Ovarian cancer epidemiology and demographics: Difference between revisions
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Ovarian cancer}} | {{Ovarian cancer}} | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Rim}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of [[cancer]] death in [[women]], the leading cause of death from [[gynecology|gynecological]] malignancy, and the second most commonly diagnosed gynecologic malignancy.<ref>[http://www.merck.com/mrkshared/mmanual/section18/chapter241/241b.jsp The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy Section 18. Gynecology And Obstetrics Chapter 241. Gynecologic Neoplasms]</ref> | Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of [[cancer]] death in [[women]], the leading cause of death from [[gynecology|gynecological]] malignancy, and the second most commonly diagnosed gynecologic malignancy.<ref>[http://www.merck.com/mrkshared/mmanual/section18/chapter241/241b.jsp The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy Section 18. Gynecology And Obstetrics Chapter 241. Gynecologic Neoplasms]</ref> In the United States, the age-adjusted [[prevalence]] of ovarian cancer is 71.3 per 100,000 in 2011.<ref name="SEER">Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z,Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/, based on November 2013 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2014.</ref> | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
Revision as of 01:54, 13 June 2014
|
Ovarian cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ovarian cancer epidemiology and demographics On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ovarian cancer epidemiology and demographics |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Ovarian cancer epidemiology and demographics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Rim Halaby, M.D. [2]
Overview
Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in women, the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancy, and the second most commonly diagnosed gynecologic malignancy.[1] In the United States, the age-adjusted prevalence of ovarian cancer is 71.3 per 100,000 in 2011.[2]
Epidemiology and Demographics
Prevalence
- Ovarian cancer is more common in industrialized nations, with the exception of Japan. In the United States, females have a 1.4% to 2.5% (1 out of 40-60 women) lifetime chance of developing ovarian cancer.
- In the United States, the age-adjusted prevalence of ovarian cancer is 71.3 per 100,000 in 2011.[2]
Incidence
- The delay-adjusted incidence of ovarian cancer in 2011 was estimated to be 12.46 per 100,000 persons in the United States.[2]
- In 2011, the age-adjusted incidence of ovarian cancer was 12.09 per 100,000 persons in the United States.[2]
Age
- Older women are at highest risk. More than half of the deaths from ovarian cancer occur in women between 55 and 74 years of age.
- While the overall age-adjusted incidence of ovarian cancer in the United States between 2007 and 2011 is 12.3 per 100,000, the age-adjusted incidence of ovarian cancer by age category is:[2]
- Under 65 years: 7.5 per 100,000
- 65 and over: 45.2 per 100,000
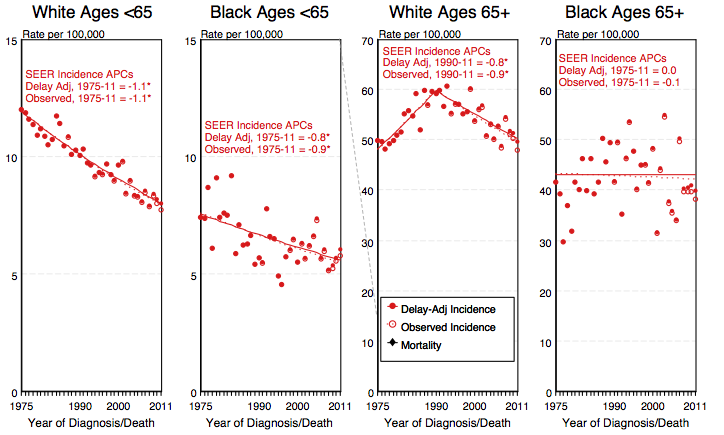
- Shown below is an image depicting the delay-adjusted incidence and observed incidence of ovarian cancer by age and race in the United States between 1975 and 2011. These graphs are adapted from SEER: The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program of the National Cancer Institute.[2]
Race
- Shown below is a table depicting the age-adjusted prevalence of ovarian cancer by race in 2011 in the United States.[2]
| All Races | White | Black | Asian/Pacific Islander | Hispanic | |
| Age-adjusted prevalence | 71.3 per 100,000 | 76.2 per 100,000 | 44.2 per 100,000 | 63.2 per 100,000 | 59.1 per 100,000 |
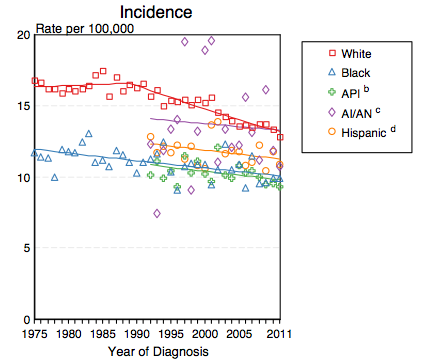
- Shown below is an image depicting the incidence of ovarian cancer by race in the United States between 1975 and 2011.[2]
API: Asian/Pacific Islander; AI/AN: American Indian/ Alaska Native
Percent Distribution of Ovarian Cancer by Histology
Among patients with histologically confirmed cases of ovarian cancer, the percent distribution of the types of the disease between 2007 and 2011 in the United States are:[2]
- Carcinoma: 91.7%
- Epidermoid carcinoma: 0.7%
- Adenocarcinoma: 84%
- Adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified: 12.3%
- Papillary adenocarcinoma: 1,5%
- Clear cell adenocarcinoma: 5.2%
- Endometrioid carcinoma: 9.7%
- Cystadenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified: 0.4%
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma: 20.9%
- Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma: 23.5%
- Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: 1.5%
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma: 3.5%
- Mucin-producing adenocarcinoma: 0.2%
- Other adenocarcinoma: 5.3%
- Other specific carcinoma: 2.3%
- Stromal cell tumor: 1.6%
- Other: 0.7%
- Unspecified carcinoma, not otherwise specified: 4.6%
- Sarcoma and other soft tissues: 0.4%
- Other specific types: 6.9%
- Mullerian mixed tumor: 3%
- Malignant teratoma: 1.5%
- Other: 2.4%
- Unspecified: 1.1%
References
- ↑ The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy Section 18. Gynecology And Obstetrics Chapter 241. Gynecologic Neoplasms
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z,Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/, based on November 2013 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2014.