JANUVIA.
- Macrovascular Outcomes
- There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with JANUVIA or any other anti-diabetic drug.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
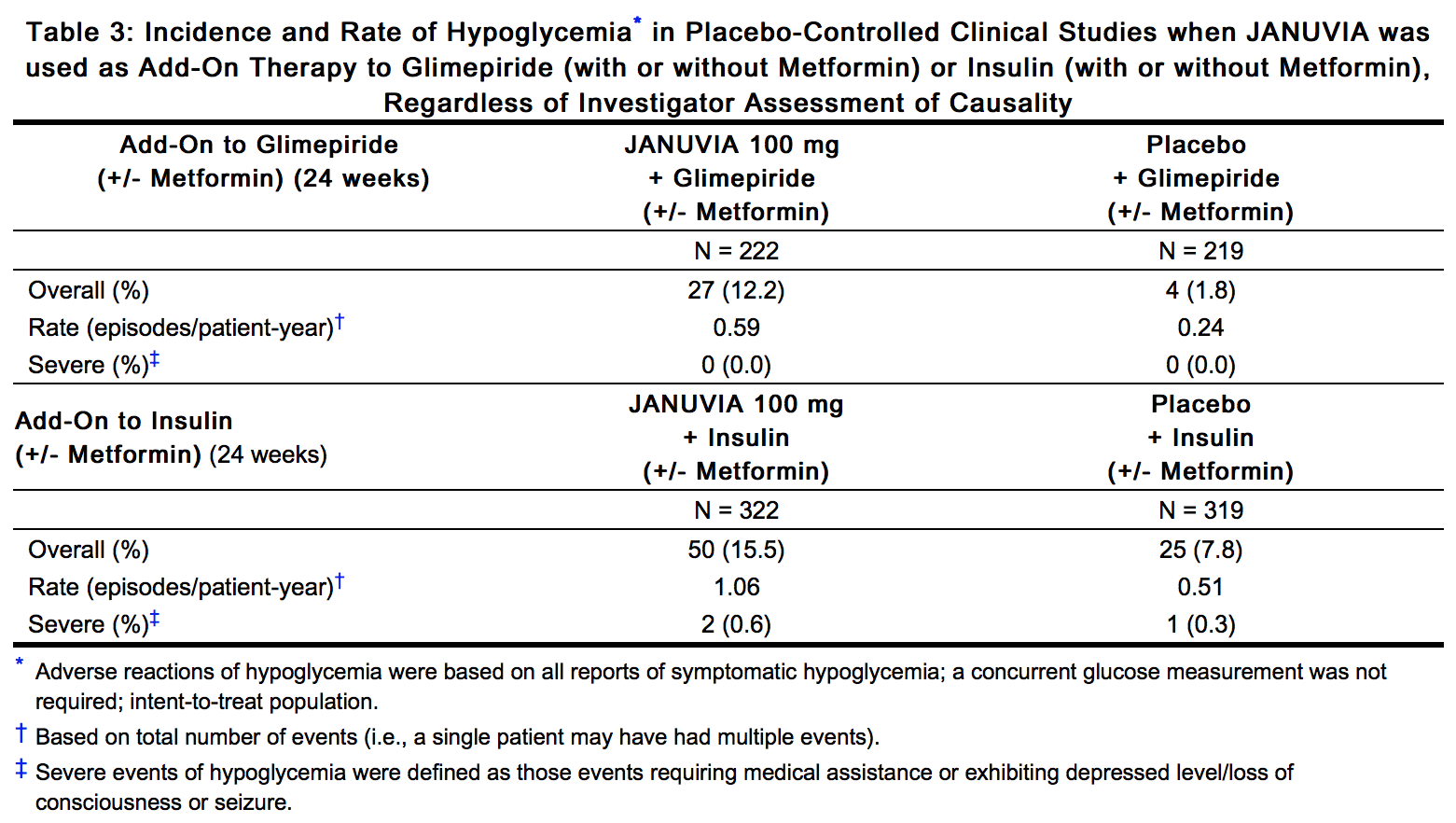
- In controlled clinical studies as both monotherapy and combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone, or rosiglitazone and metformin, the overall incidence of adverse reactions, hypoglycemia, and discontinuation of therapy due to clinical adverse reactions with JANUVIA were similar to placebo. In combination with glimepiride, with or without metformin, the overall incidence of clinical adverse reactions with JANUVIA was higher than with placebo, in part related to a higher incidence of hypoglycemia (see Table 3); the incidence of discontinuation due to clinical adverse reactions was similar to placebo.
