Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia: Difference between revisions
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
*Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia must be differentiated from other diseases that cause swelling of face and neck, such as: | *Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia must be differentiated from other diseases that cause swelling of face and neck, such as: | ||
:*Kimura’s disease | :*Kimura’s disease | ||
:*Acial granuloma | |||
:*Insect bite reaction | |||
:*Cutaneous lymphoma | |||
:*Sarcoidosis | |||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 9 May 2016
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Kiran Singh, M.D. [2] Ammu Susheela, M.D. [3]
Synonyms and Keywords: Epithelioid hemangioma; Histiocytoid hemangioma; Inflammatory angiomatous nodule; Intravenous atypical vascular proliferation; Papular angioplasia; Inflammatory arteriovenous hemangioma; Pseudopyogenic granuloma; ALHE
Overview
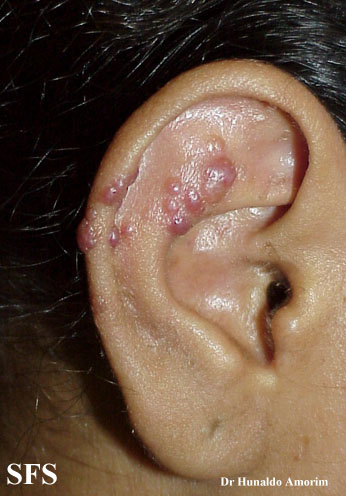
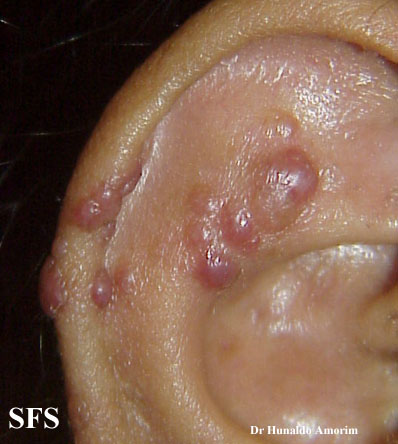
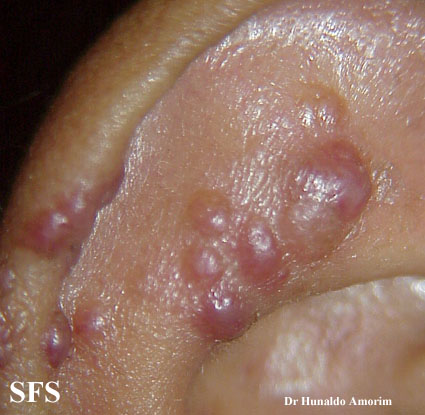
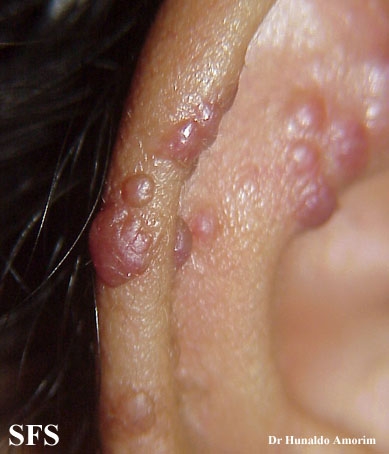
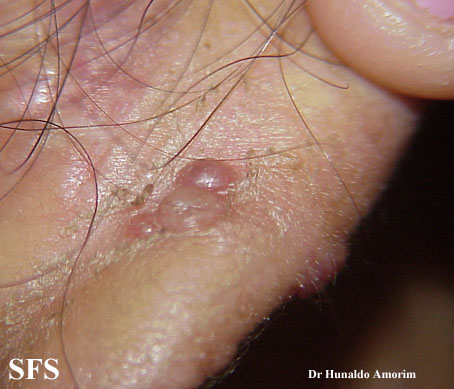
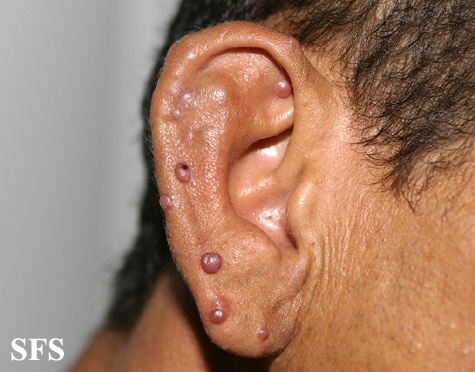
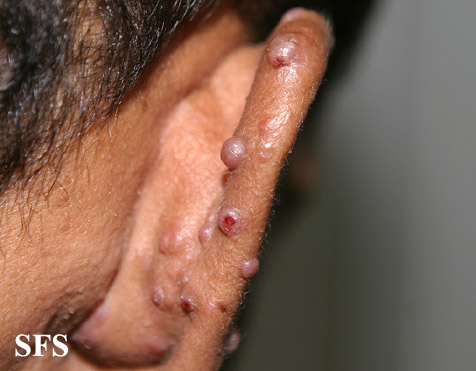
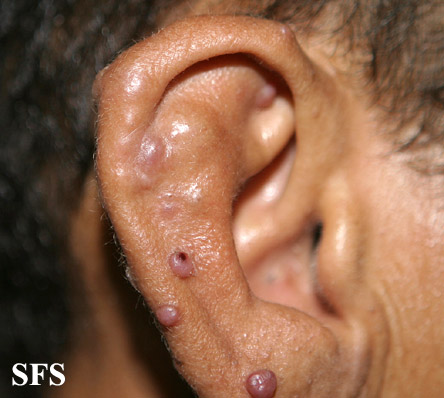
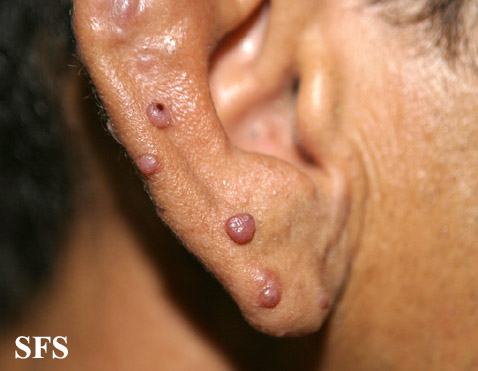
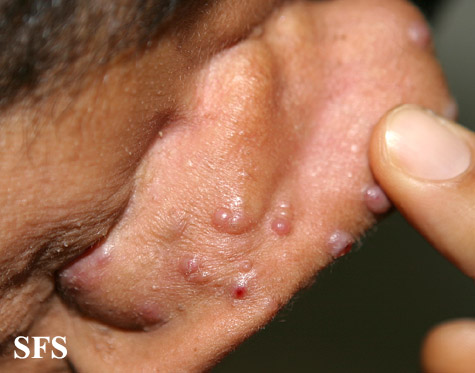
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia [1] is defined as red-brown, dome-shaped, dermal papule or nodule, present in the head or neck, specifically around the ears and on the scalp.[2]
Historical Perspective
- [Disease name] was first discovered by [scientist name], a [nationality + occupation], in [year] during/following [event].
- In [year], [gene] mutations were first identified in the pathogenesis of [disease name].
- In [year], the first [discovery] was developed by [scientist] to treat/diagnose [disease name].
Classification
- [Disease name] may be classified according to [classification method]
into [number] subtypes/groups:
- [group1]
- [group2]
- [group3]
- Other variants of [disease name] include [disease subtype 1],
[disease subtype 2], and [disease subtype 3].
Pathophysiology
- The pathogenesis of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia is characterized by red to brown papules or nodules dislocated in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue.
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE) is a rare and idiopathic vascular disorder.
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE) is an uncommon benign lesion, primarily occurring in the head and neck.
- The [gene name] gene/Mutation in [gene name] has been associated with the development of [disease name], involving the [molecular pathway] pathway.
