|
|
| (62 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ |
| {{Infobox_Disease | | {{Infobox_Disease |
| | Name = Bell's palsy | | | Name = Bell's palsy |
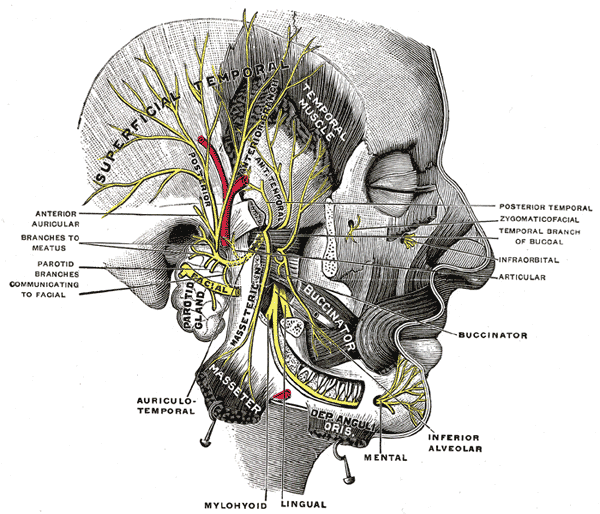
| | Image = Gray781.png | | | Image = Gray781.png |
| | Caption = | | | Caption = |
| | DiseasesDB = 1303
| | |
| | ICD10 = {{ICD10|G|51|0|g|50}}
| |
| | ICD9 = {{ICD9|351.0}}
| |
| | ICDO =
| |
| | OMIM =
| |
| | MedlinePlus = 000773
| |
| | eMedicineSubj = emerg
| |
| | eMedicineTopic = 56
| |
| | eMedicine_plus = {{eMedicine2|neuro|413}} {{eMedicine2|ent|719}} {{eMedicine2|oph|508}}
| |
| | MeshID = D020330
| |
| }} | | }} |
| {{SI}} | | {{Bell's palsy}} |
|
| |
|
| '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' | | '''For patient information click [[{{PAGENAME}} (patient information)|here]]''' |
|
| |
|
| '''Editor-in-Chief:''' Gilbert Dagher, M.D.
| | {{CMG}}; {{AE}}{{M.B}} ,{{MMJ}} {{NE}} |
|
| |
|
| {{Editor Join}} | | {{SK}} Idiopathic facial paralysis,Idiopathic facial nerve paresis,Facial nerve disorder |
| | ==[[Bell's palsy overview|Overview]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==Overview== | | ==[[Bell's palsy historical perspective|Historical Perspective]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Bell's palsy''' (or '''facial [[palsy]]''') is characterised by facial drooping on the affected half, due to malfunction of the [[facial nerve]] (VII [[cranial nerve]]), which controls the [[muscle]]s of the face. Named after Scottish anatomist Charles Bell, who first described it, Bell's palsy is the most common acute [[mononeuropathy]] (disease involving only one [[nerve]]), and is the most common cause of [[acute facial nerve paralysis]]. The paralysis is of the infranuclear/lower motor neuron type. Bell’s palsy affects about 40,000 people in the United States every year. It affects approximately 1 person in 65 during a lifetime. Until recently, its cause was unknown in most cases, but it has now been related to both [[Lyme disease]] and [[Herpes Zoster]].
| | ==[[Bell's palsy classification|Classification]]== |
|
| |
|
| ==Epidemiology== | | ==[[Bell's palsy pathophysiology|Pathophysiology]]== |
|
| |
|
| The annual incidence rate is between 13 and 34 cases per 100,000 population.
| | ==[[Bell's palsy causes|Causes]]== |
| There is no race, geographic, or gender predilection.
| |
| The risk is three times greater during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester or in the first postpartum week.
| |
| Diabetes is present in about 5 to 10 percent of patients.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Etiology== | | ==[[Bell's palsy differential diagnosis|Differentiating Bell's Palsy from other Diseases]]== |
|
| |
|
| Many cases likely due to [[Herpes Simplex Virus]] (HSV) reactivation
| | ==[[Bell's palsy epidemiology and demographics|Epidemiology and Demographics]]== |
|
| |
|
| '''Infectious causes ''' | | ==[[Bell's palsy natural history, complications and prognosis|Natural History, Complications and Prognosis]]== |
|
| |
|
| :Herpes simplex virus activation is the likely cause of Bell's Palsy in most cases.
| | ==Diagnosis== |
| :Herpes Zoster may be the second most common associated viral infection.
