Paget-Schroetter disease CT: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
'''Editor-In-Chief:''' [[User:C Michael Gibson|C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D.]] [[Mailto:charlesmichaelgibson@gmail.com|[1]]]; '''Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:''' | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
* [[Computed tomography]] (CT) is useful in the presence of atypical symptoms or in the setting of a normal [[ultrasound]] in a highly suspected patient.<ref name="HanggeRotellini-Coltvet2017">{{cite journal|last1=Hangge|first1=Patrick|last2=Rotellini-Coltvet|first2=Lisa |last3=Deipolyi|first3=Amy R. |last4=Albadawi|first4=Hassan |last5=Oklu|first5=Rahmi |title=Paget-Schroetter syndrome: treatment of venous thrombosis and outcomes|journal=Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy|volume=7|issue=S3|year=2017|pages=S285–S290|issn=22233652|doi=10.21037/cdt.2017.08.15}}</ref> | * [[Computed tomography]] (CT) is useful in the presence of atypical symptoms or in the setting of a normal [[ultrasound]] in a highly suspected patient.<ref name="HanggeRotellini-Coltvet2017">{{cite journal|last1=Hangge|first1=Patrick|last2=Rotellini-Coltvet|first2=Lisa |last3=Deipolyi|first3=Amy R. |last4=Albadawi|first4=Hassan |last5=Oklu|first5=Rahmi |title=Paget-Schroetter syndrome: treatment of venous thrombosis and outcomes|journal=Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy|volume=7|issue=S3|year=2017|pages=S285–S290|issn=22233652|doi=10.21037/cdt.2017.08.15}}</ref> | ||
== CT == | == CT == | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
* [[Computed tomography]] (CT) is helpful to confirm or exclude the diagnosis whenever [[Paget-Schroetter disease]] is highly suspected, but there are no abnormal ultrasound findings. This imaging method could also be used to study other possible etiologies of [[Subclavian]]-[[Axillary vein]] compression.<ref name="Rosa SalazarOtálora Valderrama2015">{{cite journal|last1=Rosa Salazar|first1=Vladimir|last2=Otálora Valderrama|first2=Sonia del Pilar|last3=Hernández Contreras|first3=María Encarnación|last4=García Pérez|first4=Bartolomé|last5=Arroyo Tristán|first5=Andrés del Amor|last6=García Méndez|first6=María del Mar|title=Multidisciplinary Management of Paget-Schroetter Syndrome. A Case Series of Eight Patients|journal=Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition)|volume=51|issue=8|year=2015|pages=e41–e43|issn=15792129|doi=10.1016/j.arbr.2015.05.026}}</ref> | * [[Computed tomography]] (CT) is helpful to confirm or exclude the diagnosis whenever [[Paget-Schroetter disease]] is highly suspected, but there are no abnormal ultrasound findings. This imaging method could also be used to study other possible etiologies of [[Subclavian]]-[[Axillary vein]] compression.<ref name="Rosa SalazarOtálora Valderrama2015">{{cite journal|last1=Rosa Salazar|first1=Vladimir|last2=Otálora Valderrama|first2=Sonia del Pilar|last3=Hernández Contreras|first3=María Encarnación|last4=García Pérez|first4=Bartolomé|last5=Arroyo Tristán|first5=Andrés del Amor|last6=García Méndez|first6=María del Mar|title=Multidisciplinary Management of Paget-Schroetter Syndrome. A Case Series of Eight Patients|journal=Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition)|volume=51|issue=8|year=2015|pages=e41–e43|issn=15792129|doi=10.1016/j.arbr.2015.05.026}}</ref> | ||
* [[CT angiography]] is an accurate diagnostic tool capable of detecting valuable findings suggestive of [[Paget-Schroetter disease]]. Such as: | * [[CT angiography]] is an accurate diagnostic tool capable of detecting valuable findings suggestive of [[Paget-Schroetter disease]]. Such as: | ||
** [[Axillary vein|Axillary]]-[[Subclavian vein]] occlusion | **[[Axillary vein|Axillary]]-[[Subclavian vein]] occlusion | ||
** Point stenosis of Axillary-Subclavian vein at level of the [[first rib]]<ref name="Thompson20122">{{cite journal|last1=Thompson|first1=Robert|title=Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis|journal=Seminars in Interventional Radiology|volume=29|issue=01|year=2012|pages=044–051|issn=0739-9529|doi=10.1055/s-0032-1302451}}</ref> | ** Point stenosis of Axillary-Subclavian vein at level of the [[first rib]]<ref name="Thompson20122">{{cite journal|last1=Thompson|first1=Robert|title=Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis|journal=Seminars in Interventional Radiology|volume=29|issue=01|year=2012|pages=044–051|issn=0739-9529|doi=10.1055/s-0032-1302451}}</ref> | ||
** Determining the presence of dilated collateral veins<ref name="Thompson2012">{{cite journal|last1=Thompson|first1=Robert|title=Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis|journal=Seminars in Interventional Radiology|volume=29|issue=01|year=2012|pages=044–051|issn=0739-9529|doi=10.1055/s-0032-1302451}}</ref> | ** Determining the presence of dilated collateral veins<ref name="Thompson2012">{{cite journal|last1=Thompson|first1=Robert|title=Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis|journal=Seminars in Interventional Radiology|volume=29|issue=01|year=2012|pages=044–051|issn=0739-9529|doi=10.1055/s-0032-1302451}}</ref> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
* [[Computed tomography|CT venography]] can detect [[thrombus]] in venous system.