Atazanavir: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|drugClass= | |drugClass= | ||
protease inhibitor | [[protease inhibitor]] | ||
|indication= | |indication= | ||
HIV-1 infection | [[HIV-1 infection]] | ||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
|adverseReactions= | |adverseReactions= | ||
nausea, jaundice/scleral icterus, rash, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, insomnia, peripheral neurologic symptoms, dizziness, myalgia, diarrhea, depression, and fever | [[nausea]], jaundice/scleral icterus, rash, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, insomnia, peripheral neurologic symptoms, dizziness, myalgia, diarrhea, depression, and fever | ||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
Revision as of 13:44, 13 August 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Atazanavir is a protease inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of HIV-1 infection. Common adverse reactions include nausea, jaundice/scleral icterus, rash, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, insomnia, peripheral neurologic symptoms, dizziness, myalgia, diarrhea, depression, and fever.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
HIV-1 infection
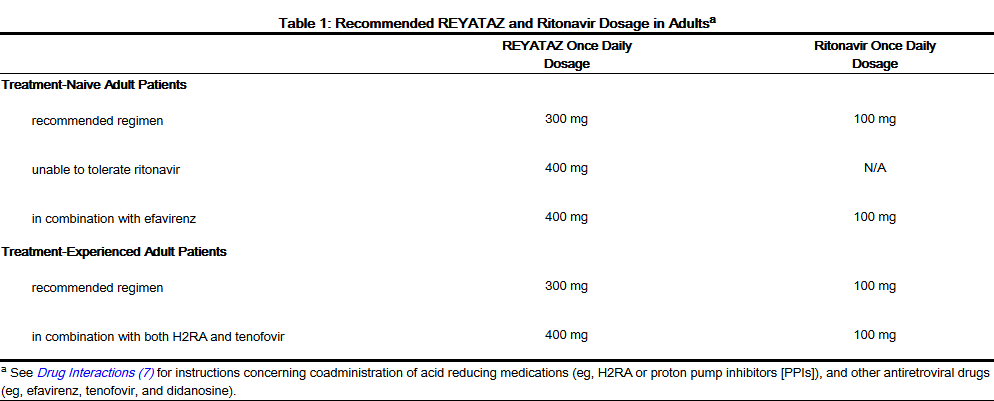
- Table 1 displays the recommended dosage of REYATAZ capsules in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced adults. Table 1 also displays recommended dosage of REYATAZ and ritonavir when given concomitantly with other antiretroviral drugs and H2-receptor antagonists (H2RA). Ritonavir is required with several REYATAZ dosage regimens (see the ritonavir complete prescribing information about the safe and effective use of ritonavir). The use of REYATAZ in treatment-experienced adult patients without ritonavir is not recommended.
- Dosage Adjustments in Pregnant Patients
- Table 4 includes the recommended dosage of REYATAZ capsules and ritonavir in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced pregnant patients. In these patients, REYATAZ must be administered with ritonavir. There are no dosage adjustments for postpartum patients (see Table 1 for the recommended REYATAZ dosage in adults). [See Use in Specific Populations (8.1).]
- Renal Impairment
- For patients with renal impairment, including those with severe renal impairment who are not managed with hemodialysis, no dose adjustment is required for REYATAZ. Treatment-naive patients with end stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis should receive REYATAZ 300 mg with ritonavir 100 mg. REYATAZ should not be administered to HIV-treatment-experienced patients with end stage renal disease managed with hemodialysis. [See Use in Specific Populations (8.7).]
- Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- Table 5 displays the recommended REYATAZ dosage in treatment-naive patients with hepatic impairment. The use of REYATAZ in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) is not recommended. The coadministration of REYATAZ with ritonavir in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment is not recommended.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Atazanavir in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Atazanavir in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
HIV-1 infection
- Dosage of REYATAZ Capsules in Pediatric Patients
- The recommended daily dosage of REYATAZ capsules and ritonavir in pediatric patients (6 years of age to less than 18 years of age) is based on body weight (see Table 2).
