WBR0391: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Sergekorjian (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Biostatistics/Epidemiology | |MainCategory=Biostatistics/Epidemiology | ||
|SubCategory=Renal | |SubCategory=Renal | ||
|Prompt=Investigators of a case-control study are investigating the association between the chronic use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) over a one year duration and impaired renal function. 2000 men and women over the age of 50 are surveyed, and the results of the study are categorized in the table shown below. | |Prompt=Investigators of a case-control study are investigating the association between the chronic use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) over a one year duration and impaired renal function. 2000 men and women over the age of 50 are surveyed, and the results of the study are categorized in the table shown below. What is the odds ratio of having impaired renal function with chronic NSAID use based on the data below?<br> | ||
[[Image:NSAID use WBR.png|300px]] | [[Image:NSAID use WBR.png|300px]] | ||
|Explanation=[[Image:NSAID use WBR odds ratio.png|300px]] | |Explanation=[[Image:NSAID use WBR odds ratio.png|300px]] | ||
Odds ratio is | Odds ratio is a relative measure of effect that compares the 2 groups of a case-control study (chronic NSAID use vs. no chronic NSAID use). In this case-control study, the effect the investigators are measuring is renal impairment following one year of NSAID use. Accordingly, the odds ratio (OR) is calculated using the equation: | ||
OR = ad/bc = (800 x 300)/(400 x 500) = 240000/200000 = 1.2.<br> | OR = ad/bc = (800 x 300)/(400 x 500) = 240000/200000 = 1.2.<br> | ||
*OR = 1 implies that there is no difference between the control group (no chronic NSAID use) and the intervention group (chronic NSAID use). In this study, had OR been = 1, then the use of chronic NSAID has no effect on renal impairment compared with no chronic NSAID use. | *OR = 1 implies that there is no difference between the control group (no chronic NSAID use) and the intervention group (chronic NSAID use). In this study, had OR been = 1, then the use of chronic NSAID has no effect on renal impairment compared with no chronic NSAID use. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
|AnswerBExp=0.500 does not correspond to any relevant value. | |AnswerBExp=0.500 does not correspond to any relevant value. | ||
|AnswerC=1.066 | |AnswerC=1.066 | ||
|AnswerCExp=1.066 represents the relative risk (RR), which is often used in cohort studies. RR is calculated using the following equation: | |AnswerCExp=1.066 represents the relative risk (RR), which is another relative measure of effect often used in cohort studies. RR is calculated using the following equation: | ||
RR = (a/[a+b]) / (c/[c+d]) | RR = (a/[a+b]) / (c/[c+d]) | ||
|AnswerD=1.200 | |AnswerD=1.200 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
|AnswerE=1.500 | |AnswerE=1.500 | ||
|AnswerEExp=1.500 does not represent any relevant value. | |AnswerEExp=1.500 does not represent any relevant value. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Odds ratio is defined as | |EducationalObjectives=Odds ratio is defined as a relative measure of effect that compares the 2 groups of the case-control study. The odds ratio (OR) is calculated using the equation: OR = ad/bc | ||
|References=First Aid 2014 page 50 | |References=First Aid 2014 page 50 | ||
|RightAnswer=D | |RightAnswer=D | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 1 June 2015
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Biostatistics/Epidemiology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Renal |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::Investigators of a case-control study are investigating the association between the chronic use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) over a one year duration and impaired renal function. 2000 men and women over the age of 50 are surveyed, and the results of the study are categorized in the table shown below. What is the odds ratio of having impaired renal function with chronic NSAID use based on the data below? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::0.041 |
| Answer A Explanation | [[AnswerAExp::0.041 represents the attributable risk, which is calculated using the following equation:
Attributable Risk = (a/[a+b]) – (c/[c+d])]] |
| Answer B | AnswerB::0.500 |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::0.500 does not correspond to any relevant value. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::1.066 |
| Answer C Explanation | [[AnswerCExp::1.066 represents the relative risk (RR), which is another relative measure of effect often used in cohort studies. RR is calculated using the following equation:
RR = (a/[a+b]) / (c/[c+d])]] |
| Answer D | AnswerD::1.200 |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::1.200 correctly represents the OR |
| Answer E | AnswerE::1.500 |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::1.500 does not represent any relevant value. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::D |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::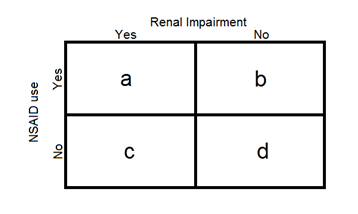
Odds ratio is a relative measure of effect that compares the 2 groups of a case-control study (chronic NSAID use vs. no chronic NSAID use). In this case-control study, the effect the investigators are measuring is renal impairment following one year of NSAID use. Accordingly, the odds ratio (OR) is calculated using the equation:
OR = ad/bc = (800 x 300)/(400 x 500) = 240000/200000 = 1.2.
Educational Objective: Odds ratio is defined as a relative measure of effect that compares the 2 groups of the case-control study. The odds ratio (OR) is calculated using the equation: OR = ad/bc |
| Approved | Approved::Yes |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Odds ratio, WBRKeyword::OR, WBRKeyword::Case-control, WBRKeyword::Equation, WBRKeyword::NSAID, WBRKeyword::Renal impairment |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |
