Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound: Difference between revisions
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
*Limitations of ultrasound include: | *Limitations of ultrasound include: | ||
**Poor visualization with intraluminal gas between probe and gallbladder | **Poor visualization with intraluminal gas between probe and gallbladder | ||
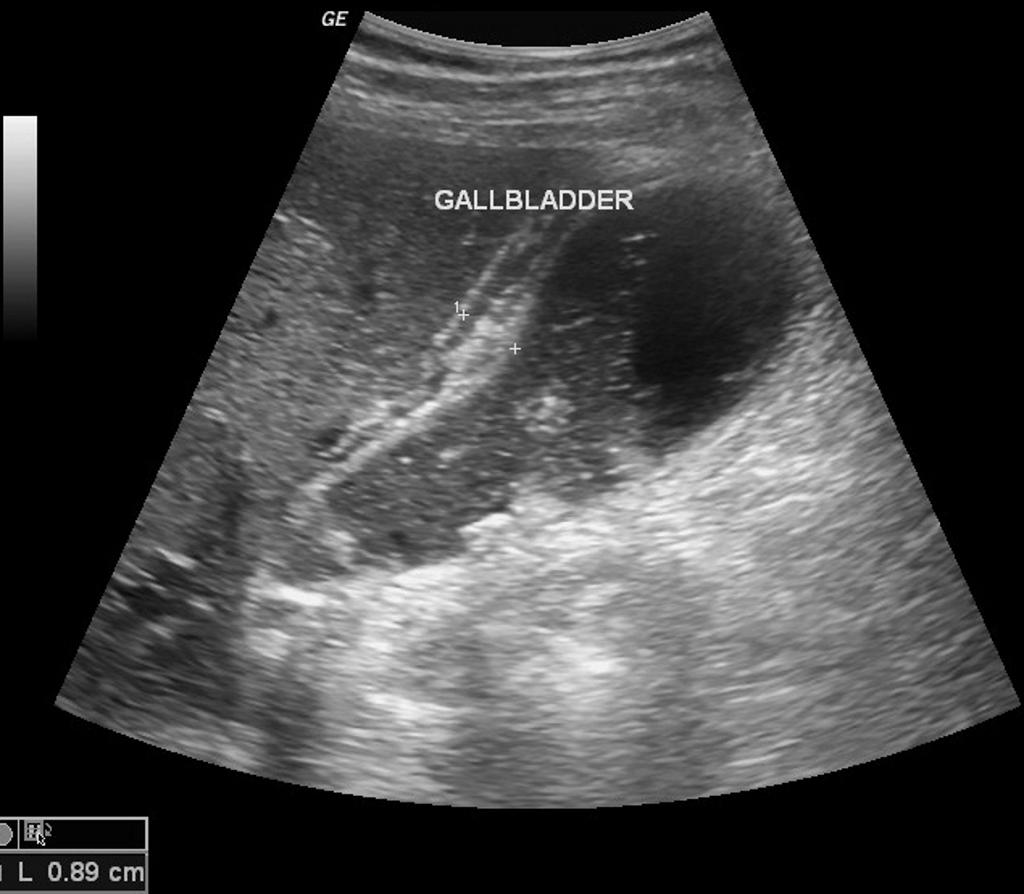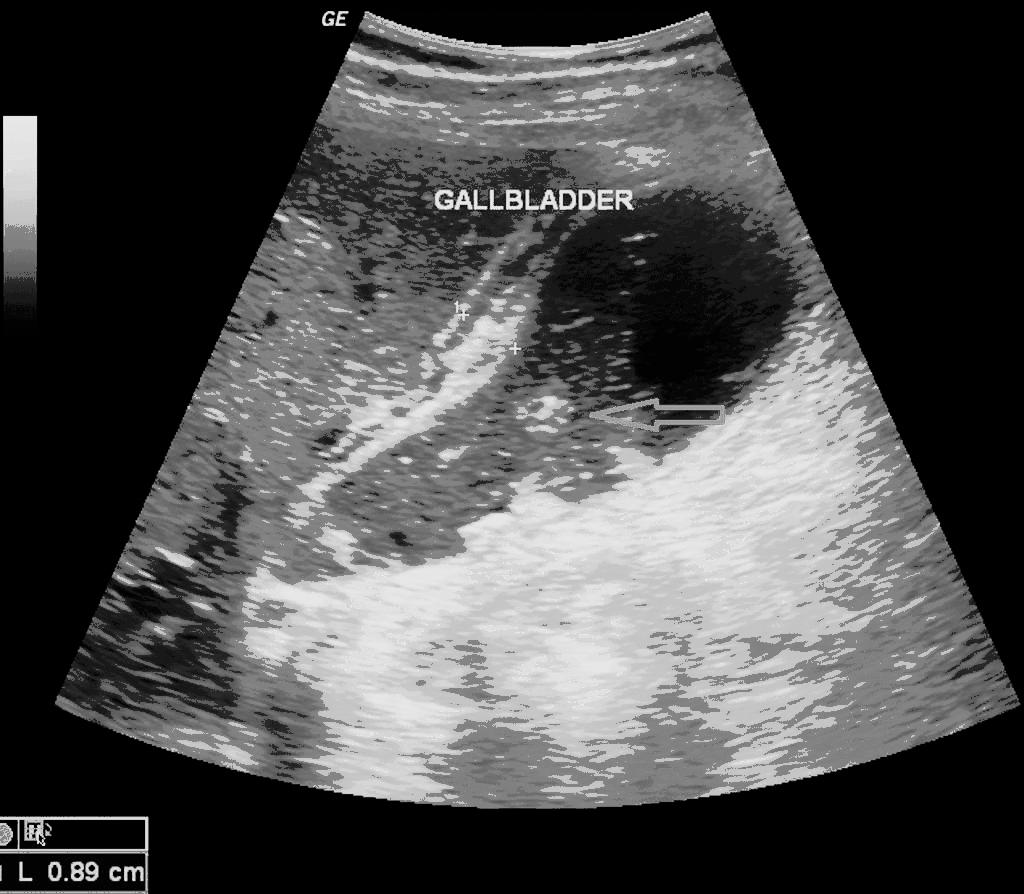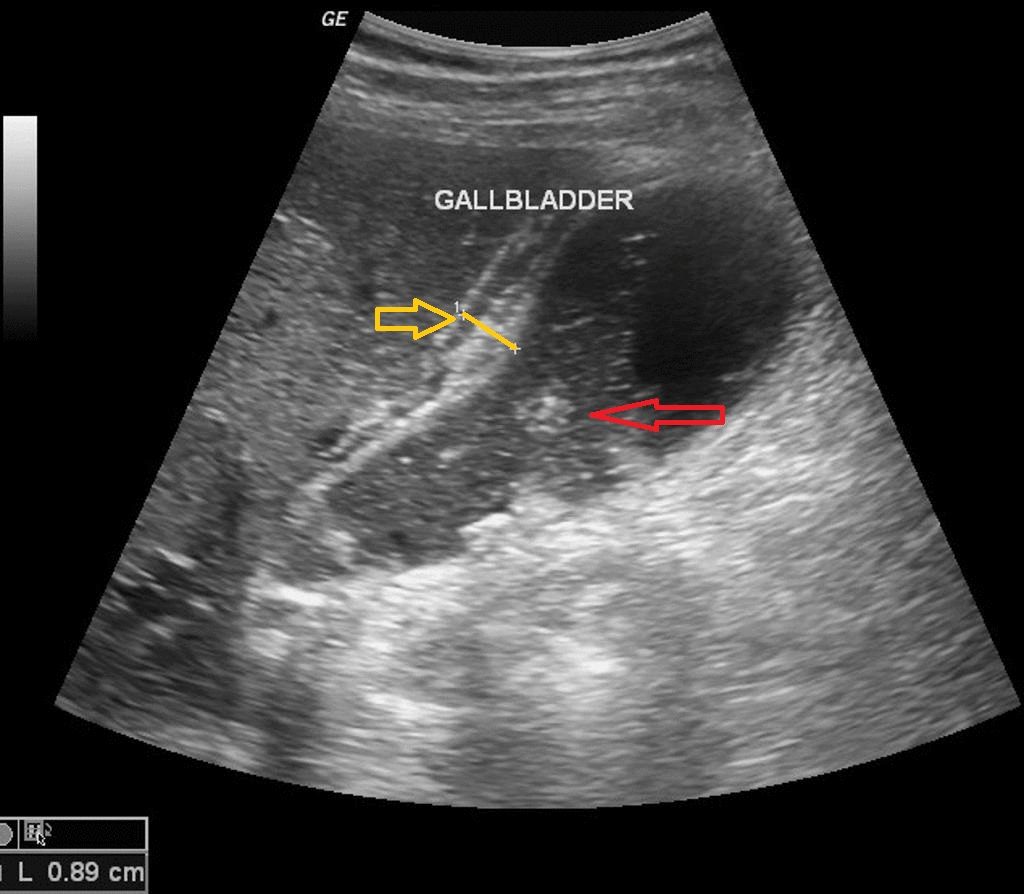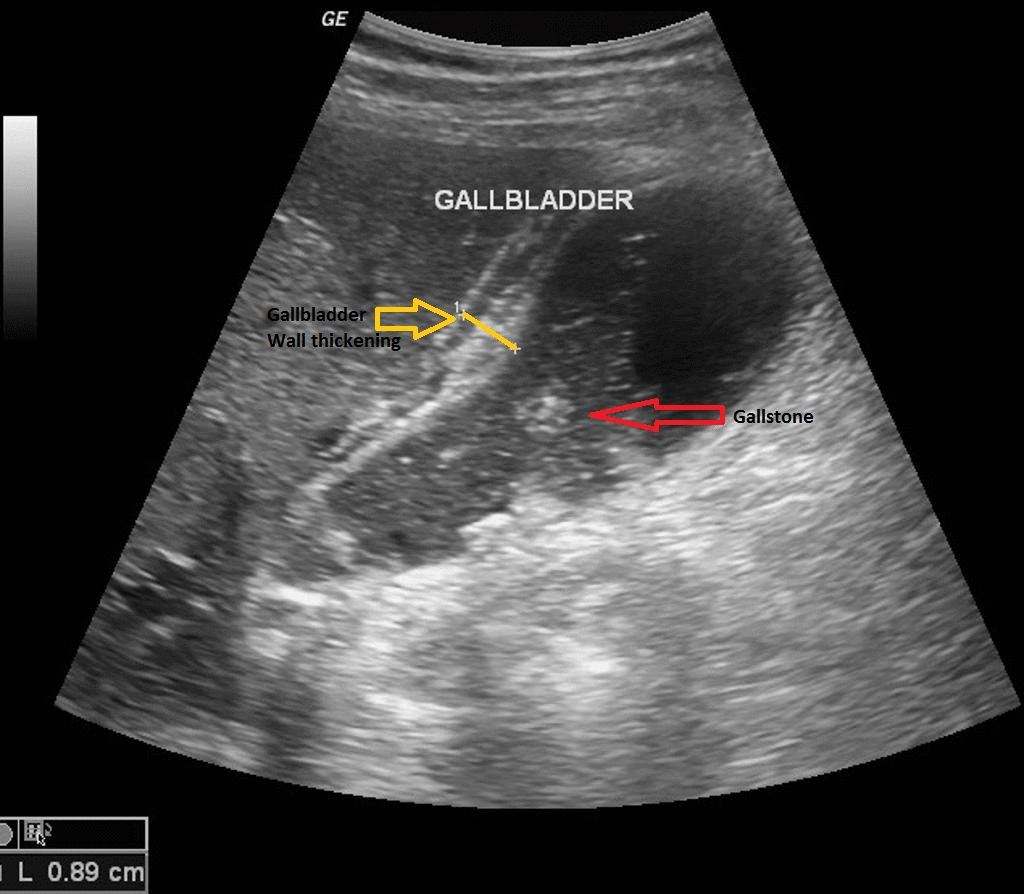
[[File:USG acute cholecystitis.gif|900px|thumb|center| | [[File:USG acute cholecystitis.gif|900px|thumb|center|USG of acute cholecystitis; Red arrow shows gallstone and yellow arrow shows gallblader wall thickening. <small> Case courtesy of Dr Maulik S Patel, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 20542 Source:<ref name="urlAcute cholecystitis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org">{{cite web |url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/acute-cholecystitis |title=Acute cholecystitis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref>]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 19 December 2017