- Dosage and Administration of REYATAZ Oral Powder in Pediatric Patients
- REYATAZ oral powder is for use in treatment-naive or treatment-experienced pediatric patients who are at least 3 months of age and weighing at least 10 kg and less than 25 kg. REYATAZ oral powder must be mixed with food or beverage for administration and ritonavir must be given immediately afterwards. Table 3 displays the recommended dosage of REYATAZ oral powder and ritonavir.
- Instructions for Mixing REYATAZ Oral Powder [see FDA-approved Instructions for Use]
- It is preferable to mix REYATAZ oral powder with food such as applesauce or yogurt. Mixing REYATAZ oral powder with a beverage (milk, infant formula, or water) may be used for infants who can drink from a cup. For young infants (less than 6 months) who cannot eat solid food or drink from a cup, REYATAZ oral powder should be mixed with infant formula and given using an oral dosing syringe. Administration of REYATAZ and infant formula using an infant bottle is not recommended because full dose may not be delivered.
- Determine the number of packets (4 or 5 packets) that are needed.
- Prior to mixing, tap the packet to settle the powder. Use a clean pair of scissors to cut each packet along the dotted line.
- Mixing with food: Using a spoon, mix the recommended number of REYATAZ oral powder packets with a minimum of one tablespoon of food (such as applesauce or yogurt). Feed the mixture to the infant or young child. Add an additional one tablespoon of food to the small container, mix, and feed the child the residual mixture.
- Mixing with a beverage such as milk or water in a small drinking cup: Using a spoon, mix the recommended number of REYATAZ oral powder packets with a minimum of 30 mL of the beverage. Have the child drink the mixture. Add an additional 15 mL more of beverage to the drinking cup, mix, and have the child drink the residual mixture. If water is used, food should also be taken at the same time.
- Mixing with liquid infant formula using an oral dosing syringe and a small medicine cup: Using a spoon, mix the recommended number of REYATAZ oral powder packets with 10 mL of prepared liquid infant formula. Draw up the full amount of the mixture into an oral syringe and administer into either right or left inner cheek of infant. Pour another 10 mL of formula into the medicine cup to rinse off remaining REYATAZ oral powder in cup. Draw up residual mixture into the syringe and administer into either right or left inner cheek of infant.
- Administer ritonavir immediately following REYATAZ powder administration.
- Administer the entire dosage of REYATAZ oral powder (mixed in the food or beverage) within one hour of preparation (may leave the mixture at room temperature during this one hour period). Ensure that the patient eats or drinks all the food or beverage that contains the powder. Additional food may be given after consumption of the entire mixture.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Atazanavir in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Atazanavir in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- REYATAZ is contraindicated:
- in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, or toxic skin eruptions) to any of the components of REYATAZ capsules or REYATAZ oral powder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- when coadministered with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A or UGT1A1 for clearance, and for which elevated plasma concentrations of the interacting drugs are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (see Table 6).
- when coadministered with drugs that strongly induce CYP3A and may lead to lower exposure and loss of efficacy of REYATAZ (see Table 6).
- Table 6 displays drugs that are contraindicated with REYATAZ.
Warnings
- Description
Precautions
- Description
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Clinical Trial Experience of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Body as a Whole
Cardiovascular
Digestive
Endocrine
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Metabolic and Nutritional
Musculoskeletal
Neurologic
Respiratory
Skin and Hypersensitivy Reactions
Special Senses
Urogenital
Miscellaneous
Drug Interactions
- Drug
- Description
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Atazanavir in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Atazanavir during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Atazanavir in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Atazanavir in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Atazanavir in the drug label.
- Description
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Description
Management
- Description
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Atazanavir Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Atazanavir in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Atazanavir Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Atazanavir |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Atazanavir |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Atazanavir in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Atazanavir interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Atazanavir |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Atazanavir |Label Name=Atazanavir11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Atazanavir |Label Name=Atazanavir11.png
}}