Statin therapy for ASCVD prevention: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
*CK | *CK | ||
*Consider evaluation for other secondary causes | *Consider evaluation for other secondary causes | ||
* | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!Secondary Cause | |||
!Elevated LDL-C | |||
!Elevated Triglycerides | |||
|- | |||
|Diet | |||
|Saturated or trans fats | |||
Weight gain | |||
Anorexia nervosa | |||
|Weight gain, | |||
Very-low-fat diets | |||
High intake of refined carbohydrates | |||
Excessive alcohol intake | |||
|- | |||
|Drugs | |||
|Diuretics | |||
Cyclosporine | |||
Glucocorticoids | |||
Amiodarone | |||
|Oral estrogens | |||
Glucocorticoids | |||
Bile acid sequestrants | |||
Protease inhibitors, Retinoic acid, | |||
Anabolic steroids, sirolimus, | |||
Raloxifene, | |||
Tamoxifen | |||
Beta blockers | |||
|- | |||
|Diseases | |||
|Biliary obstruction | |||
Nephrotic syndrome | |||
|Nephrotic syndrome | |||
Chronic renal failure | |||
Lipodystrophies | |||
|- | |||
|Disorders and altered states of metabolism | |||
|Hypothyroidism | |||
Obesity | |||
Pregnancy | |||
|Diabetes (poorly controlled) | |||
Hypothyroidism | |||
Obesity | |||
Pregnancy | |||
|} | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 21:39, 27 October 2016
Template:Hypercholesterolemia Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Major Recommendations for Statin Therapy for ASCVD Prevention
The following is a treatment algorithm proposed by the AHA/ACC guidelines committee:[1]
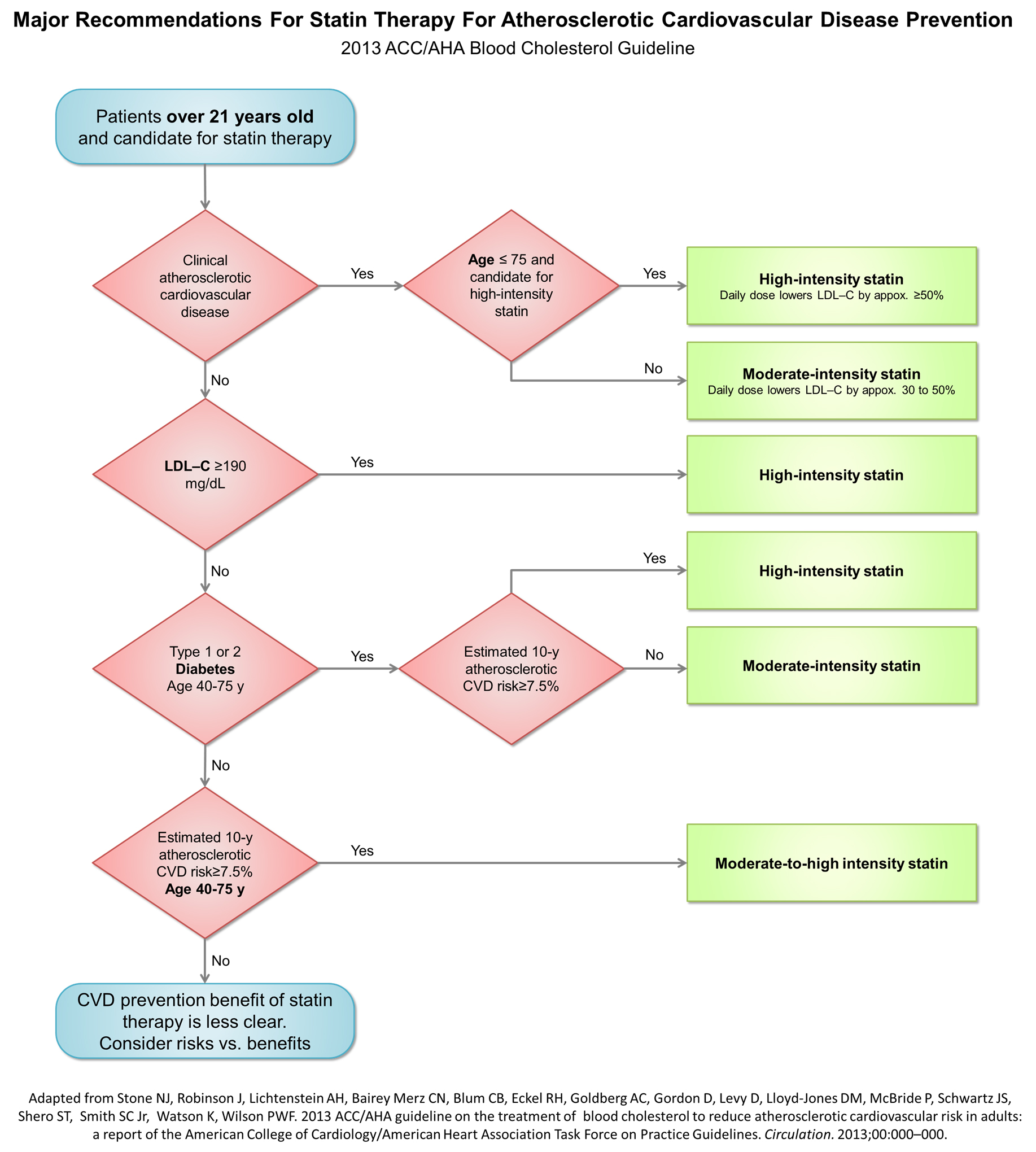
Initial evaluation prior to statin initiation
Initial evaluation prior to statin initiation include:
- Fasting lipid panel
- Fasting lipid panel preferred. In a nonfasting individual, a non–HDL-C level !220 mg/dL could indicate genetic hypercholesterolemia that requires further evaluation or a secondary etiology. If nonfasting triglycerides are !500 mg/dL, a fasting lipid panel is required.
- ALT
- CK
- Consider evaluation for other secondary causes
| Secondary Cause | Elevated LDL-C | Elevated Triglycerides |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Saturated or trans fats
Weight gain Anorexia nervosa |
Weight gain,
Very-low-fat diets High intake of refined carbohydrates Excessive alcohol intake |
| Drugs | Diuretics
Cyclosporine Glucocorticoids Amiodarone |
Oral estrogens
Glucocorticoids Bile acid sequestrants Protease inhibitors, Retinoic acid, Anabolic steroids, sirolimus, Raloxifene, Tamoxifen Beta blockers |
| Diseases | Biliary obstruction
Nephrotic syndrome |
Nephrotic syndrome
Chronic renal failure Lipodystrophies |
| Disorders and altered states of metabolism | Hypothyroidism
Obesity Pregnancy |
Diabetes (poorly controlled)
Hypothyroidism Obesity Pregnancy |
- ↑ Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH; et al. (2014). "2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines". Circulation. 129 (25 Suppl 2): S1–S45. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000437738.63853.7a. PMID 24222016.