| |
| :Cytomegalovirus
| |
| :Epstein Barr virus
| |
| :Adenovirus
| |
| :Rubella virus
| |
| :Mumps
| |
| :Influenza B
| |
| :Coxsackievirus
| |
| :Rickettsial infection
| |
| :Ehrlichiosis
| |
|
| |
|
| | | [[Bell's palsy history and symptoms|History and Symptoms]] | [[Bell's palsy physical examination|Physical Examination]] | [[Bell's palsy laboratory findings|Laboratory Findings]] | [[Bell's palsy CT|CT]] | [[Bell's palsy MRI|MRI]] | [[Bell's palsy other diagnostic studies|Other Diagnostic Studies]] |
| '''Non-infectious causes''' | |
| | |
| :Inactivated intranasal influenza vaccine that was introduced and since withdrawn from the market in Switzerland
| |
| :Genetic predisposition in some cases
| |
| :Ischemia of the facial nerve
| |
| :Tumors and compression of the facial nerve
| |
| :Temporal bone fracture
| |
| :Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
| |
| :Sarcoidosis
| |
| | |
| == Histopathology ==
| |
| | |
| :The facial nerve has a thickened, edematous perineurium with a diffuse infiltrate of inflammatory cells between nerve bundles and around intraneural blood vessels.
| |
| :The ppearance similar to that found with Herpes Zoster infection, consistent with an inflammatory and possibly an infectious cause
| |
| | |
| ==Peripheral versus central lesions ==
| |
| | |
| :Sparing of the forehead muscles is suggestive of a central (upper motor neuron) lesion because of bilateral innervation to this area.
| |
| :However, it does not exclude a peripheral site of pathology in all cases.
| |
| | |
| == History and Symptoms ==
| |
| | |
| Sudden onset, usually over hours, of unilateral facial paralysis(maximal symptoms by 48 hours)
| |
| | |
| :*Eyebrow sagging with inability to close the affected eye
| |
| :*Nasolabial fold flattening with mouth drawn to the non affected side
| |
| :*Inability to wrinkle forehead (peripheral lesion)
| |
| :*May be associated with ear pain, impaired taste sensation on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, decreased tearing, and hyperacusis
| |
| | |
| ==Diagnostic Tests==
| |
| | |
| :Electrodiagnostic studies help determine the prognosis, and imaging studies can define potential surgical causes of facial palsy.
| |
| :These tests are not necessary in all patients.
| |
| :Patients with a typical lesion that is incomplete and recovers do not need further study.
| |
| | |
| :Electrodiagnostic studies (EMG, or motor nerve conduction study) and Imaging (CT, or MRI) are warranted if the physical signs are atypical, there is slow progression beyond three weeks, or if there is no improvement at six months.
| |
| :Screening blood studies for underlying systemic disease or infection should also be considered in these cases.
| |
| :No test provides prognostic information sufficiently early as to be used for determining who should or should not be treated
| |
| | |
| == Risk Stratification and Prognosis==
| |
| | |
| :The House-Brackmann grading system was devised both as a clinical indicator of severity and also an objective record of progress.
| |
| :Related to the severity of the lesion.
| |
| :Clinically incomplete lesions tend to recover.
| |
| :The natural history without treatment was described in a study of 1011 patients in 1982.
| |
| | |
| -67% had incomplete paralysis, with 94% rate of return to normal function
| |
| -33% had complete paralysis, with 60% rate of return to normal function
| |
| -By 3 weeks, 71% had complete recovery, 13% had slight sequelae , and 16% had residual weakness
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Treatment== | | ==Treatment== |
| | [[Bell's palsy medical therapy|Medical Therapy]] | [[Bell's palsy surgery|Surgery]] | [[Bell's palsy primary prevention|Primary Prevention]] | [[Bell's palsy secondary prevention|Secondary Prevention]] | [[Bell's palsy cost-effectiveness of therapy|Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy]] | [[Bell's palsy future or investigational therapies|Future or Investigational Therapies]] |
| | == Case Studies == |
| | [[Bell's palsy case study one|Case #1]] |
|
| |
|
| '''Eye care:''' nocturnal patch, lacrilube, artificial tears if poor lid closure
| | ==Related Chapters== |
| | | *[[Central facial palsy]] |
| === Pharmacotherapy ===
| |
| | |
| '''Glucocorticoids:''' +/- higher rate of recovery if reaction at onset <br>
| |
| '''Antivirals:''' ACV 400 mg 5xd + prednisone better than prednisone alone <br>
| |
| '''Valacyclovir:''' 1 g tid x 7d = easier alternative to ACV <br>
| |
|
| |
|
| Treatment is a matter of controversy. In patients presenting with incomplete facial palsy, treatment may be unnecessary. However, patients presenting with complete [[paralysis]], marked by an inability to close the eyes and mouth on the involved side, are usually treated with anti-inflammatory [[corticosteroids]]. [[Prednisolone]], a corticosteroid, if used early in treatment of Bell's palsy, significantly improves the chances of complete recovery at 3 and 9 months when compared to treatment with [[acyclovir]], an anti-viral drug, or no treatment at all. The likely association of Bell's palsy with the herpes virus has led most American neurologists to prescribe a course of anti-viral medication (such as [[acyclovir]]) to all patients with unexplained facial palsy.<ref> Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, et al. Early treatment with prednisolone or acyclovir in Bell's palsy. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1598-1607. [[Surgical]] procedures to decompress the facial nerve have been attempted, but have not been proven beneficial. [[Acupuncture]] has also been studied, with inconclusive results.<ref>He, L., D. Zhou, B. Wu, N. Li, and M.K. Zhou. (2004). [http://www.cochrane.org/reviews/en/ab002914.html "Acupuncture for Bell's palsy."] ''Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews'' 2004, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD002914. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002914.pub2. Retrieved on 2007-09-06.</ref>
| |
|
| |
| People who think they may have Bell's Palsy should consult their doctor as soon as possible. Many times, the medications will not be effective if administered too late after the onset.
