Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Robot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} +, -{{EH}} +, -{{EJ}} +, -{{Editor Help}} +, -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Category:Obstetrics]] | [[Category:Obstetrics]] | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
Revision as of 14:54, 20 August 2012
For patient information, click here
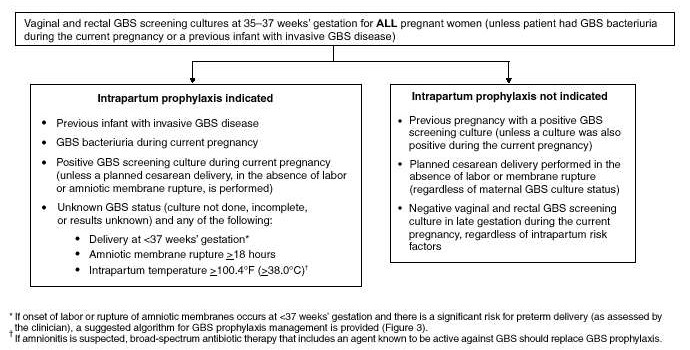
Overview
Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease a leading infectious cause of morbidity and mortality among newborns.
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) bacteria can be passed from a pregnant woman who is a carrier of the bacteria to her baby during labor. Since the bacteria can come and go, testing for GBS is needed every pregnancy. Toward the end of a pregnancy, the vagina and rectum are cultured with a swab at a prenatal appointment. Women with GBS are given an antibiotic during labor. Evidence based research studies show that using this test can reduce infant infections. [1]