Circle of Willis
|
WikiDoc Resources for Circle of Willis |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Circle of Willis Most cited articles on Circle of Willis |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Circle of Willis |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Circle of Willis at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Circle of Willis Clinical Trials on Circle of Willis at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Circle of Willis NICE Guidance on Circle of Willis
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Circle of Willis Discussion groups on Circle of Willis Patient Handouts on Circle of Willis Directions to Hospitals Treating Circle of Willis Risk calculators and risk factors for Circle of Willis
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Circle of Willis |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
The circle of Willis (also called the cerebral arterial circle or arterial circle of Willis) is a circle of arteries that supply blood to the brain. It is named after Thomas Willis (1621-1673), an English physician.[1]
Components
- Anterior cerebral artery (left and right)
- Anterior communicating artery
- Internal carotid artery (left and right)
- Posterior cerebral artery (left and right)
- Posterior communicating artery (left and right)
The basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries, though they supply the brain, are not considered part of the circle.[2]
Physiologic significance
The arrangement of the brain's arteries into the Circle of Willis creates redundancies in the cerebral circulation. If one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed (stenosed) or one of the arteries supplying the circle is blocked or narrowed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can often preserve the cerebral perfusion well enough to avoid the symptoms of ischemia.[3]
Anatomic variation
Considerable anatomic variation exists in the circle of Willis. The "textbook version" of the circle, based on a series of 1413 brains, is only seen in 34.5% of cases.[4] In one common variation the proximal part of the posterior cerebral artery is narrow and its ipsilateral posterior communicating artery is large, so the internal carotid artery supplies the posterior cerebrum. In another variation the anterior communicating artery is a large vessel, such that a single internal carotid supplies both anterior cerebral arteries.
Subclavian steal and the circle of Willis
The redundancies that the circle of Willis introduce can also lead to reduced cerebral perfusion.[5][6] In subclavian steal syndrome, which results from a proximal stenosis (narrowing) of the subclavian artery (a vessel that is supplied by the same vessel (the Aorta) that eventually feeds the circle of Willis via the Common carotid artery), blood is "stolen" from the circle of Willis to preserve blood flow to the upper limb.
Origin of arteries
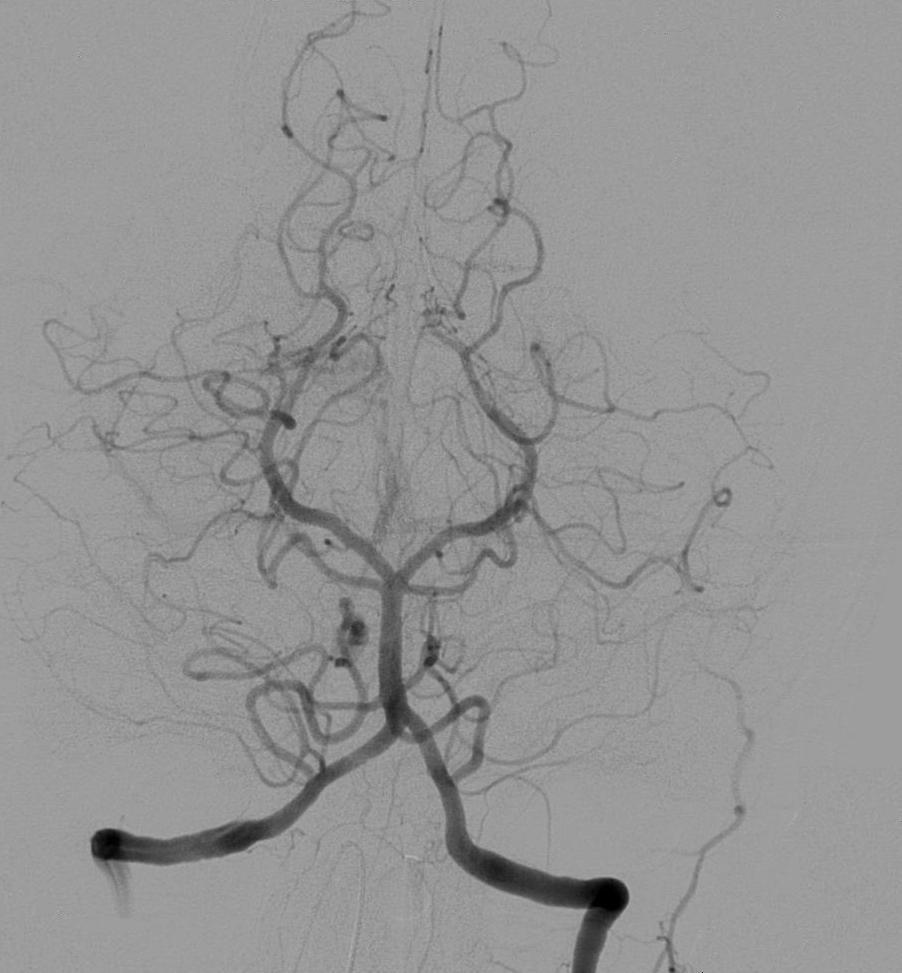
The left and right internal carotid arteries arise from the right and left common carotid arteries.
The Posterior Communicating Artery is given off as a branch of the Internal Carotid Artery just before it divides into its terminal branches - the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries. The Anterior Cerebral Artery forms the anterolateral portion of the Circle of Willis, while the Middle Cerebral Artery does not contribute to the Circle.
The right and left posterior cerebral arteries arise from the basilar artery, which is formed by the left and right vertebral arteries. The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries.
The anterior communicating artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries and could be said to arise from either the left or right side.
All arteries involved give off cortical and central branches. The central branches supply the interior of the Circle of Willis, more specifically, the Interpeduncular fossa. The cortical branches are named for the area they supply. Since they do not directly affect the Circle of Willis, they are not dealt with here.
References
- ↑ Uston C. Dr. Thomas Willis' famous eponym: the circle of Willis. J Hist Neurosci. 2005 Mar;14(1):16-21. PMID 15804755. Free Full Text.
- ↑ Moore KL, Dalley AR. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 4th Ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Toronto. Copyright 1999. ISBN 0-683-06141-0.
- ↑ "Spect measurements of regional cerebral perfusion and carbondioxide reactivity: Correlation with cerebral collaterals in internal carotid artery occlusive disease". J Neurol. PMID 17063318.
- ↑ Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R, Circle of Willis. Illustrated Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation, URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/Cardiovascular/Text/Arteries/CircleofWillis.shtml. Accessed on November 6, 2005.
- ↑ Klingelhofer J, Conrad B, Benecke R, Frank B. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography of carotid-basilar collateral circulation in subclavian steal. Stroke. 1988 Aug;19(8):1036-42. PMID 3041649.
- ↑ Lord RS, Adar R, Stein RL. Contribution of the circle of Willis to the subclavian steal syndrome. Circulation. 1969 Dec;40(6):871-8. PMID 5377222.
Template:Arteries of head and neck