| |
|
| |
| Although most patients (60–80%) recover completely from Bell's palsy within several weeks, some require several months, and others may be left with deficits of varying degrees.
| |
|
| |
| ==Complications==
| |
|
| |
| Major complications of the condition are chronic loss of taste ([[ageusia]]), chronic facial [[spasm]] and corneal infections. To prevent the latter, the eyes may be protected by covers, or taped shut during sleep and for rest periods, and tear-like eye drops or eye ointments may be recommended, especially for cases with complete [[paralysis]]. Where the eye does not close completely, the reflex is also affected; great care should be taken to protect the eye from injury.
| |
|
| |
| Another complication can occur in case of incomplete or erroneous regeneration of the damaged facial nerve. The nerve can be thought of as a bundle of smaller individual nerve connections which branch out to their proper destinations. During regrowth, nerves are generally able to track the original path to the right destination - but some nerves may sidetrack leading to a condition known as synkinesis. For instance, regrowth of nerves controlling muscles attached to the eye may sidetrack and also regrow connections reaching the muscles of the mouth. In this way, movement of one also affects the other. For example, when the person closes the eye, the corner of the mouth will lift, or when smiling, the eye will close (synkinesis).
| |
|
| |
| In addition, around 6% of patients exhibit [[Tears#Diseases and disorders|crocodile tear syndrome]] on recovery, where they will shed tears while eating. This is thought to be due to faulty regeneration of the facial nerve, a branch of which controls the lacrimal and salivary glands.
| |
|
| |
| ==References==
| |
| {{reflist|2}}
| |
|
| |
| ==Additional Resources==
| |
| * Sullivan FM, Swan IRC, Donnan PT, et al. Early treatment with prednisolone or acyclovir in Bell's palsy. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1598-1607.
| |
| * "The Merck Manual"
| |
| * ''New England Journal of Medicine'', Sept. 2004
| |
| * Lambert, Michael. (2007-03-05) [http://www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic56.htm "Bell's Palsy."] (Website.) ''Emedicine''. Retrieved on 2007-09-27.
| |
|
| |
| ==External links==
| |
| *[http://www.facialparalysisinstitute.com managment and treatment of facial paralysis]
| |
| *[http://www.bellspalsy.ws/ Bell's Palsy Information Site], has a FAQ
| |
| *[http://pregnancyandbaby.com/read/articles/5398.htm Bell's Palsy and Pregnancy]
| |
| *[http://www.neurologychannel.com/bellspalsy/ Bell's Palsy Patient Info - Neurology Channel]
| |
| *[http://www.facial-palsy.com/ Living with Facial Palsy], a site for parents of children with Facial Palsy
| |
| *[http://www.lib.uiowa.edu/hardin/md/bellspalsy.html Links to pictures of Bells palsy (Hardin MD/Univ of Iowa)]
| |
| *[http://www.bellspalsy.org.uk/ Bell's Palsy Association]
| |
|
| |
| {{SIB}}
| |
| {{PNS diseases of the nervous system}} | | {{PNS diseases of the nervous system}} |
| [[Category:Neurological disorders]]
| |
| [[Category:Otolaryngology]]
| |
|
| |
| [[ar:شلل العصب الوجهي]]
| |
| [[ca:Paràlisi de Bell]] | | [[ca:Paràlisi de Bell]] |
| [[de:Fazialislähmung]] | | [[de:Fazialislähmung]] |
| Line 159: |
Line 51: |
| {{WH}} | | {{WH}} |
| {{WikiDoc Sources}} | | {{WikiDoc Sources}} |
| | |
| | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] |
| | [[Category:Otolaryngology]] |
| | [[Category:Neurology]] |
| | [[Category:Disease]] |