|
Acute cholecystitis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound |
|
Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound in the news |
|
Blogs on Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Acute cholecystitis echocardiography and ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Furqan M M. M.B.B.S[2]
Overview
Transabdominal ultrasound is the gold standard for the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis. Findings on an ultrasound diagnostic of acute cholecystitis include thickened gallbladder, gallstones or sludge, and pericholecystic fluid.
Ultrasound
- Transabdominal ultrasonography is the gold standard for the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis and gallstones.[1][2][3][4]
- Findings on an transabdominal ultrasonography diagnostic of acute cholecystitis include:
- Thickened gallbladder (>4 mm)
- Gallstones or sludge
- Pericholecystic fluid
- Findings on an transabdominal ultrasonography diagnostic of acute cholecystitis include:
Advantages of ultrasound
- Advantages of ultrasound include:
- Noninvasive
- Quick and readily available
- Relatively inexpensive
Limitations of ultrasound
- Limitations of ultrasound include:
- Poor visualization with intraluminal gas between probe and gallbladder
References
- ↑ "Gallbladder, Cholecystitis, Acute - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf".
- ↑ Foard DE, Haber AH (1970). "Physiologically normal senescence in seedlings grown without cell division after massive gamma-irradiation of seeds". Radiat. Res. 42 (2): 372–80. PMID 5442405.
- ↑ Knab LM, Boller AM, Mahvi DM (2014). "Cholecystitis". Surg. Clin. North Am. 94 (2): 455–70. doi:10.1016/j.suc.2014.01.005. PMID 24679431.
- ↑ Gomes CA, Junior CS, Di Saverio S, Sartelli M, Kelly MD, Gomes CC, Gomes FC, Corrêa LD, Alves CB, Guimarães SF (2017). "Acute calculous cholecystitis: Review of current best practices". World J Gastrointest Surg. 9 (5): 118–126. doi:10.4240/wjgs.v9.i5.118. PMC 5442405. PMID 28603584.
- ↑ "Acute cholecystitis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org".