Colloid cyst: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-{{SIB}} + & -{{EH}} + & -{{EJ}} + & -{{Editor Help}} + & -{{Editor Join}} +)) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| MeshID = | | MeshID = | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{CMG}} | |||
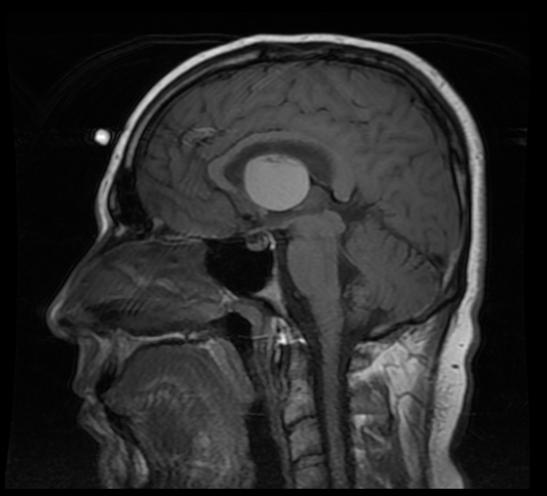
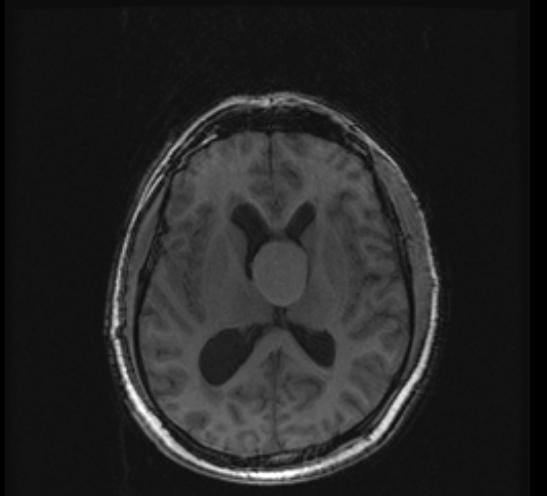
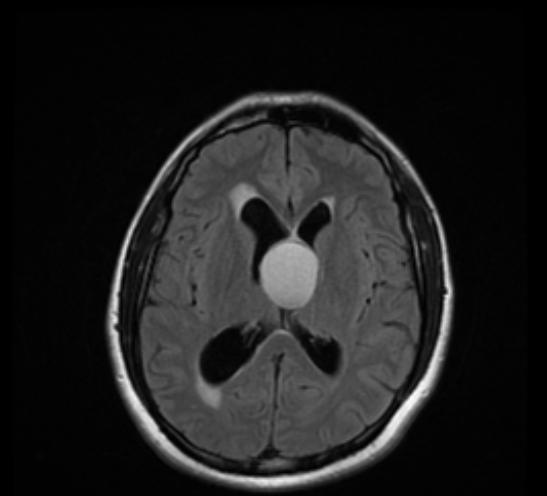
A '''colloid cyst''' is a [[cyst]] containing gelatinous material in the brain. It is almost always found just posterior to the [[foramen of Monro]] in the anterior aspect of the [[third ventricle]], originating from the roof of the ventricle. Because of its location it can cause | |||
==Overview== | |||
A '''colloid cyst''' is a [[cyst]] containing gelatinous material in the brain. It is almost always found just posterior to the [[foramen of Monro]] in the anterior aspect of the [[third ventricle]], originating from the roof of the ventricle. Because of its location it can cause obstructive hydrocephalus and [[increased intracranial pressure]]. These cysts account for approximately 1% of all intracranial tumors. Symptoms can include [[headache]], [[Vertigo (medical)|vertigo]], memory deficits, [[diplopia]] and behavioral disturbances. The developmental origin is unclear, though they may be of endodermal origin, which would explain the mucin-producing, ciliated cell type. These cysts can be surgically resected, and opinion is divided about the advisability of this. | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
=== CT === | |||
* Hyperdense mass in the anterior third ventricle | |||
* Hyperdensity is due to high protein concentration | |||
* Cyst rim may faintly enhance | |||
===MRI=== | |||
* T1: High T1 signal in 50% of cases | |||
* T2: The higher the protein concentration, the lower the signal intensity. | |||
([http://www.radswiki.net Images courtesy of RadsWiki]) | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Colloid-cyst-001.jpg|Colloid cyst | |||
Image:Colloid-cyst-002.jpg|Colloid cyst | |||
Image:Colloid-cyst-003.jpg|Colloid cyst | |||
</gallery> | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
* [http://rad.usuhs.edu/medpix/medpix.html?mode=image_finder&action=search&srchstr=colloid%20cyst&srch_type=all#top Images of Colloid Cyst] | * [http://rad.usuhs.edu/medpix/medpix.html?mode=image_finder&action=search&srchstr=colloid%20cyst&srch_type=all#top Images of Colloid Cyst] | ||
* [http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu/Programs/BrainTumor/BrainTumor_Colloid%20cyst.html UCLA Neurosurgery: Colloid cysts (with video of removal procedure)] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | [[Category:Neurology]] | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | |||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | |||
Latest revision as of 00:03, 9 August 2012
| Colloid cyst | |
| eMedicine | med/2906 radio/96 |
|---|---|
|
WikiDoc Resources for Colloid cyst |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Colloid cyst Most cited articles on Colloid cyst |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Colloid cyst |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Colloid cyst at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Colloid cyst at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Colloid cyst
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Colloid cyst Discussion groups on Colloid cyst Patient Handouts on Colloid cyst Directions to Hospitals Treating Colloid cyst Risk calculators and risk factors for Colloid cyst
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Colloid cyst |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
A colloid cyst is a cyst containing gelatinous material in the brain. It is almost always found just posterior to the foramen of Monro in the anterior aspect of the third ventricle, originating from the roof of the ventricle. Because of its location it can cause obstructive hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure. These cysts account for approximately 1% of all intracranial tumors. Symptoms can include headache, vertigo, memory deficits, diplopia and behavioral disturbances. The developmental origin is unclear, though they may be of endodermal origin, which would explain the mucin-producing, ciliated cell type. These cysts can be surgically resected, and opinion is divided about the advisability of this.
Diagnosis
CT
- Hyperdense mass in the anterior third ventricle
- Hyperdensity is due to high protein concentration
- Cyst rim may faintly enhance
MRI
- T1: High T1 signal in 50% of cases
- T2: The higher the protein concentration, the lower the signal intensity.
-
Colloid cyst
-
Colloid cyst
-
Colloid cyst
External links