Ogilvie syndrome CT: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[Abdominal]] CT scan is performed in suspected cases of colonic pseudo-obstruction to detect the site of the [[obstruction]]. Abdominal CT scan may show the presence of [[dilation]] of the [[large bowel]] without evidence of [[Obstruction|mechanical obstruction]] and the colonic dilation may extend to [[Rectum|the rectum]]. | |||
==CT== | ==CT== | ||
*Abdominal CT scan can be performed in suspected cases of acute colonic pseduo-obstruction in order to detect the site of the obstruction. The CT scan also can detect the underlying cause or risk factor that lead to the colonic obstruction. | *[[Abdominal]] CT scan can be performed in suspected cases of acute colonic pseduo-obstruction in order to detect the site of the [[obstruction]]. The CT scan also can detect the underlying cause or risk factor that lead to the colonic obstruction.<ref name="pmid10457342">{{cite journal| author=Schermer CR, Hanosh JJ, Davis M, Pitcher DE| title=Ogilvie's syndrome in the surgical patient: a new therapeutic modality. | journal=J Gastrointest Surg | year= 1999 | volume= 3 | issue= 2 | pages= 173-7 | pmid=10457342 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10457342 }}</ref> | ||
*CT scan in cases of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction may show the following: | *CT scan in cases of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction may show the following: | ||
**The presence of | **The presence of [[dilation]] of the [[large bowel]] without evidence of an abrupt transition point or mechanically obstructing lesion | ||
**The colonic dilation may extend to the rectum | **The colonic dilation may extend to [[Rectum|the rectum]] | ||
[[Image:Ogilvie-syndrome.jpg|350px|thumb|center|Case courtesy of <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/11684">rID: 11684</a>]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Needs content]] | [[Category:Needs content]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:51, 8 February 2018
| Ogilvie syndrome Microchapters
|
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Ogilvie syndrome CT On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Ogilvie syndrome CT |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Elsaiey, MBBCH [2]
Overview
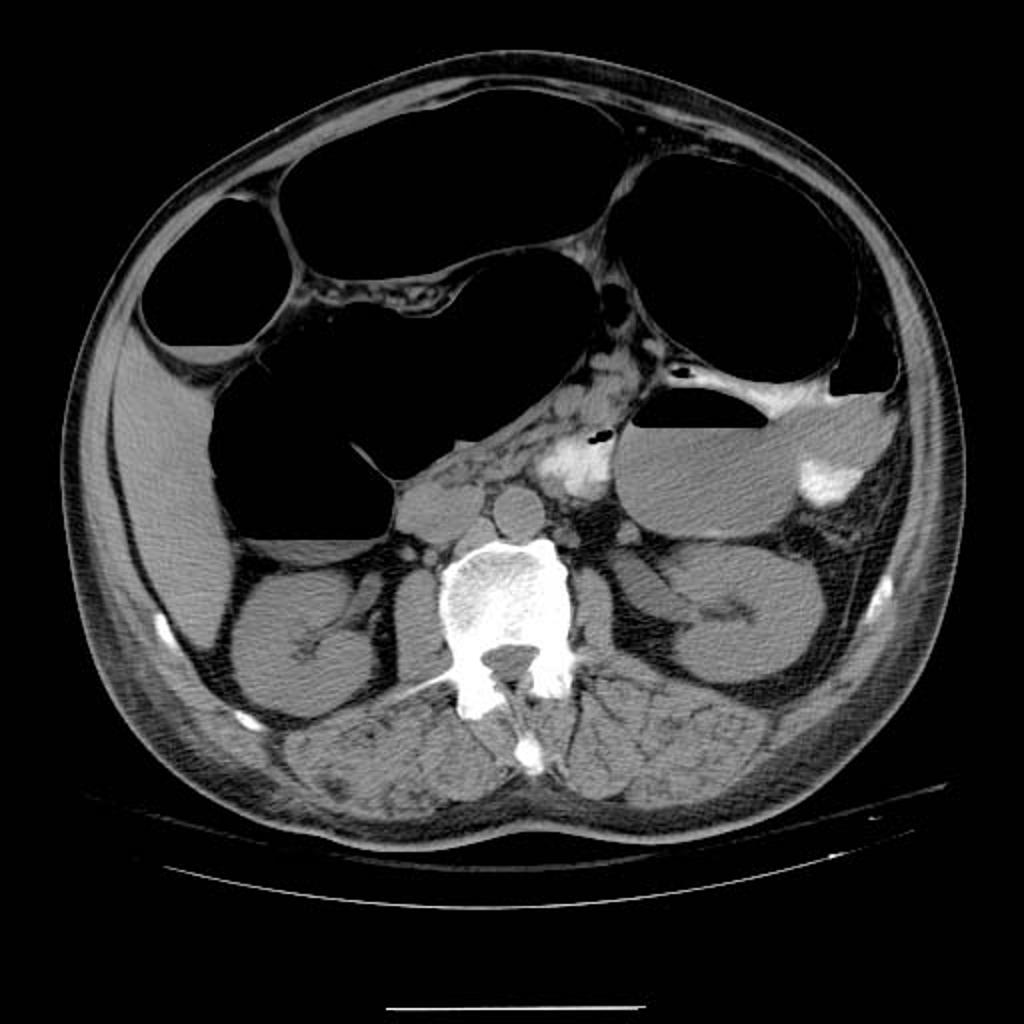
Abdominal CT scan is performed in suspected cases of colonic pseudo-obstruction to detect the site of the obstruction. Abdominal CT scan may show the presence of dilation of the large bowel without evidence of mechanical obstruction and the colonic dilation may extend to the rectum.
CT
- Abdominal CT scan can be performed in suspected cases of acute colonic pseduo-obstruction in order to detect the site of the obstruction. The CT scan also can detect the underlying cause or risk factor that lead to the colonic obstruction.[1]
- CT scan in cases of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction may show the following:
- The presence of dilation of the large bowel without evidence of an abrupt transition point or mechanically obstructing lesion
- The colonic dilation may extend to the rectum
References
- ↑ Schermer CR, Hanosh JJ, Davis M, Pitcher DE (1999). "Ogilvie's syndrome in the surgical patient: a new therapeutic modality". J Gastrointest Surg. 3 (2): 173–7. PMID 10457342.