<ref name="pmid29494023">{{cite journal| author=| title=StatPearls | journal= | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=29494023 | doi= | pmc= | url= }}</ref> It is associated with [[Radiocontrast|radio contrast]] related side effects.<ref name="pmid21079709">{{cite journal| author=Alla VM, Natarajan N, Kaushik M, Warrier R, Nair CK| title=Paget-schroetter syndrome: review of pathogenesis and treatment of effort thrombosis. | journal=West J Emerg Med | year= 2010 | volume= 11 | issue= 4 | pages= 358-62 | pmid=21079709 | doi= | pmc=2967689 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21079709 }}</ref> | * [[Computed tomography|CT venography]] can detect [[thrombus]] in venous system.<ref name="pmid29494023">{{cite journal| author=| title=StatPearls | journal= | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=29494023 | doi= | pmc= | url= }}</ref> It is associated with [[Radiocontrast|radio contrast]] related side effects.<ref name="pmid21079709">{{cite journal| author=Alla VM, Natarajan N, Kaushik M, Warrier R, Nair CK| title=Paget-schroetter syndrome: review of pathogenesis and treatment of effort thrombosis. | journal=West J Emerg Med | year= 2010 | volume= 11 | issue= 4 | pages= 358-62 | pmid=21079709 | doi= | pmc=2967689 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=21079709 }}</ref> | ||
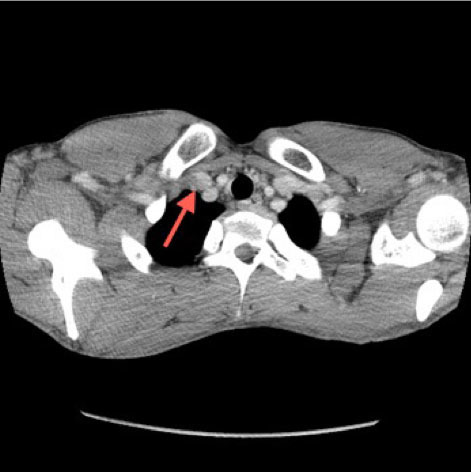
[[File:Subclavian and Axillary vein occlusion.jpg|alt=Subclavian and Axillary vein occlusion on CT angiogram|center|thumb|472x472px|Computed tomography angiogram chest reveals a thrombosis of the right subclavian and axillary veins with subtle filling defect at the junction of the right subclavian, jugular and brachiocephalic veins (red arrow). Case courtesy by Jesse Kellar, MD<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4100831/|title=Thoracic Outlet Syndrome with Secondary Paget Schröetter Syndrome: A Rare Case of Effort-Induced Thrombosis of the Upper Extremity|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref>]] | |||
<br /> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 17:20, 9 June 2020
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [[1]]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Overview
- Computed tomography (CT) is useful in the presence of atypical symptoms or in the setting of a normal ultrasound in a highly suspected patient.[1]
CT
- Computed tomography (CT) is helpful to confirm or exclude the diagnosis whenever Paget-Schroetter disease is highly suspected, but there are no abnormal ultrasound findings. This imaging method could also be used to study other possible etiologies of Subclavian-Axillary vein compression.[2]
- CT angiography is an accurate diagnostic tool capable of detecting valuable findings suggestive of Paget-Schroetter disease. Such as:
- Axillary-Subclavian vein occlusion
- Point stenosis of Axillary-Subclavian vein at level of the first rib[3]
- Determining the presence of dilated collateral veins[4]
- Positional subclavian vein obstruction (when performed at rest with elevated upper limb)[5]
- CT venography can detect thrombus in venous system.[6] It is associated with radio contrast related side effects.[7]
References
- ↑ Hangge, Patrick; Rotellini-Coltvet, Lisa; Deipolyi, Amy R.; Albadawi, Hassan; Oklu, Rahmi (2017). "Paget-Schroetter syndrome: treatment of venous thrombosis and outcomes". Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. 7 (S3): S285–S290. doi:10.21037/cdt.2017.08.15. ISSN 2223-3652.
- ↑ Rosa Salazar, Vladimir; Otálora Valderrama, Sonia del Pilar; Hernández Contreras, María Encarnación; García Pérez, Bartolomé; Arroyo Tristán, Andrés del Amor; García Méndez, María del Mar (2015). "Multidisciplinary Management of Paget-Schroetter Syndrome. A Case Series of Eight Patients". Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition). 51 (8): e41–e43. doi:10.1016/j.arbr.2015.05.026. ISSN 1579-2129.
- ↑ Thompson, Robert (2012). "Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 29 (01): 044–051. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1302451. ISSN 0739-9529.
- ↑ Thompson, Robert (2012). "Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 29 (01): 044–051. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1302451. ISSN 0739-9529.
- ↑ Thompson, Robert (2012). "Comprehensive Management of Subclavian Vein Effort Thrombosis". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 29 (01): 044–051. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1302451. ISSN 0739-9529.
- ↑ "StatPearls". 2020. PMID 29494023.
- ↑ Alla VM, Natarajan N, Kaushik M, Warrier R, Nair CK (2010). "Paget-schroetter syndrome: review of pathogenesis and treatment of effort thrombosis". West J Emerg Med. 11 (4): 358–62. PMC 2967689. PMID 21079709.
- ↑ "Thoracic Outlet Syndrome with Secondary Paget Schröetter Syndrome: A Rare Case of Effort-Induced Thrombosis of the Upper Extremity".