- On gross pathology, smooth-surface red to brown papules or nodules on the head, neck, trunk, extremities, genitalia, lips and oral mucosa; extracutaneous involvement are characteristic findings of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, florid vascular proliferation with atypical endothelial cells surrounded by a lymphocytic and eosinophilic infiltrate are characteristic findings of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
Causes
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia may be caused by either allergic reactions, traumas, or autoimmune disorders.
Differentiating Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia from other Diseases
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia must be differentiated from other diseases that cause swelling of face and neck, such as:
- Kimura’s disease
- Acial granuloma
- Insect bite reaction
- Cutaneous lymphoma
- Sarcoidosis
Epidemiology and Demographics
- The prevalence of [disease name] is approximately [number or range] per 100,000 individuals worldwide.
- In [year], the incidence of [disease name] was estimated to be [number or range] cases per 100,000 individuals in [location].
Age
- Patients of all age groups may develop [disease name].
- [Disease name] is more commonly observed among patients aged [age range] years old.
- [Disease name] is more commonly observed among [elderly patients/young patients/children].
Gender
- Females are more commonly affected with angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia than males.
Race
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia usually affects predominently individuals of the Asian race.
Risk Factors
- Common risk factors in the development of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia are allergic reactions, traumas or autoimmune disorders.
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- The majority of patients with [disease name] remain asymptomatic for
[duration/years].
- Early clinical features include [manifestation 1], [manifestation 2],
and [manifestation 3].
- If left untreated, [#%] of patients with [disease name] may progress
to develop [manifestation 1], [manifestation 2], and [manifestation 3].
- Common complications of [disease name] include [complication 1],
[complication 2], and [complication 3].
- Prognosis is generally [excellent/good/poor], and the [1/5/10year
mortality/survival rate] of patients with [disease name] is approximately [#%].
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Criteria
- The diagnosis of [disease name] is made when at least [number] of the
following [number] diagnostic criteria are met:
- [criterion 1]
- [criterion 2]
- [criterion 3]
- [criterion 4]
Symptoms
- [Disease name] is usually asymptomatic.
- Symptoms of [disease name] may include the following:
- [symptom 1]
- [symptom 2]
- [symptom 3]
- [symptom 4]
- [symptom 5]
- [symptom 6]
Physical Examination
- Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance].
- Physical examination may be remarkable for:
- [finding 1]
- [finding 2]
- [finding 3]
- [finding 4]
- [finding 5]
- [finding 6]
Laboratory Findings
- There are no specific laboratory findings associated with [disease
name].
- A [positive/negative] [test name] is diagnostic of [disease name].
- An [elevated/reduced] concentration of
[serum/blood/urinary/CSF/other] [lab test] is diagnostic of [disease name].
- Other laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of [disease
name] include [abnormal test 1], [abnormal test 2], and [abnormal test 3].
Imaging Findings
- There are no [imaging study] findings associated with [disease name].
- [Imaging study 1] is the imaging modality of choice for [disease
name].
- On [imaging study 1], [disease name] is characterized by [finding 1],
[finding 2], and [finding 3].
- [Imaging study 2] may demonstrate [finding 1], [finding 2], and
[finding 3].
Other Diagnostic Studies
- [Disease name] may also be diagnosed using [diagnostic study name].
- Findings on [diagnostic study name] include [finding 1], [finding 2],
and [finding 3].
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- There is no treatment for [disease name]; the mainstay of therapy is
supportive care.
- The mainstay of therapy for [disease name] is [medical therapy 1] and
[medical therapy 2].
- [Medical therapy 1] acts by [mechanism of action1].
- Response to [medical therapy 1] can be monitored with [test/physical
finding/imaging] every [frequency/duration].
Surgery
- Surgery is the mainstay of therapy for angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia.
Prevention
- There are no primary preventive measures available for [disease
name].
- Effective measures for the primary prevention of [disease name]
include [measure1], [measure2], and [measure3].
- Once diagnosed and successfully treated, patients with [disease name]
are followedup every [duration]. Followup testing includes [test 1], [test 2], and [test 3].
Diagnosis
Ear
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite
-
Epithelioid hemangioma. Adapted from Dermatology Atlas.<ref name="Dermatology Atlas">{{Cite