- Two placebo-controlled monotherapy studies, one of 18- and one of 24-week duration, included patients treated with JANUVIA 100 mg daily, JANUVIA 200 mg daily, and placebo. Five placebo-controlled add-on combination therapy studies were also conducted: one with metformin; one with pioglitazone; one with metformin and rosiglitazone; one with glimepiride (with or without metformin); and one with insulin (with or without metformin). In these trials, patients with inadequate glycemic control on a stable dose of the background therapy were randomized to add-on therapy with JANUVIA 100 mg daily or placebo. The adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, reported regardless of investigator assessment of causality in ≥5% of patients treated with JANUVIA 100 mg daily and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo, are shown in Table 1 for the clinical trials of at least 18 weeks duration. Incidences of hypoglycemia are shown in Table 3.
- In the 24-week study of patients receiving JANUVIA as add-on combination therapy with metformin, there were no adverse reactions reported regardless of investigator assessment of causality in ≥5% of patients and more commonly than in patients given placebo.
- In the 24-week study of patients receiving JANUVIA as add-on therapy to insulin (with or without metformin), there were no adverse reactions reported regardless of investigator assessment of causality in ≥5% of patients and more commonly than in patients given placebo, except for hypoglycemia (see Table 3).
- In the study of JANUVIA as add-on combination therapy with metformin and rosiglitazone (Table 1), through Week 54 the adverse reactions reported regardless of investigator assessment of causality in ≥5% of patients treated with JANUVIA and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo were: upper respiratory tract infection (JANUVIA, 15.5%; placebo, 6.2%), nasopharyngitis (11.0%, 9.3%), peripheral edema (8.3%, 5.2%), and headache (5.5%, 4.1%).
- In a pooled analysis of the two monotherapy studies, the add-on to metformin study, and the add-on to pioglitazone study, the incidence of selected gastrointestinal adverse reactions in patients treated with JANUVIA was as follows: abdominal pain (JANUVIA 100 mg, 2.3%; placebo, 2.1%), nausea (1.4%, 0.6%), and diarrhea (3.0%, 2.3%).
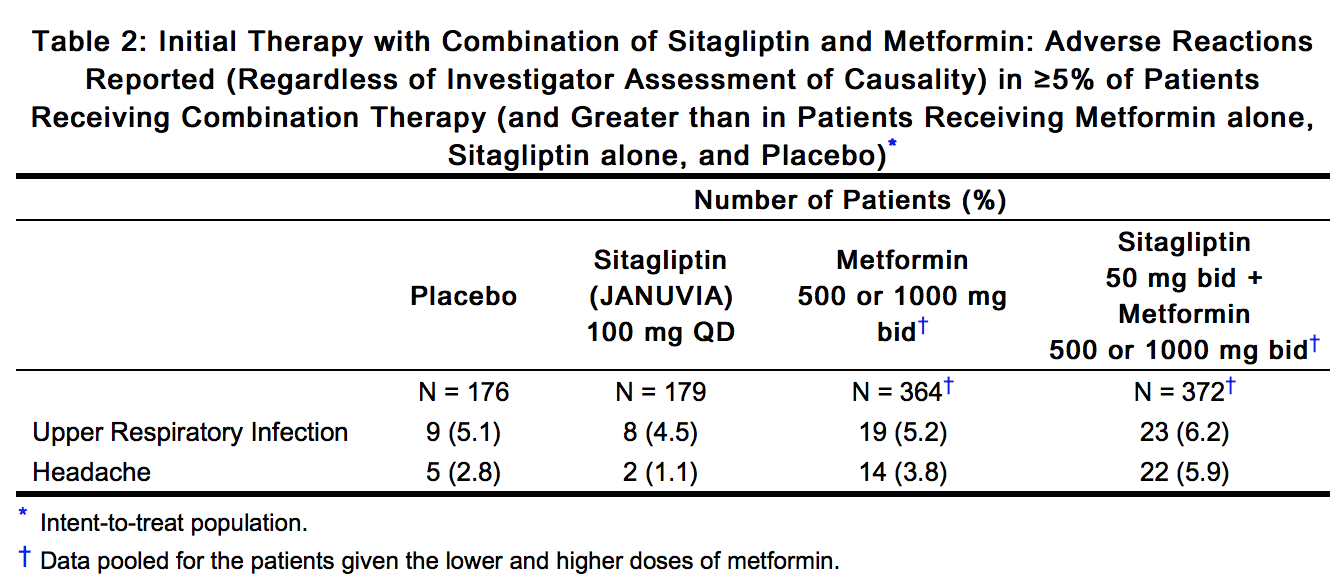
- In an additional, 24-week, placebo-controlled factorial study of initial therapy with sitagliptin in combination with metformin, the adverse reactions reported (regardless of investigator assessment of causality) in ≥5% of patients are shown in Table 2.
