WBR0465: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
|MainCategory=Microbiology | |MainCategory=Microbiology | ||
|SubCategory=Genitourinary | |SubCategory=Genitourinary | ||
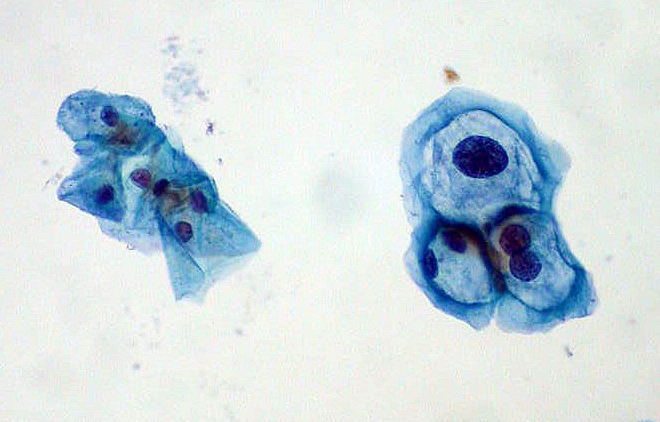
|Prompt=A | |Prompt=A 60 year old female patient presents to her physician’s office for post-coital bleeding. Following appropriate work-up, the pathology identified in this patient is similar to the image shown below. Which of the following characteristics appropriately describes the etiology of the patient's condition? | ||
[[Image:ThinPrep Pap smear HPV.jpeg|350px]] | [[Image:ThinPrep Pap smear HPV.jpeg|350px]] | ||
|Explanation=The patient is presenting with [[genital warts]] or [[condyloma accuminatum]] caused by [[human papilloma virus]] ([[HPV]]). The image shown above shows a normal cervical cell on the left, and a [[koilocyte]] defined as an HPV-infected cell, on the right side that is characterized by large nuclei with [[perinuclear halo]]. | |Explanation=The patient is presenting with [[genital warts]] or [[condyloma accuminatum]] caused by [[human papilloma virus]] ([[HPV]]). The image shown above shows a normal cervical cell on the left, and a [[koilocyte]] defined as an HPV-infected cell, on the right side that is characterized by large nuclei with [[perinuclear halo]]. | ||