WBR0843: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rim Halaby (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
YazanDaaboul (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WBRQuestion | {{WBRQuestion | ||
|QuestionAuthor={{ | |QuestionAuthor={{YD}} (Reviewed by {{YD}}) | ||
|ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | |ExamType=USMLE Step 1 | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Dermatology | |SubCategory=Dermatology | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|MainCategory=Pathology | |MainCategory=Pathology | ||
|SubCategory=Dermatology | |SubCategory=Dermatology | ||
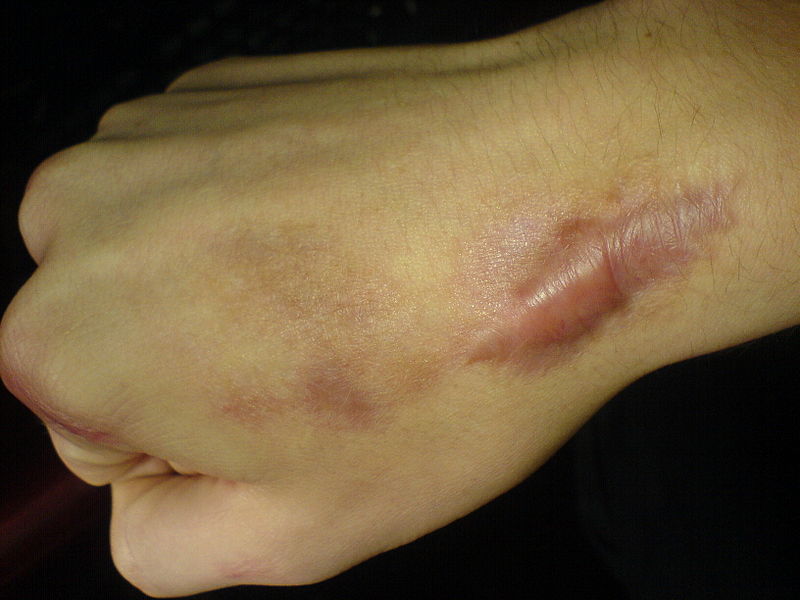
|Prompt=A 28 year old | |Prompt=A 28-year-old man presents to the dermatology clinic with a lesion on his right hand. Upon further questioning, he informs the physician that he sustained a burn to the dorsum of his hand at the site of the lesion one year ago. On physical examination, the physician notes a raised lesion shown in the image below. Which of the following is an appropriate treatment option for this patient's condition? | ||
[[Image:WBR0843.jpg|500px]] | |||
Intralesional corticosteroids are | |Explanation=The patient is presenting with a keloid scar. Hypertrophic scars and keloids are characterized by the high rates of recurrence following excision by surgery. Treatment options for keloids are numerous with varying rates of success. Intralesional corticosteroids are considered the mainstay of therapy for hypertrophic keloid scars. Other first line options include silicone sheeting and pressure dressingss, whereas ptients with smaller lesions may benefit from cryotherapy. Surgical resection is reserved for large scars that are unlikely to improve with any first line treatment option. However, surgical excision alone exacerbates the keloid scar. Thus, surgery must be combined with other treatment modalities, such as radiotherapy, pulsed dye lasers, or imiquimod creams. Novel therapies are currently emerging for the treatment of established keloid scars, including intalesional calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil, and chemotherapeutic agents, such as fluorouracil and bleomycin injections. | ||
|AnswerA=Intralesional corticosteroids | |AnswerA=Intralesional corticosteroids | ||
|AnswerAExp=Intralesional corticosteroids are | |AnswerAExp=Intralesional corticosteroids are first line therapeutic options for the treatment of keloid scars. | ||
|AnswerB=Systemic corticosteroids | |AnswerB=Systemic corticosteroids | ||
|AnswerBExp=Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. | |AnswerBExp=Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 35: | ||
|AnswerDExp=Antibiotics are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. | |AnswerDExp=Antibiotics are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. | ||
|AnswerE=Systemic chemotherapy | |AnswerE=Systemic chemotherapy | ||
|AnswerEExp=Intralesional chemotherapy | |AnswerEExp=Intralesional chemotherapy is effective for the treatment of keloid scars. In contrast, systemic chemotherapy is not a therapeutic option for keloid scars. | ||
|EducationalObjectives=Intralesional corticosteroids are helpful as first line agents for treatment of keloid scars. | |||
|References=Juckett G, Hartmann-Adams H. Management of keloids and hypertrophic scars. Am Fam Physicians. 2009;80(3):253-260. | |||
|RightAnswer=A | |RightAnswer=A | ||
|WBRKeyword= | |WBRKeyword=Keloid, Scar, Intralesional corticosteroids, CorticosteroidS, Steroids, Treatment, Burn | ||
|Approved=No | |Approved=No | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 5 January 2015
| Author | [[PageAuthor::Yazan Daaboul, M.D. (Reviewed by Yazan Daaboul, M.D.)]] |
|---|---|
| Exam Type | ExamType::USMLE Step 1 |
| Main Category | MainCategory::Pathology |
| Sub Category | SubCategory::Dermatology |
| Prompt | [[Prompt::A 28-year-old man presents to the dermatology clinic with a lesion on his right hand. Upon further questioning, he informs the physician that he sustained a burn to the dorsum of his hand at the site of the lesion one year ago. On physical examination, the physician notes a raised lesion shown in the image below. Which of the following is an appropriate treatment option for this patient's condition? |
| Answer A | AnswerA::Intralesional corticosteroids |
| Answer A Explanation | AnswerAExp::Intralesional corticosteroids are first line therapeutic options for the treatment of keloid scars. |
| Answer B | AnswerB::Systemic corticosteroids |
| Answer B Explanation | AnswerBExp::Systemic corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. |
| Answer C | AnswerC::Topical corticosteroids |
| Answer C Explanation | AnswerCExp::Topical corticosteroids are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. |
| Answer D | AnswerD::Systemic antibiotics |
| Answer D Explanation | AnswerDExp::Antibiotics are not helpful for the treatment of keloid scars. |
| Answer E | AnswerE::Systemic chemotherapy |
| Answer E Explanation | AnswerEExp::Intralesional chemotherapy is effective for the treatment of keloid scars. In contrast, systemic chemotherapy is not a therapeutic option for keloid scars. |
| Right Answer | RightAnswer::A |
| Explanation | [[Explanation::The patient is presenting with a keloid scar. Hypertrophic scars and keloids are characterized by the high rates of recurrence following excision by surgery. Treatment options for keloids are numerous with varying rates of success. Intralesional corticosteroids are considered the mainstay of therapy for hypertrophic keloid scars. Other first line options include silicone sheeting and pressure dressingss, whereas ptients with smaller lesions may benefit from cryotherapy. Surgical resection is reserved for large scars that are unlikely to improve with any first line treatment option. However, surgical excision alone exacerbates the keloid scar. Thus, surgery must be combined with other treatment modalities, such as radiotherapy, pulsed dye lasers, or imiquimod creams. Novel therapies are currently emerging for the treatment of established keloid scars, including intalesional calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil, and chemotherapeutic agents, such as fluorouracil and bleomycin injections. Educational Objective: Intralesional corticosteroids are helpful as first line agents for treatment of keloid scars. |
| Approved | Approved::No |
| Keyword | WBRKeyword::Keloid, WBRKeyword::Scar, WBRKeyword::Intralesional corticosteroids, WBRKeyword::CorticosteroidS, WBRKeyword::Steroids, WBRKeyword::Treatment, WBRKeyword::Burn |
| Linked Question | Linked:: |
| Order in Linked Questions | LinkedOrder:: |