- In a 24-week study of initial therapy with JANUVIA in combination with pioglitazone, there were no adverse reactions reported (regardless of investigator assessment of causality) in ≥5% of patients and more commonly than in patients given pioglitazone alone.
- No clinically meaningful changes in vital signs or in ECG (including in QTc interval) were observed in patients treated with JANUVIA.
- In a pooled analysis of 19 double-blind clinical trials that included data from 10,246 patients randomized to receive sitagliptin 100 mg/day (N=5429) or corresponding (active or placebo) control (N=4817), the incidence of acute pancreatitis was 0.1 per 100 patient-years in each group (4 patients with an event in 4708 patient-years for sitagliptin and 4 patients with an event in 3942 patient-years for control).
- Hypoglycemia
- In all (N=9) studies, adverse reactions of hypoglycemia were based on all reports of symptomatic hypoglycemia. A concurrent blood glucose measurement was not required although most (74%) reports of hypoglycemia were accompanied by a blood glucose measurement ≤70 mg/dL. When JANUVIA was co-administered with a sulfonylurea or with insulin, the percentage of patients with at least one adverse reaction of hypoglycemia was higher than in the corresponding placebo group (Table 3).
- In a pooled analysis of the two monotherapy studies, the add-on to metformin study, and the add-on to pioglitazone study, the overall incidence of adverse reactions of hypoglycemia was 1.2% in patients treated with JANUVIA 100 mg and 0.9% in patients treated with placebo.
- In the study of JANUVIA as add-on combination therapy with metformin and rosiglitazone, the overall incidence of hypoglycemia was 2.2% in patients given add-on JANUVIA and 0.0% in patients given add-on placebo through Week 18. Through Week 54, the overall incidence of hypoglycemia was 3.9% in patients given add-on JANUVIA and 1.0% in patients given add-on placebo.
- In the 24-week, placebo-controlled factorial study of initial therapy with JANUVIA in combination with metformin, the incidence of hypoglycemia was 0.6% in patients given placebo, 0.6% in patients given JANUVIA alone, 0.8% in patients given metformin alone, and 1.6% in patients given JANUVIA in combination with metformin.
- In the study of JANUVIA as initial therapy with pioglitazone, one patient taking JANUVIA experienced a severe episode of hypoglycemia. There were no severe hypoglycemia episodes reported in other studies except in the study involving co-administration with insulin.
- Laboratory Tests
- Across clinical studies, the incidence of laboratory adverse reactions was similar in patients treated with JANUVIA 100 mg compared to patients treated with placebo. A small increase in white blood cell count (WBC) was observed due to an increase in neutrophils. This increase in WBC (of approximately 200 cells/microL vs placebo, in four pooled placebo-controlled clinical studies, with a mean baseline WBC count of approximately 6600 cells/microL) is not considered to be clinically relevant. In a 12-week study of 91 patients with chronic renal insufficiency, 37 patients with moderate renal insufficiency were randomized to JANUVIA 50 mg daily, while 14 patients with the same magnitude of renal impairment were randomized to placebo. Mean (SE) increases in serum creatinine were observed in patients treated with JANUVIA [0.12 mg/dL (0.04)] and in patients treated with placebo [0.07 mg/dL (0.07)]. The clinical significance of this added increase in serum creatinine relative to placebo is not known.
Postmarketing Experience
- Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of JANUVIA as monotherapy and/or in combination with other antihyperglycemic agents. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria, cutaneous vasculitis, and exfoliative skin conditions including Stevens-Johnson syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]; hepatic enzyme elevations; acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic and necrotizing pancreatitis [see Indications and Usage (1.2); Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]; worsening renal function, including acute renal failure (sometimes requiring dialysis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]; constipation; vomiting; headache; arthralgia; myalgia; pain in extremity; back pain.
Drug Interactions
- Digoxin
- There was a slight increase in the area under the curve (AUC, 11%) and mean peak drug concentration (Cmax, 18%) of digoxin with the co-administration of 100 mg sitagliptin for 10 days. Patients receiving digoxin should be monitored appropriately. No dosage adjustment of digoxin or JANUVIA is recommended.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits. Doses of sitagliptin up to 125 mg/kg (approximately 12 times the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose) did not impair fertility or harm the fetus. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., maintains a registry to monitor the pregnancy outcomes of women exposed to JANUVIA while pregnant. Health care providers are encouraged to report any prenatal exposure to JANUVIA by calling the Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-986-8999.
- Sitagliptin administered to pregnant female rats and rabbits from gestation day 6 to 20 (organogenesis) was not teratogenic at oral doses up to 250 mg/kg (rats) and 125 mg/kg (rabbits), or approximately 30- and 20-times human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 100 mg/day based on AUC comparisons. Higher doses increased the incidence of rib malformations in offspring at 1000 mg/kg, or approximately 100 times human exposure at the MRHD.
- Sitagliptin administered to female rats from gestation day 6 to lactation day 21 decreased body weight in male and female offspring at 1000 mg/kg. No functional or behavioral toxicity was observed in offspring of rats.
- Placental transfer of sitagliptin administered to pregnant rats was approximately 45% at 2 hours and 80% at 24 hours postdose. Placental transfer of sitagliptin administered to pregnant rabbits was approximately 66% at 2 hours and 30% at 24 hours.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Sitagliptin in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Sitagliptin during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Sitagliptin is secreted in the milk of lactating rats at a milk to plasma ratio of 4:1. It is not known whether sitagliptin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when JANUVIA is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness of JANUVIA in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- Of the total number of subjects (N=3884) in pre-approval clinical safety and efficacy studies of JANUVIA, 725 patients were 65 years and over, while 61 patients were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between subjects 65 years and over and younger subjects. While this and other reported clinical experience have not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
- This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection in the elderly, and it may be useful to assess renal function in these patients prior to initiating dosing and periodically thereafter.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sitagliptin with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sitagliptin with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sitagliptin in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sitagliptin in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sitagliptin in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Sitagliptin in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
- Patients receiving digoxin should be monitored appropriately.
- In the event of an overdose, it is reasonable to employ the usual supportive measures, e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring (including obtaining an electrocardiogram), and institute supportive therapy as dictated by the patient's clinical status.
- Patients should also be informed about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, regular physical activity, periodic blood glucose monitoring and A1C testing, recognition and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and assessment for diabetes complications.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- During controlled clinical trials in healthy subjects, single doses of up to 800 mg JANUVIA were administered. Maximal mean increases in QTc of 8.0 msec were observed in one study at a dose of 800 mg JANUVIA, a mean effect that is not considered clinically important [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. There is no experience with doses above 800 mg in clinical studies. In Phase I multiple-dose studies, there were no dose-related clinical adverse reactions observed with JANUVIA with doses of up to 600 mg per day for periods of up to 10 days and 400 mg per day for up to 28 days.
Management
- In the event of an overdose, it is reasonable to employ the usual supportive measures, e.g., remove unabsorbed material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring (including obtaining an electrocardiogram), and institute supportive therapy as dictated by the patient's clinical status.
- Sitagliptin is modestly dialyzable. In clinical studies, approximately 13.5% of the dose was removed over a 3- to 4-hour hemodialysis session. Prolonged hemodialysis may be considered if clinically appropriate. It is not known if sitagliptin is dialyzable by peritoneal dialysis.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Sitagliptin Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Sitagliptin Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Sitagliptin |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Sitagliptin |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Sitagliptin in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Sitagliptin interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Januvia®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Januvia® — Enjuvia®[2]
- Januvia® — Jantoven®[2]
- Januvia® — Janumet®[2]
- sitaGLIPtin® — SUMAtriptan®[2]
- sitaGLIPtin® — ZOLMitriptan®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "JANUVIA (sitagliptin) tablet, film coated".
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Sitagliptin |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sitagliptin |Label Name=Sitagliptin11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sitagliptin |Label Name=Sitagliptin11.png
}}